Design and test of the separate and combined double row wide strip seed guiding device for wheat
-
摘要:
针对稻茬田小麦机械化带状播种时受黏重土壤与秸秆还田耦合作用制约存在导种装置壅堵导致断条的问题,该研究设计了一种分引组合式双行宽条带导种装置,导种过程中利用球面弹籽部件对下落种群左右均匀分种、借助坡度斜面对分流种群宽带引种。运用质点运动学理论建立了小麦分种、引种过程的力学模型,明确了球面弹籽部件直径和斜面坡度对导种均匀性有影响。运用EDEM软件对小麦导种装置关键结构参数进行优化设计,以球面弹籽部件直径和斜面坡度为试验因素,以各行排量一致性变异系数和行内横向均匀度变异系数为评价指标,通过单因素和二次正交旋转组合试验获取相关试验数据,应用Design-Expert软件对试验数据进行回归分析,建立了试验因素与试验指标之间的回归方程。结果表明,球面弹籽部件直径对各行排量一致性影响显著(P<0.05),斜面坡度对行内横向均匀度有极显著影响(P<0.01),斜面底板导种装置最优结构参数为球面弹籽部件直径40 mm、斜面坡度10°。并与市场上已有的波浪底板、弧面底板、平面底板3种型式导种装置进行3种播量下的仿真对比试验。仿真试验结果表明,各播量下的各行排量一致性变异系数和行内横向均匀度变异系数由大到小均为平面底板、弧面底板、波浪底板和斜面底板型导种装置,在播量450 kg/hm2下,斜面底板型导种装置播种效果最佳,各行排量一致性变异系数为2.92%,行内横向均匀度变异系数为14.19%。台架与田间对比试验表明,斜面底板型导种装置的各行排量一致性变异系数和行内横向均匀度变异系数均最小,此时各行排量一致性变异系数均不大于4.0%,行内横向均匀度变异系数均不大于16%;田间对比试验中,在播量450 kg/hm2下,斜面底板型导种装置较其他3种导种装置各行排量一致性变异系数最低下降了2.73个百分比,行内横向均匀度变异系数最低下降了10.61个百分点。试验结果与仿真结果误差不超过5%,表明装置结构参数优化结果可靠,满足国家播种机质量评价技术规范及大田播种农艺要求。研究结果可为稻茬黏壤土环境下小麦宽条带导种装置优化设计提供参考。
Abstract:Aiming at the problem that mechanized strip sowing of wheat in rice stubble fields can be constrained to the coupling effect of clay-heavy soil and straw return to the field. The seed guide device can be blocked to cause the breakage. In this study, a double-row wide strip seed introduction device was designed to combine with the spherical collision seed part, in order to evenly divide the falling population left and right during introduction. The broadband introduction of the diverted population was also carried out with the help of beveled bottom plate slope. The mechanical model of wheat seeding and introduction was established using particle kinematics. A systematic investigation was implemented to clarify the influencing mechanism of the spherical collision seed part diameter and beveled bottom plate slope on the uniformity of seed introduction. EDEM software was then used to optimize the key structural parameters of the wheat seed introduction device. Among them, the spherical collision seed part diameter and beveled bottom plate slope were taken as the test factors. The evaluation indexes were taken as the coefficient of variation of each row seeding quantity consistency and coefficient of variation of transverse uniformity in row. The test data was obtained to combine the univariate and quadratic orthogonal rotation. Design-Expert software was also selected to perform the regression analysis on experimental data. The regression equation was established between the test factors and indicators. The results show that the spherical collision seed part diameter posed a significant coefficient of variation of each row seeding quantity consistency, whereas, the beveled bottom plate slope was some impact on the coefficient of variation of transverse uniformity in row. The optimal structural parameters were achieved in the seed guiding device spherical collision seed part diameter of 40mm, and the beveled bottom plate slope of 10°. The beveled bottom plate guide device was evaluated under optimal structural parameters. Three types (flat plate,curved bottom plate,wavy plate) of seed guide devices were selected to compare under the three sowing amounts. The simulation results show that the coefficient of variation of each row seeding quantity consistency and coefficient of variation of transverse uniformity in row were ranked in the descending order: flat plate,curved bottom plate,wavy plate,beveled bottom plate. The optimal coefficient of variation of each row seeding quantity consistency was 2.92% of the beveled bottom plate-type seed guiding device. The coefficient of variation of transverse uniformity was 14.19% in the row. The bench and