Assessing risk and governing of agricultural non-point source pollution in Three Gorges Reservoir Areas
-
摘要:
针对三峡库区农业面源污染风险评估指标体系不完善、个别指标计算时基础数据获取难度大的问题,该研究充分考虑农业面源污染产生、形成及调控全过程因素,构建了基于层次分析法的三峡库区面源污染风险评价指标体系,以更易获取的数据为基础参数、应用韦伯-费希纳定律克服个别风险指标过大的问题,给定了三峡库区面源污染风险评估指标计算方法,评估了三峡库区农业面源污染风险,并提出了三峡库区县域单元的纵向和横向污染治理清单。研究结果表明,三峡库区各县域农业面源污染总体处于中风险,库区内湖北省夷陵区、重庆市南岸区风险值最高,其次是重庆市大渡口区、沙坪坝区等市辖区、巫溪县以及湖北省兴山县和秭归区,之后是开州区、万州区、丰都县、云阳县等区域;化肥强度指数、畜禽养殖强度指数、降雨侵蚀指数、环保投资指数是三峡库区农业面源污染风险的主要影响指标;三峡库区各县域化肥强度指数以及畜禽养殖强度指数风险值之和占总压力指数风险值的比例平均为79%,巫溪县、巴东县、巫山县甚至达到90%;重庆市南岸区、大渡口区以及湖北省各县域化肥施用强度较高,建议开展茶果树施肥技术提升,畜禽养殖强度相对较大的区域主要集中在重庆市云阳县、开州区、巫溪县、巫山县以及湖北省各县区,建议更多开展猪和羊畜禽废污处理能力提升,此外还应加大环保投入以及合理调整种植结构;从纵向管控来看,三峡库区农业面源污染治理应以南岸区和夷陵区为优先管控区域,河流水质优先治理区域为大渡口区、九龙坡区以及湖北省的各县区,从横向管控来看,大部分县域的主要污染防控因素为化肥减量和畜禽养殖治理,其中三峡库区上游和下游地区应当更多关注化肥减量,中游则应更多关注畜禽养殖的污染防控。该研究成果可为三峡库区农业面源污染政策制定提供有力参考。
Abstract:Non-point source pollution is required to consider the whole process factors of generation, formation, and regulation. In this study, the risk assessment system was constructed to evaluate the non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area using an analytic hierarchy process. Taking the availability of data as an essential source, an operable index system was then proposed to overcome the excessive indicators of individual risk using Weber-Fechner. Finally, the horizontal and vertical lists of pollution control were determined for the decision-making. The result showed that agricultural non-point source pollution was predicted as the middle-risk level in the study area. The higher scores of risks were found in the Yiling District in Hubei Province and Nanan District in Chongqing Municipality. The next high-risk scores were distributed in Dadukou District, Shapingba District, Wuxi County in Chongqing Municipality and Xingshan County, Zigui County in Hubei Province, and the following were Kaizhou District, Wanzhou District, Fengdu County, and Yunyang County in Chongqing Municipality. The influencing indexes were obtained as fertilizer intensity, livestock/poultry breeding intensity, rainfall erosion, and environmental protection investment index in the risk system of agricultural non-point source pollution. The ratio between the risk scores of fertilizer intensity and livestock/poultry breeding intensity index accounted for 79% of the total risk scores of press indexes. By contrast, the ratios were more than 90% in Wuxi, Badong, and Wushan County. The average ratios of risk score were 32%, 25%, 24%, and 19%, respectively, for the stress, transformation, state, and governance index to the comprehensive one. Among them, the stress index still occupied the largest proportion of the risk score. Fertilizer intensity was higher in Nanan District, Dadukou District of Chongqing Municipality, and the counties in Hubei Province. Some suggestions were then proposed to improve the fertilization of fruit trees. The relatively high intensity of livestock and poultry breeding was concentrated mainly in Yunyang County, Kaizhou District, Wuxi County, Wushan County in Chongqing Municipality, and the counties in Hubei Province. Particularly, it was necessary to improve the waste treatment of pigs and sheep. In addition, the planting structure was required to adjust reasonably to increase the investment in environmental protection. In the vertical lists of pollution control, Yiling and Nanan District should be given priority to the agricultural non-point source pollution control, where the priority areas of river water quality control were Dadukou, Jiulongpo District, and the counties in Hubei Province. In the horizontal lists of pollution control, the pollution control factors in most counties were fertilizer reduction and livestock breeding control. More attention should be paid to fertilizer reduction in the upstream and downstream areas, while the pollution prevention and control caused by livestock and poultry breeding in the middle reaches. Furthermore, the slope length index of each county was evaluated, according to the average value of 0.026. Soil erodibility of each county was chosen from 0.015 to 0.019 ·hm2·h/(MJ·mm·hm2) for the better performance of risk assessment. This finding can provide a strong reference for the policy formulation of agricultural non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges reservoir area.