field tests were combined to further verify the smallest coefficient of variation of each row seeding quantity consistency and coefficient of variation of transverse uniformity in row of the beveled bottom plate seed guiding device. Specifically, the mean coefficient of variation of each row seeding quantity consistency was 2.31%, whereas, the mean coefficient of variation of transverse uniformity in row was 14.21%. The field experimental results showed that coefficient of variation of each row seeding quantity consistency decreased by at least 2.73 percentage points, and the coefficient of variation of transverse uniformity in row decreased by at least 10.61 percentage points, compared with the other three types of seed guide devices. The error was not more than 5% between the actual and the simulation. Therefore, it was reliable for the optimized structural parameters of the split-citation combined wide strip guide device using the discrete element method. At the same time, the national technical specifications were fully met for the quality evaluation of seeders and the agronomic requirements for field seeding. The findings can provide a strong reference for the optimal design of wheat wide strip seed introduction device under a rice stubble clay loam environment.
-
Keywords:
- agricultural machinery /
- test /
- wheat /
- seed guiding device /
- wide strips /
- EDEM
-
0. 引 言
《联合国气候变化框架公约》中将气候变化定义为“除在类似时期内所观测的气候的自然变异之外,由于直接或间接的人类活动改变了地球大气的组成而造成的气候变化”[1],以此来区分由人类活动引起的“气候变化”和自然产生的“气候变率”。气候变化主要表现为气温升高、降水模式改变、二氧化碳浓度升高等形式,会影响生态过程、威胁生物多样性、改变物种栖息地的适宜性、影响物种分布[2]。气温升高会影响植物物候,改变叶芽发芽、开花和结果的时间[3-4]。降水模式的变化可能导致水分胁迫或内涝,影响植物的生长和生存[5]。大气二氧化碳浓度升高会影响光合作用和水分利用效率,从而影响植被生产力[6]。热浪、暴雨、干旱和飓风等极端天气事件可能变得更加频繁和强烈[7]。根据世界气象组织的数据,2011—2020年是自有记录以来最热的十年,全球平均气温与工业化前水平相比高出了约1.2 ℃[8]。可以说,气候变化是当今世界面临的最大环境挑战之一。
气候变化的主要驱动因素之一是农业生产、土地利用和交通运输等人类活动排放的温室气体[9]。联合国环境规划署在其《2022年排放差距报告》中指出,根据《巴黎协定》,为了在21世纪末将全球增温限制在1.5 ℃以内,至2030年必须减少45%的温室气体排放量,至2050年需达到净零排放[10]。土壤碳库既是陆地生态系统中最大的碳库,也是全球碳循环中的重要组成部分,气候变化会对土壤碳储量产生重要影响。同时,土壤中的有机物质分解也会影响大气中二氧化碳浓度,进而影响全球气候。已有研究表明,土壤对大气二氧化碳浓度的贡献是矿物燃料燃烧的10倍之多[11]。全球农田土壤碳储量约为140~170 Pg C,大约占全球陆地土壤碳库总量的10%,在全球碳循环中具有重要地位[12]。相比于森林、草地等生态系统,农田土壤碳库相对活跃,极易受到人为活动的影响,但同样也更容易自我恢复[13]。农耕活动扰动了土壤与大气碳库之间的碳平衡,使农田土壤排放二氧化碳[14]。同时,农田土壤碳储量与土壤有机质含量密切相关,是衡量农田土壤质量的重要因素,其含量减少不仅会降低农田的可持续利用能力,还可能引起农田生态系统的退化[15]。因此,评估农田土壤碳储量及其缓解气候变化影响的潜力,对深入了解气候变化对农田生态系统的影响具有重要意义。
农田土壤碳储量评估方法可分为经典评估方法和气候变化影响评估方法两类。经典评估方法包括土壤类型法、生命带法、经验参数法、二氧化碳通量法等。这些方法主要利用土壤有机质含量或碳密度等实测数据,结合土壤类型、植被类型进行外推,以估算土壤总碳储量。应用3S技术可以帮助分析土壤碳储量的时空分布和演化过程。尽管这些方法使用方便、技术成熟、广泛应用,但前期采集的土壤样点数据质量和数量直接影响后期评估的准确性。不同学者使用不同的统计方法也可能导致数据可信度下降和结果误差较大。气候变化影响评估方法综合考虑气候、土壤、地形、植被、遥感等多种复杂参数,通过模拟土壤-作物-大气系统或土壤碳循环过程,实现对土壤碳储量的模拟[16-17]。相较于经典评估方法,气候变化影响评估方法可以通过调整输入参数和敏感性分析等方式,量化土壤碳储量与影响因素之间的关系。在当前气候变化背景下,这类方法得到了越来越广泛的应用[17-18]。
许多研究分析了气候变化因子对农田土壤碳储量变化的影响[16, 19],气候变化影响的农田土壤碳储量评估方法也从最初的单组分模型发展到多组分模型以及组合模型。然而,气候变化包括多种具体表现形式,不同气候变化因子对农田土壤碳储量的影响各不相同。同时,不同模型在机理、结构和参数设置上存在差异,导致评估结果的不确定性较大;模型的验证和对比研究还相对缺乏,限制了评估方法的推广应用。因此,本研究在总结前人研究成果的基础上,从模型机理层面入手,综合分析气候变化各因子的相互作用和复合效应,评价和对比不同评估方法的优势与局限,提出未来的研究重点。这将有助于提升农田土壤碳储量评估的准确性和可靠性,为制定农业领域的碳中和策略、促进生态健康和可持续发展提供更加科学的决策依据。
1. 气候变化对农田土壤碳储量的影响
气候变化主要表现为气温升高、降水模式变化、二氧化碳浓度增加、大气氮沉降等多种形式(图1)。气候变化的单因子对农田土壤碳储量的影响各不相同,而其多因子联合作用可能导致协同或拮抗作用,从而放大或减轻气候因素对土壤碳储存的个体影响。
1.1 气候变化单因子对农田土壤碳储量的影响
气温升高通过提高土壤有机质的分解速率使土壤中的碳以二氧化碳的形式排放到大气中[20],并通过影响作物物候期、作物产量和农业生产活动[21],间接影响农田土壤碳储量。降水模式变化通过影响土壤呼吸[22]和作物生长[23-24]等方式去影响农田土壤的碳储量。二氧化碳浓度升高通过影响作物的光合作用效率和生长过程对农田土壤碳储量产生间接影响[25-26]。同时,大气二氧化碳浓度升高可能会增强土壤的呼吸作用,进而抑制土壤有机碳的增加[27]。大气氮沉降通过影响碳输入与输出之间的平衡来影响土壤碳储量。通常情况下,大气中的氮沉降的增加会刺激植物的生长[28]。
气候变化不仅导致极端天气频率增加,而且影响程度也不断增强。干旱会极大降低陆地植被生产,长期严重干旱会使植被大范围死亡[29]。极端高温天气会导致小麦产量明显下降[30]。作物产量下降使得植物生物量降低,导致以作物残茬和植被形式储存在农田土壤中的碳储量减少。极端降水事件会引发土壤侵蚀,冲走富含有机物的表层土壤,直接导致土壤中碳储量的损失[31]。野火会破坏植被,降低净初级生产力,消耗地表凋落物中的碳和养分,增加土壤碳损失[32]。另外,积雪厚度增加会延迟土壤二氧化碳排放峰值[33],太阳辐射增强能够加强土壤呼吸作用[34]。