-
0. 引 言
全面推动长江经济带发展,坚持生态优先、绿色发展是中国十四五规划纲要中的重要内容。三峡库区地跨湖北省西部和重庆市中东部,是长江流域重要的生态屏障区,是贯彻落实长江经济带“共抓大保护、不搞大开发”的重要区域[1],也是生态环境保护与移民安稳致富交叉问题并存的区域。2021年三峡库区重庆市36条一级支流72个断面中,水质呈富营养的断面比例为34.7%,嘉陵江监测断面中仍有15.7%的比例为Ⅳ和Ⅴ类[2]。开展三峡库区农业面源污染风险评估及防控对策研究,对促进三峡库区推行绿色生产生活方式、持续改善长江水质、实现农业农村发展与资源环境相协调、助力长江经济带高质量发展具有重要的支撑作用。
现有面源污染风险评估方法主要包括系统多因子指数集成评价方法、输出风险模型法、分布式面源污染模型评价法和层次分析法等[3-5]。多因子指数集成评价方法和分布式面源污染模型评价法参数获取难以及操作复杂限制了该方法的使用[6],同时评价会受到空间数据精度的影响[7]。输出风险模型法以输出系数法为基础,不考虑中间过程和内在机制,操作简单、所需参数少、易获取资料[8],层次分析法中可考虑污染的产生、形成的多因素,结合权重确定综合风险值[9-10],其参数获取及操作也比较简单,更适合无经验人员操作或参数获取难度较大的区域面源污染评估。
三峡库区面源污染研究自2003年开始逐年加强,主要集中于面源污染负荷估算和变化规律分析、子流域面源污染现状分析等方面[11-14],但对于近年三峡库区面源污染风险评价及防治措施研究尚少[15]。本文充分考虑数据的易获得程度以及面源污染产生、形成及调控等全过程因素,基于层次分析法构建三峡库区面源污染风险评价体系,给定操作性更好的指标计算方法,同时提出相应的治理清单,为三峡库区面源污染宏观治理提供参考。
1. 材料和方法
考虑到资料收集、污染治理投资主体通常为县域,因此以县域为主要的划分单元,分析县域范围农业面源污染风险。共划分27个风险单元,其中重庆市22个,湖北省5个,其中湖北省夷陵区和宜昌市区划分为2个单元。
1)风险评价指标体系
面源污染风险评价指标体系的建立是进行面源污染风险评价的前提和基础,在遵循科学性、全面性、代表性、方便性等原则基础上,构建三峡库区县域农业面源污染风险评价指标体系。重庆市农业面源污染风险评估技术规范[16](以下简称“规范”)给出了包括压力指数、转化指数和状态指数三类指标的评价体系,其中压力指数即为风险来源,包括化肥强度指数、农药强度指数、地膜强度指数、畜禽养殖强度指数等单项指标;转化指数和状态指数主要反映污染物迁移和转化过程参数,其中转化指数包括降雨侵蚀指数、坡长坡度指数、土壤可蚀性指数、坡耕地指数等单项指标,状态指数包括水环境质量指数、水环境容量指数、水网密度指数、水田滞留指数等单项指标。然而在面源污染形成的全过程中除了污染物来源、影响污染物迁移的自然因素和人为因素,还应当考虑人为调节对污染治理影响,汪嘉杨等[17]在对太湖流域水环境承载力评价中考虑了水环境管理的作用,任晓强[5]在对白洋淀上游水环境风险评价体系中也考虑了水污染治理能力。因此,本文增加治理指数作为与压力指数、转化指数、状态指数同级别的二级指标,并以环保投资指数表示,形成三峡库区县域农业面源污染风险评估指标体系,见表1。
表 1 三峡库区农业面源污染风险评估指标体系Table 1. Risk assessment index system of agricultural non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area一级指标
The first level index二级指标
The second level index三级指标
The third level index三峡库区农业面源污染风险评估综合指数Comprehensive index of agricultural non-point source pollution risk assessment in Three Gorges Reservoir Area 压力指数 化肥强度指数I11 农药强度指数I12 地膜强度指数I13 畜禽养殖强度指数I14 转化指数 降雨侵蚀指数I21 坡长坡度指数I22 土壤可蚀性指数I23 坡耕地指数I24 状态指数 水环境质量指数I31 水环境容量指数I32 水网密度指数I33 水田滞留指数I34 治理指数 环保投资指数I41 2)风险评价指标计算
风险评价指标的计算总体上参考规范中给定的计算方法,但考虑到数据可获取程度和适用度,对个别指标计算进行调整。规范中不同指数计算方法主要为该指标的当前数值与指标参比值(安全阈值)或该指标区域平均值的比例,参照该计算方法,对畜禽养殖强度指数、坡长坡度指数、坡耕地指数、水环境质量指数、水网密度指数、水田滞留指数、环保投资指数等指标计算方法进行调整。
畜禽养殖强度指数I14在规范中估算时需要实际畜禽养殖量、理论畜禽养殖量、规模化养殖环保设施配套率、非规模化养殖量、社会养殖量等参数,实际操作中获取难度大且难以保证数据的精度,因此对畜禽养殖强度指数I14计算方法进行改进,计算式如下:
I14=D1×P/(85×G) (1) 式中D1为畜禽养殖猪当量,头。根据畜禽粪污土地承载力测算技术指南[18],对于其他品类畜禽需与猪进行度量换算,牛的猪当量为4.45、羊为0.4、家禽为0.0004;P为单位数量猪污染物排放量, kg/头,猪排氮量按照11 kg/头进行计算[18];G为耕地面积,hm2;选取50%粪肥年施氮限量标准(170 kg/hm2)作为环境容量安全值[19-20],即以85 kg/hm2为单位耕地面积下畜禽养殖安全排放参比值。
坡长坡度指数I22计算式如下:
I22=F/1.47 (2) F=LS (3) L=(λ/22.13)η (4) η=β/(β+1) (5) β=(sinθ/0.0896)/[3(sinθ)0.8+0.56] (6) S={10.8sinθ+0.03,θ<5∘16.8sinθ−0.50,5∘⩽ (7) 式中F为坡度坡长因子值,主要通过DEM数据进行ArcGIS栅格提取得到;1.47为按照30 m×30 m网格划分后计算得到的各县区平均值。L为标准化到22.13 m坡长上的土壤侵蚀量;λ为像元大小与栅格数量乘积;η为坡长因子指数;β为细沟侵蚀量与细沟侵蚀间侵蚀量的比值;θ为坡度;S为坡度因子。
坡耕地指数I24在规范中采用大于5°的坡耕地面积作为参数,该数据获取通常需要基于DEM数据处理后得到,其精度易受DEM数据精度影响。考虑到第三次国土调查主要数据公报中耕地坡度统计的划分为0~2°、>2°~6°、>6°~15°、>15°~25°和>25°共5个等级,因此采用更易获取的大于6°的坡耕地比例H1作为计算参数,坡耕地指数I24计算式如下:
{I_{24}} = \left\{ {\begin{aligned} &3.5{H_1}, &{{H_1} \in \left[ {0,0.2} \right)} \\ &1.5{H_1} + 0.4, &{{H_1} \in \left[ {0.2,0.4} \right)} \\ &10{H_1} - 3, &{{H_1} \in \left[ {0.4,1} \right]} \end{aligned}} \right. (8) 水环境质量指数I31规范中以各污染物指标的监测浓度为参数,需要开展大量的监测,数据获取较难,考虑到政府工作网站上通常可以获得河流水质的类别,因此采用公布的县域现状水质类别与目标水质类别限值比值的平均值进行计算,简化计算方法如下:
{J_{u1}} = {J_{u2}}/{J_{u3}} (9) {I_{31}} = \sum\limits_{u = 1}^{{dn}} {{J_{u1}}} /{{dn}} (10) 式中Ju1为第u个断面污染物的水质指数;Ju2为第u个断面现状水质对应的地表水环境质量标准限值,对于综合评价可选用地表水环境中氨氮的标准限值,对于单一污染物评价则可选用相应污染物的标准限值;Ju3为第u个断面目标水质对应的地表水环境质量标准限值,dn为县域内水质监测断面数量。
水网密度指数I33计算采用第三次国土调查数据中涉及的部分水体面积数据,本文明确风险评估中县域水域面积采用第三次国土资源调查结果中河流面积、水库面积、坑塘面积以及沟渠面积累加之和进行计算,参比值为区域平均值0.04 km2/km2,计算式如下:
{I_{33}} = 0.04/{W_a} (11) 式中Wa为县域水域面积占县域面积的比例,km2/km2;
水田滞留指数I34采用规范中给出的计算方法时会出现巴东县、巫溪县等水田面积很小的县域水田滞留指数过大的情况而影响评价结果,因此在原有水田滞留指数I34原计算方法基础上进行重新分级和指标计算。根据韦伯-费希纳定律(W-F定律)计算指标的分级标准界限值,W-F定律是一项描述心理量和物理量之间关系的定律,该定律可以避免人为划分指标等级的主观性,客观确定指标标准限值,能够反映评价指标各个评价等级之间的突变特性,不受地域影响。该定律的表达式如下:
k = a{\mathrm{lg}} c (12) 式中k是人体产生的反应量;a是韦伯常数;c是客观环境刺激量。
将韦伯-费希纳定律应用到环境风险评估中,假设c是影响环境风险的外部因素即风险评价指标;把人体产生的反应量k 视为评价指标对环境风险的影响程度,式(12)进行差分得到式(13)
\Delta k = a(\Delta c/c) (13) 式(13)表明风险评价指标值成等比变化时对生态环境产生的危害程度成等差变化;为此,将水田滞留指数的变化范围划分为0、1、……9共10个级别,其中0、1、5和9对应的风险评分值的限值分别为0.7、1、3和5[21]。同时根据式(13)可得:
{a_f} = {({c_{fn}}/{c_{f0}})^{\tfrac{1}{9}}} (14) 式中af是指标f在同一等级上下界限的比值;cfn是指标f 的最大值;cf0是指标f 的最小值。按照规范中计算得到I34原最大值为14.92,最小值为0.79,可计算得到对应风险评分限值0.7、1、3和5对应的I34原分别为0.79、1.09、4.04和14.92,建立I34与I34原的数学关系,即I34=1.486ln(I34原)+0.957(R2=0.998),得到新的水田滞留指数计算式如下:
{I_{34}} = 1.486\ln (0.4675/M) + 0.957 (15) 式中M为水田占耕地面积的比例。
环保投资指数I41反映了县域对环保的重视程度,以环保投资占GDP比重进行表征。根据国际经验,当治理环境污染的投资占GDP 的比例达1.0%~1.5%时,可控制环境恶化的趋势[5,17]。因此以1.0%作为安全限值,计算环保投资指数:
{I_{41}} = 1.0\%/O (16) 式中O为环保投资占GDP的比例,%。
3)风险指标权重确定
规范中已给出压力指数、转化指数和状态指数以及各分项指标的权重比例,本文仅确定治理指数的权重即可。考虑到熵权法根据指标的变异程度,能够客观计算出指标的权重值[22-24],因此采用熵权法确定权重,具体计算步骤如下:
① 数据标准化
正向指标:
{\mu _{ij}} = \dfrac{{{x_{ij}} - \min ({x_{1j}},{x_{2j}}, \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot ,{x_{nj}})}}{{\max ({x_{1j}},{x_{2j}}, \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot ,{x_{nj}}) - \min ({x_{1j}},{x_{2j}}, \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot ,{x_{nj}})}} (17) 负向指标:
{\mu _{ij}} = \dfrac{{\max ({x_{1j}},{x_{2j}}, \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot ,{x_{nj}}) - {x_{ij}}}}{{\max ({x_{1j}},{x_{2j}}, \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot ,{x_{nj}}) - \min ({x_{1j}},{x_{2j}}, \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot \cdot ,{x_{nj}})}} (18) 式中xij为第i个县区第j个指标的计算值,i=1,2,···,n,j=1,2,···,m;μij为第i个县区第j个指标的标准化值。
② 熵值
第j个指标的熵值ej计算式如下:
{e_j} = - \dfrac{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{R_{ij}}\ln {\mu _{ij}}} }}{{\ln n}},{R_{ij}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _{ij}}}}{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{\mu _{ij}}} }} (19) ③ 权重
第j个指标的权重Wj计算式如下:
{W_j} = \dfrac{{{h_j}}}{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^m {{h_j}} }},{h_j} = 1 - {e_j} (20) 计算得到治理指数的权重为0.122,压力指数、转化指数和状态指数权重之和为0.878,治理指数的权重与文献[17]中反映治理措施的水环境响应指标权重0.135相差不大,基于规范中给定的权重按照比例进行重新换算,得到三峡库区农业面源污染风险评估指标权重见表2。
表 2 三峡库区农业面源污染风险评估指标权重Table 2. Weight of agricultural non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area一级指标
The first level index二级指标
The second level index三级指标
The third level index指标名称
Index name权重
Weight指标名称
Index name权重
Weight三峡库区农业
面源污染风险
评估综合指数
Comprehensive
index of
agricultural
non-point source
pollution risk
assessment in
Three Gorges
Reservoir Area压力指数 0.378 化肥强度指数I11 0.370 农药强度指数I12 0.229 地膜强度指数I13 0.077 畜禽养殖强度指数I14 0.324 转化指数 0.203 降雨侵蚀指数I21 0.396 坡长坡度指数I22 0.134 土壤可蚀性指数I23 0.248 坡耕地指数I24 0.222 状态指数 0.297 水环境质量指数I31 0.347 水环境容量指数I32 0.293 水网密度指数I33 0.153 水田滞留指数I34 0.207 治理指数 0.122 环保投资指数I41 1 4)风险综合评分计算及风险等级划分
风险综合评分值的计算采用综合指数加权求和法,即用各评估指标的评分值与其权重系数相乘并求和来反映面源污染风险的大小,其数学表达式为
R = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^m {{S_j}{W_j}} (21) 式中R为水环境风险综合评分值;Sj为第j个评价指标的评分值;Wj为各评价指标的权重值;j为第j个评价指标;m为评价指标的个数。风险综合评分值的计算结果越大,污染风险程度越大,反之越小。风险综合评分值分级见表3。
表 3 风险分级Table 3. Grading of the risk级别Level 风险类别Risk description 评分值Score Ⅰ 无风险或者可接受风险 (0,0.7] Ⅱ 低风险 (0.7,1.0] Ⅲ 中风险 (1.0,3.0] Ⅳ 高风险 (3.0,5.0] Ⅴ 极高风险 (5.0,∞) 4)数据来源
数据主要来自于各县域统计年鉴、生态环境质量公报、国土调查数据、水资源公报等,数据年份主要为2020年,主要数据来源见表4,仅坡长坡度指数计算时需要DEM数据。河流水质数据共收集135个断面,包括国考断面、市考断面、长江经济带断面、水华(非汇水区断面)以及常规监测断面等,各县域断面数量分布见表5。