1.2 气候变化多因子对农田土壤碳储量的复合影响
气温升高而降水减少会导致干旱胁迫,从而使植物生长速率和作物产量降低[35]。气温、降水、二氧化碳浓度对土壤中的有机碳含量有协同影响,在二氧化碳浓度、气温和降水同时增加的情况下,土壤中存储的有机碳将以二氧化碳的形式返回到大气中[36]。但部分全球气候碳循环模型预测,大气二氧化碳浓度升高会提高土壤有机碳含量,或至少能够部分低消气温升高带来的土壤有机碳分解对土壤碳库的影响[37]。二氧化碳、大气氮沉降、臭氧多因子组合效应可能影响土壤中微生物的活动[38]。
不同的气候变化因子对土壤碳储量的影响是复杂的(表1)。为了更好地理解气候变化在农业生态系统碳循环中的作用,考虑不同气候变化因子下的综合影响并探索其潜在机制至关重要。
表 1 气候变化因子对农田土壤碳储量的影响Table 1. Impacts of climate change on agricultural soil carbon storage气候变化因子
Factors of climate change影响
Impacts气温升高
Rising temperature气温升高会提高土壤有机质的分解速
率[20];气温升高将会对生物物候和农业生产活动产生直接影响[21]。降水模式变化
Change in precipitation patterns降水模式变化会影响土壤呼吸作用[22];降水的频率和强度变化会影响陆地植被的生产力[23-24]。 二氧化碳浓度升高
Increasing carbon dioxide concentrations大气二氧化碳浓度升高会提升植物的光合效率[25- 26];大气二氧化碳浓度升高也可能对土壤碳储量造成负面影响[27]。 大气氮沉降
Atmospheric nitrogen deposition大气氮沉降增加会刺激植物的
生长[28]。极端天气
Extreme weather events极端高温、干旱将会极大降低陆地植被生产[29-30];极端降水事件会引发土壤侵蚀[31];野火会增加土壤碳损失[32]。 气温、降水组合
Temperature-precipitation interactions气温升高而降水减少会导致干旱
胁迫[35]。气温、降水、二氧化碳浓度组合
Temperature-precipitation-carbon dioxide interactions气温、降水、二氧化碳浓度对土壤中的有机碳含量有协同影响[36];但大气二氧化碳浓度升高与气温升高、降水模式改变之间也可能发生拮抗作用[37]。 二氧化碳、大气氮沉降、臭氧组合
Carbon dioxide-nitrogen deposition-ozone interactions二氧化碳、大气氮沉降、臭氧组合效应可能促进有机碳分解[38]。 2. 气候变化影响的农田土壤碳储量评估方法
2.1 统计分析方法
统计分析方法包括线性回归模型、机器学习模型等。此类方法利用统计学原理构建数学统计模型来估算农田土壤碳储量。统计分析法具有适应性强、应用简便、可解释性强的特点,并可以量化各种环境因素对碳储量的贡献[39]。环境变量选取是建立回归分析模型的重点。植被指数、气候、地形和成土母质等成土关键指标是常用且易于获取的环境变量。需要注意的是,输入数据的质量对统计分析方法的输出结果影响较大。如果输入数据数量较少、质量较差或存在误差,则构建的模型及其输出结果可能不准确。统计分析法通常用于预测现有数据范围内的情况,对未来或超出条件下的外推预测可能存在不确定性。
2.1.1 线性回归模型
线性回归模型包括简单线性回归模型、岭回归模型、逐步回归模型等多种变体,其基本原理类似。经典的多元线性回归模型是一种检验因变量和两个或多个自变量之间线性关系的统计模型。模型为每个自变量分配一个系数,该系数用以表示其与因变量关系的强度和方向。模型通常使用普通最小二乘法计算使因变量的观测值与预测值之间的差异最小的最佳拟合线,使残差平方和最小化。多元线性回归模型是一个全局模型,模型对所有数据的估计参数求解一次,参数的值在空间上是恒定的。例如,使用土壤平均有机碳含量、平均容重、砾石体积分数、土层厚度等数据测算剖面深度内的土壤有机碳密度,以土层平均有机碳含量为横坐标、各土层中点深度为纵坐标构建线性函数、双曲函数、幂函数、指数函数、对数函数和S型函数7个曲线方程,并采用数值计算方法对所得深度范围的积分值进行求解,最后计算山东省各土壤亚类的有机碳密度和储量[40];基于全国第二次土壤调查2 000多个土壤剖面的碳储量与年均温和年降水量之间的关系,得出不同温度带的土壤碳储量与温度的相关性存在显著差异[41];基于小型无人机和高分辨率光谱仪的回归分析可作为反演土壤有机碳的新技术[42]。线性回归模型具有计算简单、解释性强等优点,但要求输入数据符合正态分布、自变量和因变量之间存在相关关系且无多重共线性,因此使用场景受限,通常作为其他模型的参照基准。
2.1.2 机器学习模型
机器学习模型包括随机森林、支持向量机、神经网络等。随机森林模型因为具有可以同时处理线性和非线性数据、预测精度较高、稳定性强等特点,被广泛应用于土壤有机碳空间分布模拟。随机森林源于决策树模型,其将多棵决策树组合成为一个“森林”来执行分类或回归任务,并通过投票(分类)或平均(回归)获得最终模拟结果[43]。同时,随机森林通过计算袋外数据的均方误差或基尼指数来确定输入变量的重要性,量化环境变量的影响。例如,使用随机森林、支持向量机和普通克里格模型对福建东部耕地土壤有机碳的空间分布特征进行预测,发现随机森林预测结果最佳,高程和降水量是最重要的影响因子[39];基于土壤样本、环境变量和共享社会经济路径情景,结合增强回归树和随机森林模型,评估得出2015年东北地区表层土壤(0~20 cm)有机碳储量为
5293 Tg C,2090年SSP245情景下的碳储量增加1.9%,SSP585情景下的碳储量减少0.4%[18]。其他机器学习模型也在预测土壤碳储量方法有广泛应用,如基于静态和动态环境变量,使用CatBoost模型预测1971—1990年全球表层土壤(0~30 cm)有机碳储量为1249.29 Pg C[16],基于两点机器学习模型(two-point machine learning,TPML)提升土壤有机质的空间分布预测能力[44]。由于机器学习模型是对区域整体的土壤有机碳储量进行预测,因此仅以农田为研究对象的较少。机器学习模型具有稳定性强、预测精度高、适应性强等优点,但由于模型内部为黑箱结构,其运行过程较为复杂且难以解释。同时,机器学习模型及由此衍生的深度学习模型在进行大规模运算时对算力要求较高,运行效率较低。2.2 基于机理的过程模拟模型方法
基于机理的过程模拟模型方法结合生物物理数学公式、实测数据和遥感影像,通过模拟土壤碳循环过程,构建土壤碳评价与预测模型,以预测区域乃至全球的土壤碳储量。根据模型中是否显示表达微生物分解作用,基于机理的过程模拟模型方法可分为面向过程的模型和面向微生物的模型;面向过程的模型关注控制能量和物质转换的过程,面向微生物的模型关注通过食物网的能量和物质流动[45]。基于机理的过程模拟模型方法从机理角度研究土壤碳储量,其输出结果能精细区分出不同的土壤碳库,对土壤碳循环过程进行精确模拟。此外,在初始运行阶段,不同的模型考虑了不同的气候、土壤、管理等参数,综合反映自然条件对作物和土壤的影响,并根据这些参数对其进行模拟和预测。但是,基于机理的过程模拟模型存在参数选择和设置复杂、预测精度难以验证等问题。
2.2.1 过程模型
土壤碳循环的早期研究主要集中在对土壤有机质的形成、分解、迁移和影响因素等方面的探讨。早期提出的土壤有机碳单组分方程描述了土壤碳随时间变化的动态过程,表明状态变量的变化速率取决于其输入率和分解速率[46]。之后,单组分模型被用于分析不同条件下的土壤碳循环[47-49]。但是,土壤有机质中存在多种不同的成分,其分解速度也各不相同。基于长达10年的碳标记田间试验结果,土壤有机碳双组分变化模型通过对两个组分的指数函数相加来描述土壤中有机碳的整体变化[50]。面向过程的模型包括Roth C模型(Rothamsted carbon)、EPIC模型(environmental policy integrated climate)、SCNC模型(soil carbon and nitrogen cycle model)等。
Roth C模型于20世纪70年代由英国洛桑实验室基于长期定位试验数据构建[50-51]。Roth C模型是非涝渍表层土壤中有机碳周转的模型,考虑了土壤类型、温度、含水率和植物覆盖对周转过程的影响[52-53]。模型能够以月尺度计算多年的土壤总有机碳和微生物碳。模型将土壤有机碳分为4个活性有机物库和一个惰性有机物库(inert organic matter, IOM)(图2)。4个活性碳库分别是易分解植物残体库(decomposable plant material, DPM)、耐分解植物残体库(resistant plant material, RPM)、土壤微生物库(microbial biomass, BIO)和腐殖质库 (humus, HUM)。每个碳库通过具有自身特征速率的一阶过程分解,该速率受温度、湿度和土壤覆盖率的影响[54]。每月输入的有机碳通过DPM/RPM比例在DPM和RPM之间分配。不同的植物DPM/RPM比例不同,当比值为1.44,适用于大多数农作物和改良草地[54]。DPM、RPM、BIO和HUM都会被分解成BIO、HUM和二氧化碳。模型设定当底物被分解时,所有土壤中形成的BIO与HUM的比例是相同的。IOM几乎不分解。土壤温度和土壤含水率通过改变速率常数来影响分解[53]。土壤质地通过确定二氧化碳之间的比率来影响土壤有机碳的稳定性。运用分位数随机森林模型和Roth C模型对丹麦农业生态系统在气候和土地利用变化情景下土壤有机碳的封存潜力分析发现,丹麦2018年土壤碳储量为10~181 Mg /hm2(以C计, 涉及碳密度单位时均如此),2038年无论何种场景,土壤碳储量都将损失,且损失主要受温度升高和黏土含量的强烈影响[55]。基于Roth C模型,对气候变化与农业管理相互作用影响下芬兰2021—2040年农田土壤有机碳封存潜力分析发现,碳输入将促进农田土壤的固碳潜力,然而气候变化将平均减少0.28 t /(hm2·a) [19]。植物碳输入率对于提高模型的性能至关重要[56]。但是,由于Roth C模型是根据英国洛桑实验站的长期定位实验数据进行设置参数,经验性较强,对于水田等长期淹水的土壤模拟效果较差。研究发现,Roth C模型在中国北方旱地的预测精度高于南方水田[57];模拟长江中游稻田土壤有机碳变化时该模型模拟误差较SCNC模型大[58]。
EPIC模型于20世纪80年代初由美国农业部和德克萨斯州大学共同开发,用于研究气候、环境、土壤侵蚀及其对农业生产的影响[59-60]。EPIC模型包含气象、水文、土壤侵蚀、养分循环等10个子系统构成。模型的碳模块源自对CENTURY模型[61]的改进,其将土壤有机质区分为生物库、慢性库、惰性库、结构库、代谢库5个分库。凋落物按木质素和氮含量确定进入代谢库的比例,其余则进入结构库。代谢库和结构库根据木质素含量分别区分地上和地下的分解速率,其速率受土壤温度和土壤湿度的影响。生物库包括微生物组分及其产物,分解速率受到土壤质地和田间持水量的影响。慢性库包括难分解的有机物和由土壤固定的微生物产物,分解速率较慢。惰性库中的有机物几乎不分解。EPIC模型与CENTURY模型存在淋溶方程、控制参数、碳库数量和木质素含量函数4个方面的区别[60-62]。对斯洛伐克农场在不同气候变化情景下土壤有机碳和作物产量变化模拟表明,2010—2050年表层土壤有机碳储量呈下降趋势,温度升高会加速土壤有机碳的分解,尤其是在土壤被集约化管理的情景[63]。虽然国外已有许多将EPIC模型应用到农田土壤碳储量方面的研究,但国内主要使用EPIC模型分析不同灌溉、施肥、耕作、管理措施等条件对农田土壤碳储量模拟的影响。如使用EPIC模型模拟中国作物秸秆还田对农田土壤碳储量的影响,发现秸秆还田场景可以减少碳损失,并降低农田的二氧化碳排放量[17]。需要注意的是,当使用EPIC模型模拟极端气温和降水量或非指定地点等输入变量时,模型具有不确定性,整体模型的可靠性约为56%[64]。EPIC模型目前已于2023年更新到
1102 版本,并嵌入到SWAT[65]、APEX等区域模型中。SCNC模型主要用于模拟农田土壤有机碳和养分循环[66]。模型分为平衡模式和预测模式。SCNC模型将土壤碳库区分为快速分解组分、慢速分解组分、土壤腐殖质组分、微生物组分、微生物代谢产物和残体组分、不分解组分6个库。其分解产物为二氧化碳、微生物碳、非腐殖质、腐殖质4类。模型主要考虑气候、土壤、植被和耕作类型等环境参数,使用较为简便,主要应用在中国地区的水田研究。例如,使用SCNC模型模拟2050年气温升高条件下的亚热带和黄土高原地区的农田土壤碳储量,结果表明两者将分别降低大约5.6%~10.9%和3.6%~9.4%[67]。但模型可能会低估不施肥处理的土壤有机碳储量[68]。
2.2.2 微生物模型
土壤微生物通过产生微生物产物强烈地影响土壤有机质的形成[69-70]。微生物生长效率和生长动力学等基本生理性状对凋落物分解速率和净微生物生物量产生直接影响,而随后的微生物生物量周转则强烈影响土壤有机质的投入速率[71]。微生物模型更加强调土壤微生物对土壤有机碳动态的影响,全面考虑了土壤中微生物的生长、代谢和死亡等过程,以及微生物与土壤有机碳之间的相互作用[72]。同时,由于微生物的温度敏感性较强,使得微生物模型对全球气候变暖更加敏感。面向微生物的模型主要有Enzyme模型、MIMICS模型(microbial-mineral carbon stabilization model)、MEND模型(microbial-enzyme-mediated decomposition model)等。
基于土壤酶动力学的Enzyme模型用于模拟土壤有机碳的分解过程[73]。该模型将土壤有机碳划分为土壤有机碳库(soil organic carbon,SOC),溶解有机碳库(dissolved organic carbon,DOC)、微生物库(microbial biomass,MIC)和酶库(enzymes,ENZ)(图3)。在传统的面向过程的模型中,微生物过程与土壤碳周转没有明确耦合,因此微生物生物量和酶产量的变化不能反馈分解。Enzyme 模型将温度敏感性纳入微生物模型,以探索微生物死亡输入随着持续变暖而短暂增加土壤呼吸的机制。温度敏感参数为包括酶催化、摄入、碳利用效率(carbon use efficiency, CUE)。模型假设酶产量与微生物数量成正比,微生物碳利用效率随着温度升高呈线性下降,并认为微生物生物量和酶催化SOC向DOC转化是有机碳分解的限速步骤。模型能够精细刻画全球气候变化对土壤碳储量的影响机制[74],但单独应用于农田土壤碳储量模拟的研究较少。
MIMICS模型将土壤有机碳划分为受物理保护碳库、可用碳库和受化学保护碳库[71-72]。模型中有两种微生物功能类型,分别对应于富营养的r策略和寡营养的k策略 [75-77]。MIMICS模型根据凋落物质量,将凋落物输入流转到代谢凋落物库和结构凋落物库。凋落物库和可用碳库的分解基于温度敏感的Michaelis-Menten动力学方程控制[78] 。微生物生长效率决定了进入微生物库的碳通量分配与异养呼吸。微生物生物量的周转取决于微生物的功能类型。模型中温度敏感性的动力学参数源于观测数据[79],并根据微生物功能类型、凋落物化学质量和土壤质地效应的假设进行了修改。MIMICS模型当前暂未考虑土壤湿度。MIMICS模型描述了土壤中与微生物结合的有机碳与游离态有机碳之间的动态平衡,取决于微生物的生物量、微生物对有机碳的吸收速率以及微生物对有机碳的亲和力。MIMICS模型以小时为模拟时间步长。张秀等使用MIMICS模型模拟了1980—2015年江苏南部农田表层土壤(0~20 cm)有机碳密度的时空演变情况,取得了较好的模拟效果[80]。
MEND模型分析微生物酶介导的土壤有机碳循环过程[81]。MEND模型拥有6个碳库:颗粒有机碳库、矿物伴生有机碳库、溶解有机碳库、微生物碳库、颗粒有机碳分解酶库和矿物伴生有机碳分解酶库。MEND模型中的多个土壤有机碳库阐明了不同类型有机碳对温度变化的不同响应以及各种不同碳库对整体土壤有机碳动力学信息,反映了特定酶靶向特定底物的催化功能以及微生物、酶和土壤有机碳之间的相互作用。
2.3 组合模型方法