表 4 主要数据来源Table 4. Source of main data序号No. 数据名称Data name 数据来源Data source 1 农作物播种面积 统计年鉴或经济统计
年鉴或政府工作报告2 化肥施用量 3 农药施用量 4 地膜使用量、地膜覆盖面积 5 畜禽养殖量和种类 6 县域面积 7 GDP及人口 8 节能环保投资 9 多年平均降雨量 水资源公报 10 地表径流量 11 坡耕地面积 第三次国土调查数据 12 水田面积 13 湖库沟渠面积 14 河流水质 生态环境厅环境公开数据 表 5 河流水质数据分布Table 5. Distribution of water quality data序号
No.县域名称
County name断面数量
Number
of sections河流名称
Rivers name序号
No.县域名称
County name断面数量
Number of
sections河流名称
Rivers name1 江津区 8 长江、临江河、塘河、璧南河、綦江河、笋溪河 15 忠县 7 长江、渠溪河、黄金河、汝溪河、玉溪河、 东溪河 2 巴南区 7 蒲河、一品河、花溪河、五步河、长江 16 石柱 5 普子河、龙河、磨刀溪、龙河、官渡河 3 大渡口区 1 长江 17 万州区 8 长江、新田河、浦里河、磨刀溪、石桥河、瀼渡河、五桥河、苎溪河 4 九龙坡区 1 长江 18 开州区 5 澎溪河(小江)、江里河、浦里河 5 沙坪坝区 2 嘉陵江、梁滩河 19 云阳县 6 长江、澎溪河(小江)、汤溪河、长滩河 6 渝中区 1 嘉陵江 20 巫溪县 7 汤溪河、梅溪河、大宁河、长溪河、巴岩子河、柏杨河 7 南岸区 2 长江 21 奉节县 6 长江、长滩河 、朱衣河、梅溪河、大溪河、草堂河 8 江北区 4 长江、栋梁河 22 巫山县 6 长江、大宁河、神女溪、抱龙河、三溪河、冷水溪 9 北碚区 5 嘉陵江、璧北河、梁滩河、黑水 23 巴东县 2 神农溪 10 渝北区 7 长江、后河、栋梁河、桥溪河、御临河、 大洪河 24 兴山县 2 香溪河 11 长寿区 8 御临河、大洪河、桃花溪、龙溪河、长江 25 秭归县 9 长江、青干河、叱溪河、童庄河、九畹溪 12 涪陵区 8 长江、乌江、麻溪河、碧溪河、黎香溪、清溪河 26 夷陵区 4 太平溪、黄柏河 13 武隆区 6 乌江、木棕河、芙蓉江、大溪河、石梁河 27 宜昌市区 1 黄柏河 14 丰都县 7 长江、渠溪河、碧溪河、龙河、赤溪河 2. 结果与分析
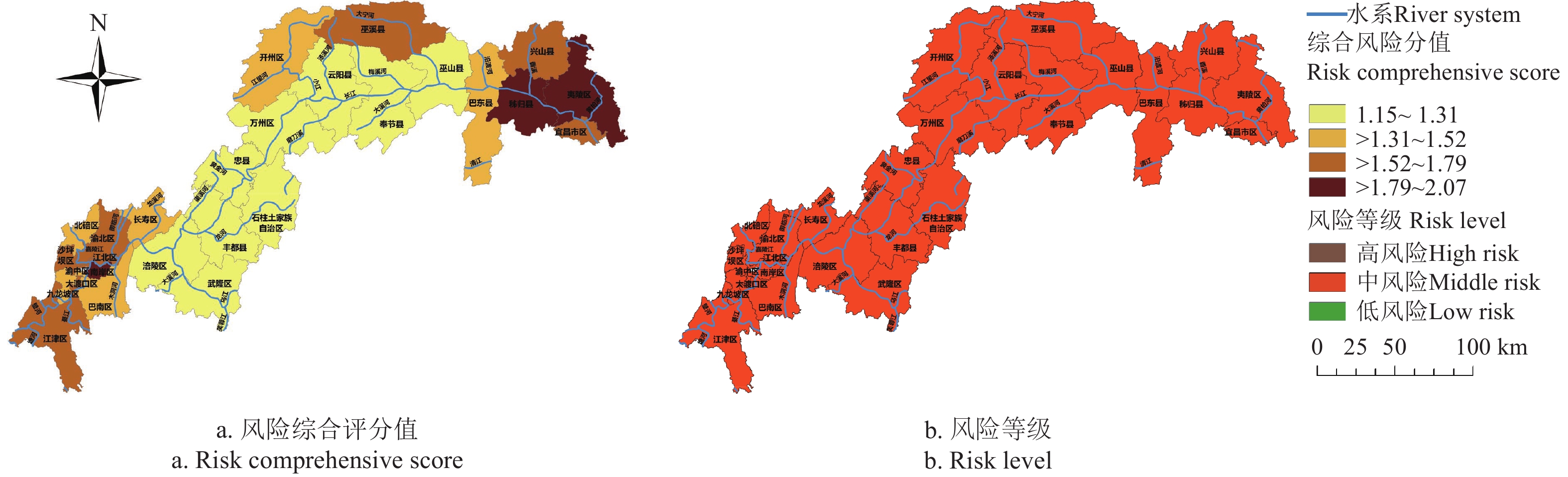
2.1 三峡库区农业面源污染风险评分及等级
计算得到三峡库区农业面源污染风险综合评分值以及风险等级见图1。可以看到,三峡库区农业面源污染风险总体处于中风险,说明风险存在或者潜在存在会造成一定损害,需要人为进行干预。从风险综合评分值来看,库区内湖北省夷陵区、南岸区分值更高,其次是重庆市大渡口区、沙坪坝区等市辖区、巫溪县以及湖北省兴山县和秭归区,之后是开州区、万州区、丰都县、云阳县等库区腹地。
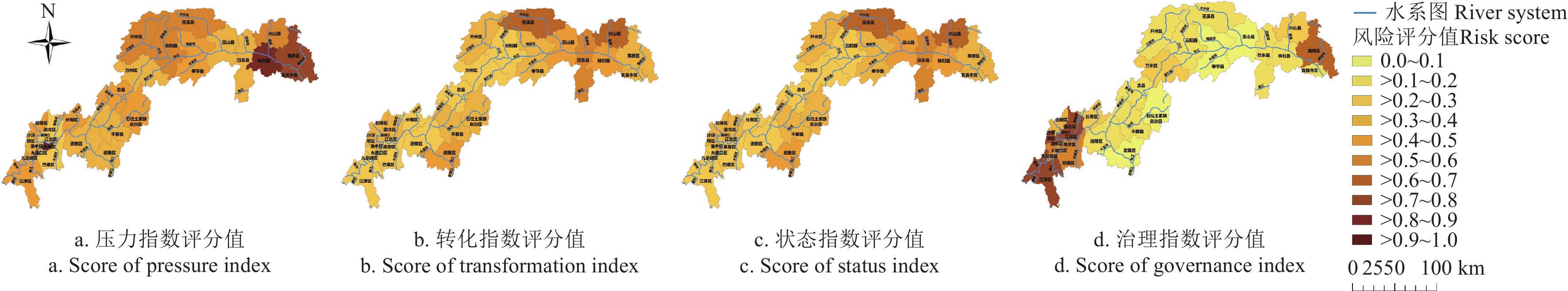
图2给出了三峡库区农业面源污染风险评价体系的二级指标风险值分布图,其中压力指数风险值较大的区域主要为湖北省秭归区、夷陵区、宜昌市区以及重庆市南岸区,转化指数较大的区域为湖北省巴东县、重庆市巫溪县、武隆区和巴南区,状态指数风险值较大的区域为湖北省巴东县、兴山县、秭归县以及重庆市巫溪县,治理指数风险值较大的区域为夷陵区以及南岸区等重庆市辖区。
由此可见,夷陵区和南岸区风险综合评分值高均主要由于压力指数和治理指数风险值较高;秭归县风险综合评分值高主要由于压力指数和状态指数风险值较高;大渡口区、沙坪坝区等市辖区风险综合评分值高则主要由于治理指数风险值较大。
2.2 三峡库区农业面源污染风险指标分析
表6给出了风险评估三级指标的风险值,总体来说,化肥强度指数、畜禽养殖强度指数、降雨侵蚀指数、环保投资指数在风险综合评分中的占比更高。降雨侵蚀系数主要受气候影响,通常为不可人为改变和控制的因素,但化肥强度指数、畜禽养殖强度指数以及环保投资指数等指标均可以通过合理的措施进行干预。
表 6 三级指标风险评估分值表Table 6. Risk assessment scores for the third level indicators县域名称
County name化肥强
度指数
Fertilizer
intensity
index农药强
度指数
Pesticide
intensity
index地膜强
度指数
Mulch
intensity
index畜禽养殖
强度指数
Livestock
breeding
intensity
index降雨侵
蚀指数
Rainfall
erosion
index坡长坡
度指数
Slope gradient
index土壤可蚀
性指数
Soil
erodibility
index坡耕地
指数
Terraced
farmland
index水环境质
量指数
Water
environmental
quality index水环境
容量指数
Water
environmental
capacity index水网密
度指数
Density
index of
water
network水田滞
留指数
Retention
index of
paddy field环保投
资指数
Environment-al
protection
investment