尽管机器学习模型具有强大的学习和预测能力,但它是一种纯粹的数据驱动方法,很难嵌入土壤学知识或与土壤相关的理化定律[82],也难以在模拟土壤有机碳的时间变化时表达物理定律[83]。虽然基于机理的过程模拟模型方法使用大量的土壤动力学方程,却产生建模过程不灵活、输入变量数量有限等局限,导致模拟空间分布时不如机器学习模型准确[82, 84-85]。因此,组合模型通过将两个或两个以上不同类型的模型组合在一起,汲取各方法的优势,以获得更高的模拟精度、更强的可靠性、更好的可解释性。比较常用的组合模型有回归克里金模型、POML模型(process-oriented-machine learning)等。
回归克里金模型通过将前述各类回归模型与地统计模型结合,综合考虑土壤碳储量与环境变量之间的关系以及土壤碳储量的空间自相关性,提升整体模拟精度。模型最终预测值为回归算法预测值与克里金法对回归算法残差项预测值的叠加。其中,回归算法可以为线性回归算法,也可以为机器学习算法。同样地,克里金法也可换用其他地统计学方法,均表现出良好的模拟效果[86-87]。例如,使用土地利用类型、海拔和植被等环境因素,基于回归克里格法测算了华北小流域土壤有机碳和全氮的空间分布特征[88]。
POML模型整合了基于机理的过程模拟模型方法(process-oriented model,PO)和机器学习模型(machine learning model,ML)(图4)[89]。POML模型结合PO模型(Roth C模型)和ML模型(随机森林模型)的优点来提高对土壤碳的空间和时间预测能力。模型的基本概念是将PO模型在未采样年份导出的模拟值作为额外的训练数据纳入ML模型中,以实现训练数据跨越全部时间段。模型包括两个主要步骤(图4中①和②),首先是产生所有采样地点从开始到结束的所有年份的土壤有机碳储量模拟值,然后是利用Roth C模型的样本数据和模拟数据校准随机森林模型,通过最小化整体损失函数得到最终的预测模型。使用POML模型模拟江苏南部农田土壤有机碳时空分布的结果表明,混合模型的精度比单个ML模型提高了19% [89]。
气候变化影响的农田土壤碳储量评估方法通过整合气候、土壤、植被、和生物过程等多种生态因素,为研究者提供了深入理解生态系统碳循环的有力工具。然而,模型的精度仍然取决于对参数的准确性和对复杂生态系统过程的深刻理解。并且,不同的模型由于其构建理论基础不同,其适用性不尽相同。因此,要根据研究的目标、对象、研究区的特点以及研究者的理论基础选择适宜的模型。同时,也要综合气候变化多因子组合效应、模型不确定性以及生态系统韧性的综合考量,推动气候变化背景下土壤碳储量评估方法的不断发展与完善。
3. 未来展望
3.1 关注微生物介导的土壤碳储存机制
土壤碳周转是一个复杂的过程,土壤碳库稳定性受碳输入、周转和稳定化过程的共同调控,但植物残体分解、根系分泌物输入、微生物碳泵效应、团聚体形成等土壤碳周转关键过程的机理研究尚不明确,气候变化对土壤碳循环速率和平衡的影响机制也存在不足。同时,土壤微生物是调控土壤碳循环过程的关键因素,在土壤有机碳的分解、转化和固存过程中发挥着重要作用。然而,目前对微生物驱动的土壤碳储存机制认识还较为有限,特别是在气候变化背景下,气温上升对微生物群落的影响将持续加大[73-74],但微生物群落结构和功能对土壤碳循环的响应和反馈机制尚不清楚。因此,未来应阐明土壤碳周转的主控因素及其相互作用机制、探究土壤碳周转的关键过程及其调控机制、加强土壤碳周转与全球变化的耦合研究。同时,深入探究气候变化对土壤微生物群落结构和功能的影响,阐明微生物介导的土壤碳稳定化机制,揭示微植物-土壤-微生物互作网络对农田碳汇功能的调控机理,为微生物介导的农田土壤碳储存提供新思路。
3.2 聚焦气候变化多因子交互效应
气候变化是一个复杂的过程,涉及温度、降水、二氧化碳浓度、氮沉降等多个因子,这些因子之间存在复杂的交互作用,对农田土壤碳储量产生综合影响。此外,极端气候事件如干旱、洪涝、热浪等的频发,对农田土壤碳循环过程也产生显著影响[30]。因此,未来的研究应该更加注重全球和区域尺度上气温升高、降水模式变化、二氧化碳浓度升高等多因子的综合效应,通过田间试验或模型模拟进行控制变量试验,以全面把握气候变化对农田生态系统的综合影响机制。加强全球气候模型与生态系统模型的耦合,提高模拟的空间分辨率和精度,以更好地模拟多因子的协同效应。加强对多因子交互影响机制的深入挖掘,尤其是在考虑不同气候区域和生态系统差异的基础上,定量评估不同气候变化因子对农田土壤碳储量、作物生长和生态系统稳定性等关键指标的协同作用。
3.3 发展综合模拟模型
当前基于气候的农田土壤碳储量评估方法虽然日趋成熟,但仍存在一些局限性。统计分析方法高度依赖于输入数据,难以可靠地外推到其他时间段。基于机理的过程模拟模型方法虽然能够反映土壤碳动力学过程,但对环境变量的考量较少[87]。综合模拟模型可以结合统计分析方法和基于机理的过程模拟模型方法的优点,既能够进行时空建模,又能够反映土壤碳对气候变化和人类活动的机理响应[85]。未来的研究可以向综合不同模型方面发展,通过整合不同模型的优势,建立更全面、准确的评估框架[55]。通过构建耦合全球气候、土壤特性、植被生长和人类活动的综合性框架,以更全面、准确地模拟不同气候情景下的农田土壤碳储量动态。应用人工智能、大数据等前沿技术,优化模型结构,提升模拟效率和精度,提高可解释性和可操作性。通过发展新一代综合模拟模型,可以为农田土壤碳储量评估和预测提供新的模型工具,为制定基于自然的碳汇策略和农业管理措施提供科学依据。
3.4 模型不确定性研究
不确定性检验在评估气候变化对农田土壤碳储量的影响研究中具有重要作用。模型不确定性可能源于数据、模型、尺度或多种因素耦合[90]。特别是生态系统过程模型,其存在计算过程复杂、输入参数多、结果验证困难等固有难题,加之未来气候变化中二氧化碳浓度、大气氮沉降速率、火灾频率、干旱、异常降水以及土地利用的变化都可能影响预测效果。微生物模型中的碳利用效率及其温度敏感性同样会在土壤有机碳反馈中产生很大的不确定性[73]。未来研究应着眼于提高气候变化与农田土壤碳储量模拟的可信度和预测精度,深入理解模型中的不确定性来源,包括参数不确定性、输入数据的不确定性以及模型结构的不确定性。通过更全面的参数敏感性分析,寻找在不同气候情景和地域条件下模型响应的不确定性。此外,要关注不同尺度下模型不确定性的传递和放大机制,以更好地理解模型在不同空间和时间尺度上的适用性。同时,为了增强模型不确定性的研究,可以将不同的不确定性检验方法集成到一个统一的模型框架中,以提供更全面的不确定性估计[91]。最终目标是建立更可靠、更稳定的模型,为研究者和决策者提供更准确的信息,促进可持续土壤管理和气候变化适应策略的制定。
-
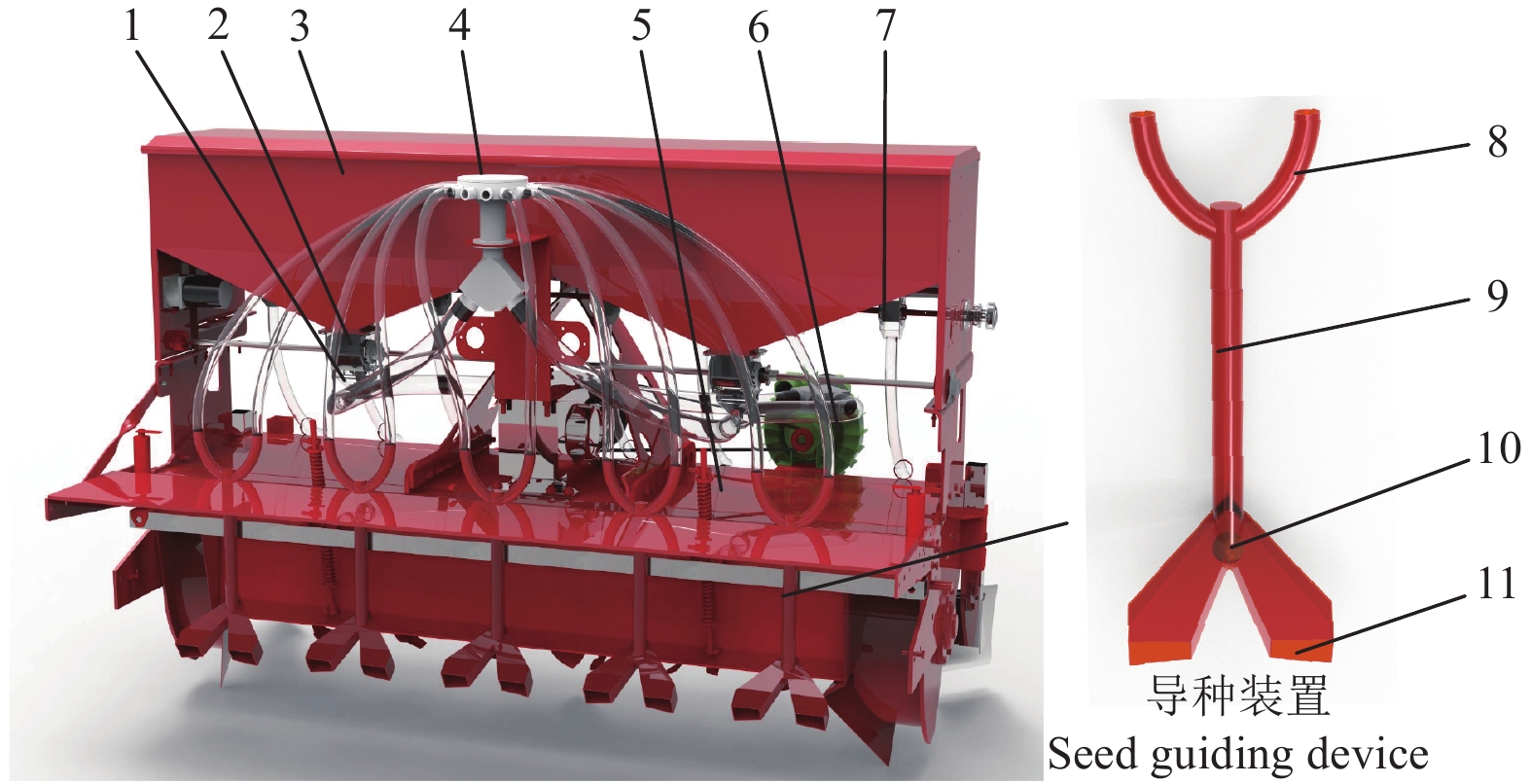
图 2 气送式小麦播种机整机及导种装置结构图
1.文丘里管 2.供种装置 3.种箱4.分配器 5.旋耕机底盘 6.风机 7.外槽轮8.Y型汇种管 9.刚性垂直输种管 10.球面弹籽部件 11.斜面底板
Figure 2. Structure diagram of air-fed wheat seeder and seed guiding device
1.Venturi tube 2.Seeding device 3.Seed box 4.Distributor 5.Rotary cultivator chassis 6.Fan 7.Outer groove wheels 8.Y-type collect seed pipe 9.Rigid vertical seed transfer pipe 10.Spherical collision seed part 11.Beveled bottom plate
图 4 小麦种子与弹籽部件碰撞受力分析图
1.外壳体 2.小麦种子 3.球面弹籽部件 4.斜面底板1.Housing 2.Wheat seed 3.Spherical collision seed part 4.Beveled bottom plate
Figure 4. Collision force analysis diagram of wheat seed and elastic seed component
注:R为球面弹籽部件的半径,mm;FG为小麦种子所受重力,N;FP为球面弹籽部件对小麦种子的支持力,N;β ′为FG与FP间的夹角,(°)。 Note:R is the radius of the spherical marbleseed part, mm; FG is the gravity of wheat seeds, N; FP is the support force of spherical bouncy seed parts for wheat seeds, N; β ′is the angle between FG and FP,(°) .