index江津区Jiangjin 0.18 0.08 0.04 0.15 0.27 0.02 0.08 0.03 0.08 0.07 0.03 0.05 0.71 巴南区Banan 0.12 0.03 0.03 0.06 0.27 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.06 0.07 0.04 0.05 0.54 大渡口区Dadukou 0.55 0.10 0.03 0.01 0.21 0.02 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.11 0.02 0.12 0.32 九龙坡区Jiulongpo 0.14 0.16 0.03 0.04 0.20 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.11 0.03 0.04 0.57 沙坪坝区Shapingba 0.26 0.06 0.03 0.02 0.21 0.02 0.08 0.01 0.09 0.11 0.05 0.09 0.71 渝中区Yuzhong 南岸区Nan'an 0.74 0.10 0.03 0.02 0.21 0.05 0.07 0.01 0.08 0.10 0.02 0.09 0.51 江北区Jiangbei 0.22 0.08 0.03 0.02 0.21 0.07 0.07 0.01 0.06 0.10 0.02 0.07 0.76 北碚区Beibei 0.24 0.11 0.04 0.03 0.23 0.06 0.08 0.02 0.10 0.09 0.05 0.10 0.34 渝北区Yubei 0.17 0.02 0.02 0.05 0.22 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07 0.09 0.06 0.08 0.72 长寿区Changshou 0.26 0.04 0.02 0.19 0.20 0.02 0.08 0.03 0.08 0.11 0.02 0.08 0.23 涪陵区Fuling 0.12 0.08 0.03 0.16 0.24 0.04 0.08 0.03 0.07 0.08 0.04 0.06 0.12 武隆区Wulong 0.10 0.03 0.03 0.21 0.30 0.01 0.07 0.02 0.08 0.06 0.12 0.15 0.10 丰都县Fengdu 0.14 0.03 0.03 0.19 0.24 0.04 0.08 0.03 0.09 0.07 0.06 0.10 0.15 忠县Zhongxian 0.16 0.06 0.03 0.16 0.24 0.03 0.08 0.04 0.08 0.08 0.04 0.08 0.16 石柱Shizhu 0.17 0.08 0.02 0.13 0.28 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.11 0.06 0.09 0.07 0.06 万州区Wanzhou 0.13 0.07 0.03 0.15 0.24 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.09 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.24 开州区Kaizhou 0.17 0.05 0.03 0.26 0.27 0.02 0.08 0.03 0.07 0.06 0.08 0.10 0.20 云阳县Yunyang 0.11 0.05 0.03 0.32 0.23 0.03 0.08 0.02 0.08 0.08 0.04 0.09 0.15 巫溪县Wuxi 0.17 0.01 0.03 0.31 0.37 0.02 0.08 0.02 0.09 0.03 0.22 0.27 0.13 奉节县Fengjie 0.12 0.05 0.03 0.21 0.23 0.02 0.07 0.02 0.09 0.06 0.08 0.15 0.08 巫山县Wushan 0.12 0.02 0.02 0.24 0.27 0.03 0.07 0.02 0.08 0.05 0.07 0.26 0.05 巴东县Badong 0.20 0.02 0.02 0.15 0.32 0.02 0.07 0.02 0.10 0.05 0.05 0.31 0.16 兴山县Xingshan 0.15 0.06 0.02 0.30 0.24 0.01 0.07 0.01 0.10 0.08 0.19 0.23 0.22 秭归县Zigui 0.36 0.14 0.02 0.33 0.26 0.02 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.07 0.04 0.28 0.18 夷陵区Yiling 0.34 0.13 0.01 0.29 0.26 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.07 0.06 0.09 0.61 宜昌市区Yichang 0.34 0.15 0.02 0.27 0.25 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.05 0.06 0.13 0.11 0.11 从压力指数来看,化肥施用以及畜禽养殖是主要的面源污染压力指数来源,三峡库区各县区化肥强度指数以及畜禽养殖强度指数风险评分值之和占其总压力指数的平均值为79%,与冯琳等[25]对三峡库区面源污染研究给出的农田化肥与畜禽养殖单元的总产污贡献率达 80%以上一致。而巫溪县、巴东县、巫山县化肥强度指数以及畜禽养殖强度指数风险评分值之和占其总压力指数比值达到90%。