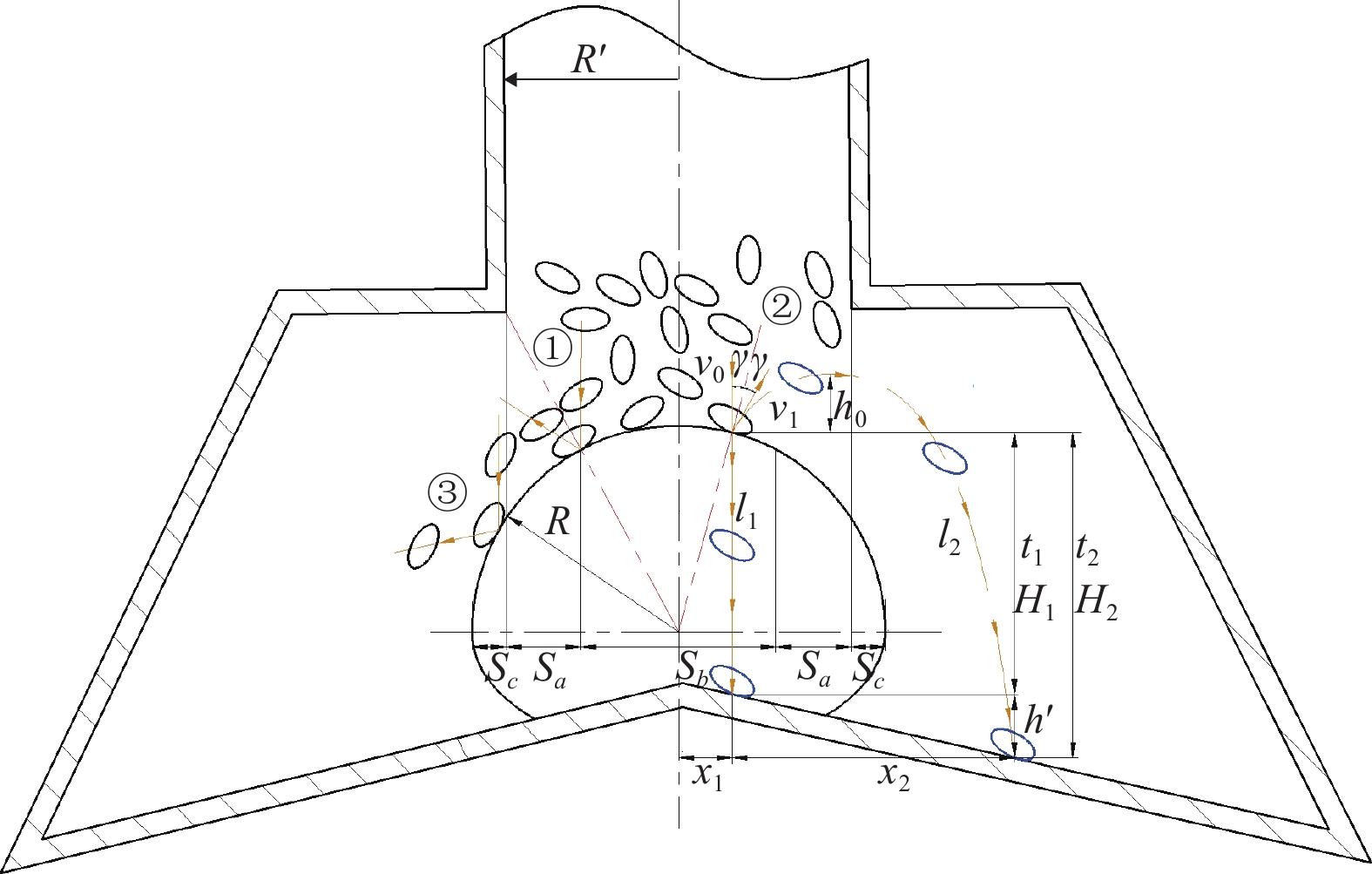
图 5 种子与弹籽部件的碰撞运动模型
注:γ为种子入射角,rad;γ′为反射角,rad;v0为种子碰撞前速度,m·s−1;v1为种子碰撞后速度,m·s-1;h0为种子沿l2运动的上升距离,mm;l1为无球面弹籽部件时种子运动轨迹;l2为有球面弹籽部件时种子运动轨迹;t1为种子沿l1运动时间,s;t2为种子沿l2运动时间,s;H1为l1高度,mm;H2为l2高度,mm;h′为有无球面弹籽部件时种子的落地高度差,mm;x1为碰撞点据中心点水平距离,mm;x2为碰撞点距落点水平距离,mm;Sa为种子碰撞区域1的球面面积,mm2;Sb为种子碰撞区域2的球面面积,mm2;Sc为种子碰撞区域3的球面面积,mm2;R′为输种管内部半径,mm。
Figure 5. Collision motion model of seed and collision seed part
Note: γ is the angle of incidence when the seeds collide, rad; γ′ is the reflection angle, rad; v0 is the velocity of the seeds before collision, m·s−1; v1 is the velocity of the seeds after collision, m·s−1; h0 is rising distance of seeds moving along l2, mm; l1 is the trajectory of seeds when a spherical bougainvillea seed part is located; l2 is the seeds movement trajectory when there is a spherical bougainvillea seed part; t1 is the time required for l1 trajectory , s; t2 is the time required for l2 trajectory , s; H1 is the height difference of l1 trajectory , mm; H2 is the height difference of l2 trajectory , mm; h′ is the difference in seed landing height of the spherical and spherical elastan seed components, mm; x1 is the horizontal distance of the collision point from the center point, mm; x2 is the horizontal distance from the collision point to the landing point, mm; Sa is the area of spherical surface of the seed collision area 1, mm2; Sb is the area of spherical surface of the seed collision area 2, mm2; Sc is the area of spherical surface of the seed collision area 3, mm2; R′ is the inner radius of rigid vertical seed transfer tube, mm.
图 6 斜面底板空间角度关系
1.球面弹籽部件 2.斜面底板1.Spherical collision seed part 2.Beveled bottom plate注:FT为种子在斜面所受总力,N;Fx为种子在斜面所受总力的X轴方向分力,N;Fy为种子在斜面所受总力的Y轴方向分力,N;β为三维斜面与水平面的夹角,(°);θ为三维斜面正视图(YOZ平面)与水平面的夹角,(°);α为三维斜面右视图(XOZ平面)与水平面的夹角,(°)。
Figure 6. Beveled bottom plate slope spatial angle relation
Note:FT is the total force of the seed on the inclined plane, N; Fx is the X-axis component of the total force exerted by the seed on the inclined plane, N;Fy is the Y-axis component of the total force of the seed on the slope, N;β is the angle between the three-dimensional inclined plane and the horizontal plane, (°) ;θ is the angle between the three-dimensional oblique front view (YOZ plane) and the horizontal plane, (°);α is the angle between the right view of the three-dimensional inclined plane (XOZ plane) and the horizontal plane, (°).