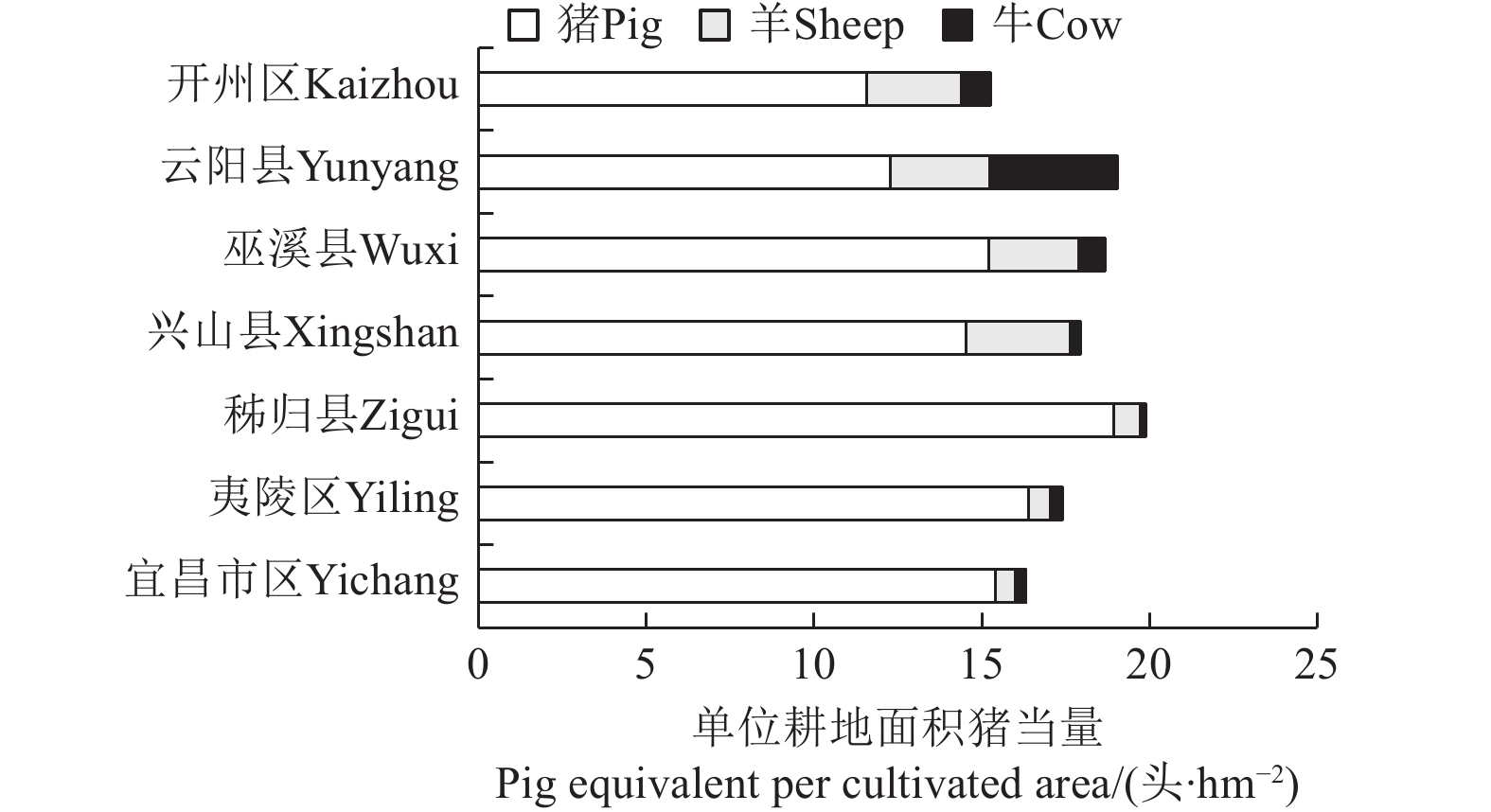
对于化肥施用量来说,重庆市南岸区、大渡口区虽然耕地面积不大,但化肥强度指数过高,单位作物播种面积的化肥施用量分别达到1323 kg/hm2和980 kg/hm2,从种植结构来看,2020 年大渡口区粮食产量为1003 t,蔬菜产量为16696 t,大渡口区蔬菜和瓜果产量明显高于粮食产量,而南岸区化肥消耗较大的蔬菜水果的产量并未明显高于其他县区,主要原因在于化肥施用量过多。此外,湖北省内县区化肥强度也普遍较高,秭归县、夷陵区以及宜昌市区的化肥施用量也超过600 kg/hm2。湖北省三峡库区致力于发展特色农业,已形成茶叶、柑橘、蔬菜、水产、中药材、烟叶等支柱产业[26],秭归县、夷陵区柑橘种植面积较大,2016年到2020年秭归县柑橘种植面积和产量分别增加21%和58%, 秭归县茶叶产量也增加了71% [27-28]。胡文杰等[29] 对三峡库区兰陵溪小流域农业面源污染的实地调查发现茶-果间作的氮素排放量最大,其次依次为茶园,果园和农田,可见茶果园的化肥施用量值得关注。从三峡库区农业生产方式来说,农户尺度上的户均粮食作物种植面积减少,果树户均种植面积增加,这对果树等产业的化肥使用提出新的要求。对于畜禽养殖来说,畜禽养殖强度相对较大的区域主要集中在库区中下游,重庆市云阳县、开州区、巫溪县、巫山县以及湖北省各县区等。图3给出了三峡库区畜禽养殖强度风险值超过0.25的县域各养殖品类换算为猪当量的情况,可以看出,重庆市各县区的主要养殖品类为猪和羊,其中云阳县养殖牛的猪当量也很大,湖北省各县区则主要以养殖猪为主要品类,开展猪和羊养殖条件下的畜禽废污处理具有重要的意义。
从治理指数来看,总体上三峡库区各县区环保投入相对较少,仅有石柱、奉节县、巫山县等少数地区环保投入相对较为合理,因此加大环保投入,增加农业面源污染防控措施实施力度,对于减少库区面源污染风险具有重要作用。
此外,对于个别县区来说,状态指数中的水网密度以及水田滞留指数的影响较大,如兴山县水网密度指数对于综合风险评分值作用较大,该区域水域面积较小,水网的纳污净化能力不足;湖北省巴东县、秭归县、重庆市巫溪县等地区由于水田面积相对较小导致水田滞留指标引起的面源污染风险较高。陈成龙等[30]研究了三峡库区涪陵段封闭性较好的王家沟小流域坡面稻田空间格局差异和子流域稻田空间格局变化对地表径流氮磷流失浓度影响,研究表明稻田可为面源氮、磷提供沉淀区,合理增加稻田数量,优化稻田空间格局是控制三峡库区面源污染有效措施;冉娇娇等[31]分析了三峡库区中部渠溪小流域2001—2019年稻转旱主要变化时期的氮素流失通量,结果显示稻转旱后流域污染负荷增加;李露等[32]在对香溪河流域面源污染分析中也指出对于不宜旱作区改植水稻,可大大减少土壤氮磷损失。由此可知,合理调整种植结构是该减少区域的农业面源污染方向的有效措施之一。
2.3 区域面源污染防控策略及管控清单
根据各风险评估指标的风险值,结合面源污染管控措施的可操作性,选取压力指数中化肥强度、农药强度、地膜强度、畜禽养殖强度、状态指数中水环境质量指数以及治理指数中的环保投资指数共6项作为三峡库区面源污染防控主要管控指标。根据不同县域不同指标的评分值,制定纵向和横向管控措施清单,纵向管控措施为三峡库区内各县域的总体管控级别和单项主控指标在各县域中实施的次序,横向管控措施则为三峡库区各县域内单项管控指标的次序。纵向管控优先级别以单项前10%风险值作为优先管控划分,以低于前10%风险值且超过库区平均风险值作为次优先管控划分,其他则设定为一般管控,详见表7和表8。
表 7 污染纵向管控优先级Table 7. Vertical priorities of pollution control县域名称
County name总体治理
Overall
governmentality化肥减量
Fertilizer
reduction农药减量
Pesticide
reduction地膜减量
Mulch
reduction畜禽养殖治理
Management of livestock
and poultry breeding河流水质提升
Water quality
improvement增加环保投资
Increase investment in
environmental protection江津区Jiangjin * * ** * 巴南区Banan * * 大渡口区Dadukou * ** * * ** * 九龙坡区Jiulongpo * ** * ** * 沙坪坝区Shapingba * * * * * 渝中区Yuzhong 南岸区Nan'an ** ** * * * 江北区Jiangbei * * * * ** 北碚区Beibei * * * ** * * 渝北区Yubei * ** 长寿区Changshou * * * 涪陵区Fuling * * * 武隆区Wulong * * 丰都县Fengdu * * * 忠县Zhongxian * * 石柱Shizhu * ** 万州区Wanzhou * * * 开州区Kaizhou * * 云阳县Yunyang * ** 巫溪县Wuxi * * * * 奉节县Fengjie * * * 巫山县Wushan * 巴东县Badong * * ** 兴山县Xingshan * * ** 秭归县Zigui * * * ** ** 夷陵区Yiling ** * * * ** * 宜昌市区Yichang * * ** * 注: **代表优先管控、*代表次优先管控,空白为一般管控
Note: ** stands for priority control, * stands for secondarypriority control and the blank is for conventional control表 8 污染横向管控优先级Table 8. Horizontal priorities of pollution control区县名称
County name化肥减量
Fertilizer
reduction农药减量
Pesticide
reduction地膜减量
Mulch
reduction畜禽养殖治理
Management of
livestock and
poultry breeding河流水
质提升
Water
quality
improvement江津区Jiangjin 
巴南区Banan 
大渡口区Dadukou 
九龙坡区Jiulongpo 
沙坪坝区Shapingba 
渝中区Yuzhong 南岸区Nan'an 
江北区Jiangbei 
北碚区Beibei 
渝北区Yubei 
长寿区Changshou 
涪陵区Fuling 
武隆区Wulong 
丰都县Fengdu 
忠县Zhongxian 
石柱Shizhu 
万州区Wanzhou 
开州区Kaizhou 
云阳县Yunyang 
巫溪县Wuxi 
奉节县Fengjie 
巫山县Wushan 
巴东县Badong 
兴山县Xingshan 
秭归县Zigui 
夷陵区Yiling 
宜昌市区Yichang 
注:圆圈中黑色面积越大,管控优先级别越高。
Note: The larger the black area of circles, the higher the control priority.从表7可以看出,三峡库区农业面源污染治理县域优先级应以重庆市南岸区和湖北省夷陵区为优先管控;化肥减量优先治理管控县域为大渡口区和南岸区;农药减量优先治理管控县域为九龙坡区和宜昌市区,地膜减量优先治理区域为江津区和北碚区;畜禽养殖优先治理区为云阳县和秭归县,河流水质优先治理区域为大渡口区、九龙坡区以及湖北省各县区;从加强环保投资的角度来看,处于优先级的县域为江北区和渝北区。从表8可以看出,大多数县区的主要污染防控因素为化肥减量和畜禽养殖治理,三峡库区上游和下游地区应当更多关注化肥减量,中游则更多关注畜禽养殖的污染防控,九龙坡区农药减量也应纳入重点防控,其风险评分值超过化肥指数的分值,同时九龙坡区的河流水质提升也亟需加强。
3. 讨 论
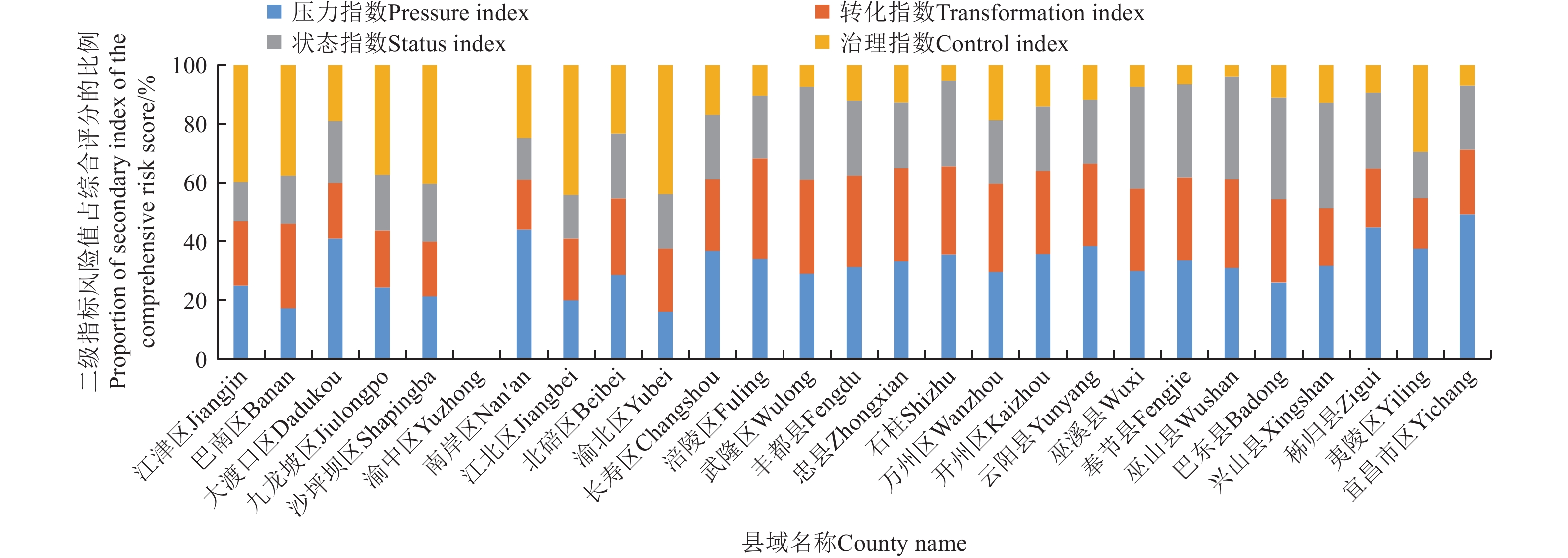
杨彦兰等[33]基于输出系数法对三峡库区重庆段农业面源污染负荷估算结果显示开州区、江津区、涪陵区和万州区的氮磷污染负荷量较大,长寿区、沙坪坝和南岸区的污染负荷强度则较大。张广纳等[34]对三峡库区重庆段农村面源污染时空格局演变研究结果表明三峡库区重庆段农业面源污染的热点区域集中区为库区腹地、冷点区域集中区为库尾都市核心区,上述研究主要考虑了污染来源的影响,与本文压力指数风险分布具有较好的一致性。丁恩俊等[35]基于MUSLE模型对三峡库区重庆市农业面源污染危险性分析结果显示危险性高、较高和中等的区域主要位于库区腹心地带,如云阳、奉节、万州、巫溪、丰都、巫山等县区,距河流越近非点源污染危险性越高,同时危险性高的地区大部分为旱地,该文献考虑了压力指数、转化指数和状态指数中相关指标,与之相比,本文压力指数、转化指数和状态指数评分值总和与之也具有较好的一致性,同时水田面积较小的巴东县、秭归县、巫山县等区域风险分值较高。然而,考虑到治理指标的影响后,重庆市辖区的污染风险不容忽视。图4给出了三峡库区面源污染风险评价二级指标风险值占风险综合评分值的比例,不同二级指标对于风险综合评分值均具有重要作用,压力指数、转化指数、状态指数、治理指数风险值占风险综合评分值的比例平均值分别为32%、25%、24%和19%,可以看出压力指数仍在风险评分中占有最大的比例,但并不直接决定风险的大小,风险评估与仅考虑污染源的负荷估算具有一定差异性,仅考虑单一的二级指标风险对于整体风险评价具有一定的限制作用。
对于指标计算的合理简化更利于实际操作和评估,本文选取的三级指标中的坡度坡长指数是需要通过GIS软件进行分析计算的,获取需要专业技术人员进行操作。在表6风险评估分值表中坡长坡度指数所占百分比很小,除江北区、北碚区和南岸区的风险评估分值超过0.05外,其他县市都小于0.05,江北区、北碚区和南岸区坡长坡度指数风险分值贡献占综合风险值的4.0%、3.8%和2.6%,因此在操作困难和无资料的条件下,三峡库区各县区坡度坡长指数可以按照平均值0.026进行取值,对于风险评估结果影响很小。此外,对于土壤可蚀性指数计算来说,需要获得不同土壤的可蚀性值,吴昌广等[36]研究结果显示三峡库区土壤可蚀性值变化在0.0072~0.0192 t·hm2·h/(MJ·mm·hm2)之间,其中在0.015~0.019 t·hm2·h/(MJ·mm·hm2)范围内的土壤面积占库区总面积的74.49%,同时也指出采用几何平均粒径修正模型对三峡库区土壤可蚀性进行估算是可行的。本文中的土壤可蚀性根据不同县区主要土壤类型参考文献[36]进行取值,若更为精准考虑则需要对三峡库区所有土壤类型计算土壤可蚀性再进行加权平均到县域范围内。当土壤可蚀性值为0.015~0.019 t·hm2·h/(MJ·mm·hm2)时,计算得到土壤可蚀性指数对应的风险评估值在0.062~0.079范围内,可见对于无法精准确定土壤类型的区域,在该范围内取值对