表 1 气送式小麦播种机主要参数与性能指标
Table 1 Main parameters and performance indicators of pneumatic wheat seeder
项目Item 值Value 整机尺寸(长×宽×高)
Overall dimensions
(length×width×height)/(mm×mm×mm)2 000×2 300×1500 导种装置型式Seed guiding type 分引组合式 各行排量一致性变异系数
Coefficient of variation of each row
seeding quantity consistency/%≤3.9 行内横向均匀度变异系数
Coefficient of variation of
transverse uniformity in row /%≤45 作业速度
working speed/(km·h−1)3~8 表 2 材料接触模型参数设置
Table 2 Factor level table of seeding performance test
材料
Material泊松比
Poisson's ratio剪切模量
Modulus of shear/Pa密度
Density/(kg∙m−3)碰撞恢复系数
Collision recovery coefficient静摩擦系数
Coefficient of static friction动摩擦系数
Dynamic friction coefficient小麦籽粒
Wheat grains0.29 5.08E+8 1350 0.02 1.25 1.24 铁Iron 0.30 7.00E+10 7800 0.41 0.32 0.18 土壤Soil 0.50 1.00E+8 1200 0.02 1.25 1.24 表 3 正交试验因素与水平
Table 3 Orthogonal test factors and levels
水平
Level斜面底板坡度
Beveled bottom plate slope A/(°)球面弹籽部件直径
Spherical collision seed part diameter B/mm+1.414 17 54 +1 15 50 0 10 40 −1 5 30 −1.414 3 26 表 4 正交试验方案与试验结果
Table 4 Orthogonal test scheme and results
试验号Test No. A/(°) B/mm δ1/% δ2/% 1 5 30 3.87 55.38 2 15 30 4.48 43.19 3 5 50 2.04 47.76 4 15 50 4.26 14.19 5 3 40 4.21 56.54 6 17 40 4.04 34.65 7 10 26 5.57 22.73 8 10 54 4.15 28.28 9 10 40 2.04 19.60 10 10 40 1.89 19.72 11 10 40 2.31 20.61 12 10 40 2.28 18.80 13 10 40 2.35 19.93 表 5 方差分析
Table 5 Analysis of variance
指标
Indicators方差来源
Source of varianceSS df MS F P δ1 a 0.84 1 0.84 2.16 0.1850 b 2.06 1 2.06 5.31 0.0447* ab 0.65 1 0.65 1.67 0.2372 a2 4.10 1 4.10 10.58 0.0140* b2 8.97 1 8.97 23.12 0.0019** 模型 15.23 5 3.05 7.85 0.0087** 残差 2.72 7 0.34 失拟 2.56 3 0.85 21.39 0.0630 误差 0.16 4 0.04 总和 17.95 12 δ2 a 735.69 1 735.69 7.19 0.0089** b 103.47 1 103.47 12.85 0.2208 ab 114.28 1 114.28 1.81 0.2006 a2 1100.30 1 1100.30 2.00 0.0032** b2 44.58 1 44.58 19.21 0.4069 模型 2059.36 5 411.87 0.78 0.0111* 残差 400.86 7 57.27 失拟 316.53 3 105.51 5.00 0.0769 误差 84.34 4 21.08 总和 2460.22 12 注:SS表示平方和;df表示自由度;MS表示均方和;a, b分别为A, B的水平值;*表示影响显著(P<0.05);**表示影响极显著(P<0.01)。 Note: SS represents the sum of squares; df represents degrees of freedom;MS stands for mean square sum; a, b is level value of A, B respectively; * indicates significant impact(P<0.05); **indicates significant impact (P<0.01). 表 6 不同播量下各导种装置型式导种性能仿真结果
Table 6 Simulation results of different seeding guiding device types on the performance of seeding
导种装置
Seed guiding deviceδ1/% δ2/% 150
kg∙hm−2300
kg∙hm−2450
kg∙hm−2150
kg∙hm−2300
kg∙hm−2450
kg∙hm−2平面底板
Flat plate10.24 8.33 7.09 52.74 48.4 44.12 弧面底板
Curved bottom plate8.80 7.53 4.56 44.38 43.23 38.65 波浪底板
Wavy plate8.21 7.35 3.94 33.48 26.19 28.75 斜面底板
Beveled bottom plate6.21 5.60 2.92 30.91 24.20 14.19 表 7 田间试验结果
Table 7 Field test results
导种装置
Seed guiding deviceδ1/% δ2/% 150
kg∙hm−2300
kg∙hm−2450
kg∙hm−2150
kg∙hm−2300
kg∙hm−2450
kg∙hm−2平面底板
Flat plate11.35 10.32 8.45 44.92 42.18 41.97 弧面底板
Curved bottom plate9.15 8.87 7.91 38.32 37.64 37.48 波浪底板
Wavy plate6.24 6.15 5.48 25.41 24.35 23.74 斜面底板
Beveled bottom plate3.15 2.65 2.75 14.71 12.28 13.13 -
[1] 佟光霁, 周伦政.双循环背景下我国粮食安全、现状、挑战及保障路径[J]. 学术交流, 2021(1): 97-108. [2] 李福建,徐东忆,吴鹏,等. 机械耕作和播种方式对稻茬小麦光合作用和产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(5):41-49. LI Fujian, XU Dongyi, WU Peng, et al. Effects of mechanical tillage and sowing on photosynthetic production and yield of rice stubble and wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(5): 41-49. (in Chinese with English abstract LI Fujian, XU Dongyi, WU Peng, et al. Effects of mechanical tillage and sowing on photosynthetic production and yield of rice stubble and wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(5): 41-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 赵淑红,谭贺文,王加一,等. 多功能集成式播种开沟器的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(11):58-67. ZHAO Shuhong, TAN Hewen, WANG Jiayi, et al. Design and test of multi-functional integrated seeding trencher[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(11): 58-67. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.11.008 ZHAO Shuhong, TAN Hewen, WANG Jiayi, et al. Design and test of multi-functional integrated seeding trencher[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(11): 58-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.11.008
[4] 刘彩玲,魏丹,都鑫,等. 宽苗带勾型窝眼轮式小麦精量排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2019,50(1):75-84. LIU Cailing, WEI Dan, DU Xin, et al. Design and test of wheeled wheat precision seeder with wide seedling with hook type socket eye[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(1): 75-84. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.01.008 LIU Cailing, WEI Dan, DU Xin, et al. Design and test of wheeled wheat precision seeder with wide seedling with hook type socket eye[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(1): 75-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.01.008
[5] 余松烈. 冬小麦精播高产栽培[J]. 山东农学院学报,1980(2):1-13. [6] 廖宜涛,李成良,廖庆喜,等. 播种机导种技术与装置研究进展分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2020,51(12):1-14. LIAO Yitao, LI Chengliang, LIAO Qingxi, et al. Research progress of seed guiding technology and device of planter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(12): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract WANG Chao, LIU Congjing, LI Hongwen, et al. Design and test of asymmetric large and small disc trenching device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(18): 28-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王希英,唐汉,王金武,等. 双列交错勺带式马铃薯精量排种器优化设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(11):82-90. WANG Xiying, TANG Han, WANG Jinwu, et al. Optimized design and experiment on double-row cross spoon-belt potato precision seed metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(11): 82-90. (in Chinese with English abstract WANG Jinwu, WANG Ziming, XU Changsu, et al. Design and test of intermittent synchronous filling device for duckbill type corn seed drainer in slope cultivated land[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(5): 57-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘全威. 高速播种机种子精准投送机构设计与试验研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017. LIU Quanwei. Design and Experiment of Seed Precise Delivery Mechanism for High-speed Planter [D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 陈晨. 精量播种机带式导种装置结构设计与性能试验研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2016. CHEN Chen. Structure Design and pErformance Test Research of the Belt Seed Guide Device of Precision Planter[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘建英,张鹏举,刘飞,等. 离散元模拟导种管高度对排种性能的影响[J]. 农机化研究,2016,38(1):12-16. LIU Jianying, ZHANG Pengju, LIU Fei, et al. The discrete element simulation guide tube height effects on seeding performance[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(1): 12-16. (in Chinese with English abstract LIU Jianying, ZHANG Pengju, LIU Fei,et al. The discrete element simulation guide tube height effects on seeding performance[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(1): 12 - 16.
[11] ENDRERUD H C. Influence of tube configuration on seed delivery to a coulter[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1999, 74(2):177-184. ENDRERUD H C. Influence of tube configuration on seed delivery to a coulter[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1999, 74(2): 177-184.
[12] 余佳佳,丁幼春,廖宜涛,等. 基于高速摄像的气力式油菜精量排种器投种轨迹分析[J]. 华中农业大学学报,2014,33(3):103-108. YU Jiajia, DING Youchun, LIAO Yitao, et al. High-speed photography analysis of dropping trajectory on pneumatic metering device for rapeseed[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014, 33(3): 103-108. (in Chinese with English abstract YU Jiajia, DING Youchun, LIAO Yitao, et al. High-speed photography analysis of dropping trajectory on pneumatic metering device for rapeseed[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2014, 33(3): 103 - 108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 祁兵,张东兴,崔涛,等. 中央集排气送式玉米精量排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(18):8-15. QI Bing, ZHANG Dongxing, CUI Tao, et al. Design and experiment of centralized pneumatic seed metering device for maize[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(18): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract KIAKI NAKAMURA. Development of cleaner and soil cultivator for live-broadcast machine in soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 1985, 47(4): 523-527.
[14] ED precision air seeder[EB/OL]. (20200810). http://www. amazone. net/1262. ED precision air seeder[EB/ OL]. (2020-08-10). http://www. amazone. net / 1262.
[15] RAJENDER S C, RAMESH K S, MAHESH K G, et al. Effects of crop establishment techniques on weeds and rice yield[J]. Crop Protection, 2014, 64(3):7-12. RAJENDER S C, RAMESH K S, MAHESH K G, et al. Effects of crop establishment techniques on weeds and rice yield[J]. Crop Protection, 2014, 64(3): 7-12.
[16] VADERSTAD A B. Zone 3-seed placement[EB/OL]. (20200810). http://www. vaderstad. com/en/planting/tempo-planter/tempor-12-18. VADERSTAD A B. Zone 3-seed placement[EB/ OL]. (2020-08-10). http://www. vaderstad. com/ en / planting / tempo-planter/ tempor-12-18.
[17] JI J, SANG Y, HE Z, et al. Designing an intelligent monitoring system for corn seeding by machine vision and Genetic Algorithm-optimized back propagation algorithm under precision positioning[J]. Plos one, 2021, 16(7):254-544. JI J, SANG Y, HE Z, et al. Designing an intelligent monitoring system for corn seeding by machine vision and Genetic Algorithm-optimized back propagation algorithm under precision positioning[J]. Plos One, 2021, 16(7): 254-544.
[18] 康建明,温浩军,王士国,等. 带式导种装置对排种均匀性影响的试验研究[J]. 中国农机化学报,2015,36(5):42-45. KANG Jianming, WEN Haojun, WANG Shiguo, et al. Experimental study on impact of belt type conductor delivery on seeding uniformity[J]. Journal of China Agricultural Mechanization, 2015, 36(5): 42-45. (in Chinese with English abstract KANG Jianming, WEN Haojun, WANG Shiguo, et al. Experimental study on impact of belt type conductor delivery on seeding uniformity [J]. Journal of China Agricultural Mechanization, 2015, 36(5): 42 - 45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 陈学庚,钟陆明. 气吸式排种器带式导种装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(22):8-15. CHEN Xuegeng, ZHONG Luming. Design and test on belt-type seed delivery of air-suction metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(22): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract CHEN Xuegeng, ZHONG Luming. Design and test on belt-type seed delivery of air-suction metering device [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(22): 8 - 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 陈玉龙,韩杰,兰玉彬,等. 精密排种器组合式导种管设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(24):14-24. CHEN Yulong, HAN Jie, LAN Yubin, et al. Design and experiment of the combined seed guiding tube for precision metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(24): 14-24. (in Chinese with English abstract CHEN Yulong, HAN Jie, LAN Yubin, et al. Design and experiment of the combined seed guiding tube for precision metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(24): 14-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 张顺,李勇,王浩宇,等. 水稻内充气力式精量穴播排种器导种管的设计与试验[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2021,47(1):71-80. ZHANG Shun, LI Yong, WANG Haoyu, et al. Design and experiment on the seed spout of inside-filling pneumatic type precision hole-seeding meter device for rice[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2021, 47(1): 71-80. (in Chinese with English abstract ZHANG Shun, LI Yong, WANG Haoyu, et al. Design and experiment on the seed spout of inside-filling pneumatic type precision hole-seeding meter device for rice[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2021, 47(1): 71–80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] YAZGI A. Effect of seed tubes on corn planter performance[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2016, 32(26):73-89. doi: 10.6090/jarq.49.227 YAZGI A. Effect of seed tubes on corn planter performance[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2016, 32(26): 73-89. doi: 10.6090/jarq.49.227
[23] KOCHER M F, COLEMAN J M, SMITH J A, et al. Corn seed spacing uniformity as affected by seed tube condition[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2011, 27(2):177-183. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2015.06.002 KOCHER M F, COLEMAN J M, SMITH J A, et al. Corn seed spacing uniformity as affected by seed tube condition[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2011, 27(2): 177-183. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2015.06.002
[24] Tang H, Xu F D, et al. The influence of a seed drop tube of the inside-filling air-blowing precision seed-metering device on seeding quality[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 204:107555. TANG H, XU F D, et al. The influence of a seed drop tube of the inside-filling air-blowing precision seed-metering device on seeding quality[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 204: 107555.
[25] Liu R, Liu L, Li Y, et al. Numerical Simulation of Seed-Movement Characteristics in New Maize Delivery Device[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12:1944. LIU R, LIU L J, LI Y J, et al. Numerical simulation of seed-movement characteristics in new maize delivery device[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12: 1944.
[26] 黄小毛,张顺,朱耀宗,等. 气送式油菜飞播装置投种过程分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(17):31-41. HUANG Xiaomao, ZHANG Shun, ZHU Yaozong, et al. Seeding process analysis and test of the air conveying rapeseed aerial seeding device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(17): 31-41. (in Chinese with English abstract Huang Xiaomao, Zhang Shun, Zhu Yaozong, et al. Seeding process analysis and test of the air conveying rapeseed aerial seeding device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(17): 31-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 雷小龙,廖宜涛,丛锦玲,等. 油菜小麦兼用气送式直播机集排器参数优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(12):16-26. LEI Xiaolong, LIAO Yitao, CONG Jinling, et al. Parameter optimization and experiment of air-assisted centralized seed-metering device of direct seeding machine for rape and wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(12): 16-26. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.11.006 LIU Lijing, YANG Hui. Three-dimensional reverse engineering design of seed guide tube based on Gemagic Design software[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31 (11): 40-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.11.006
[28] 于佳杨,卢彩云,卫如雪,等. 基于离散元法的小麦精量排种器性能模拟试验[J]. 江苏农业科学,2018,46(8):225-228. YU Jiayang, LU Caiyun, WEI Ruxue, et al. Simulation test of performance of wheat precision seed-metering device based on discrete element method[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(8): 225-228. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2018.08.057 YU Jiayang, LU Caiyun, WEI Ruxue, et al. Simulation test of performance of wheat precision seed-metering device based on discrete element method[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(8): 225-228. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2018.08.057
[29] 李兆东,王晴晴,张亚兰,等. 倾斜抛物线型孔轮式小麦供种装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2018,49(5):116-124. LI Zhaodong, WANG Qingqing, ZHANG Yalan, et al. Design and test of inclined parabolic hole wheel wheat feeding device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(5): 116-124. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.05.013 LI Zhaodong, WANG Qingqing, ZHANG Yalan, et al. Design and test of inclined parabolic hole wheel wheat feeding device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(5): 116-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.05.013
[30] 刘凡一,张舰,李博,等. 基于堆积试验的小麦离散元参数分析及标定[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(12):247-253. LIU Fanyi, ZHANG Jian, LI Bo, et al. Calibration of parameters of wheat required in discrete element method simulation based on repose angle of particle heap[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(12): 247-253. (in Chinese with English abstract LIU Fanyi, ZHANG Jian, LI Bo, et al. Calibration of parameters of wheat required in discrete element method simulation based on repose angle of particle heap[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(12): 247-253. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 朱惠斌,吴宪,白丽珍,等. 基于 EDEM-ADAMS 仿真的稻茬地双轴破茬免耕装置研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(19):10-22. ZHU Huibin, WU Xian, BAI Lizhen, et al. Development of biaxial no-till device for rice stubble breaking based on EDEM-ADAMS simulation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(19): 10-22. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.19.002 ZHU Huibin, WU Xian, BAI Lizhen, et al. Development of biaxial no-till device for rice stubble breaking based on EDEM-ADAMS simulation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(19): 10-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.19.002
[32] 雷小龙,廖宜涛,李兆东,等. 油菜小麦兼用气送式集排器搅种装置设计及充种性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(18):26-34. LEI Xiaolong, LIAO Yitao, LI Zhaodong, et al. Design and seeding performance test of seeding device for combined air-delivered collector for rapeseed wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(18): 26-34. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.18.004 LEI Xiaolong, LIAO Yitao, LI Zhaodong, et al. Design and Seeding Performance Test of Seeding Device for Combined Air-Delivered Collector for rapeseed Wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(18): 26-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.18.004
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 冼海英,肖波,姚小萌,窦韦强. 黄土高原生物结皮覆盖下表层土壤有机碳组分对模拟气候暖湿化的响应. 应用生态学报. 2025(01): 132-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄艳平,罗贵文,高林海,付金霞,李志. 东北平原土体厚度和土壤水分的空间变异. 水土保持研究. 2025(03): 108-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李斯佳,王冰,王子昊,张秋良. 基于PLUS-InVEST模型的大兴安岭农林交错区碳储量时空变化及驱动力分析. 农业工程学报. 2024(21): 232-241 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 张龙江,陈国平,林伊琳,赵俊三,刘俸汝,彭苏芬. 基于MOP-PLUS-InVEST模型的碳储量多情景模拟及驱动机制分析. 农业工程学报. 2024(22): 223-233 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 夏楠 ,李安澜 ,全伟琳 ,唐梦迎 ,唐玉倩 ,徐战江 . 基于GTWR的中国近地面臭氧污染及驱动因素分析. 农业工程学报. 2024(23): 283-293 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载: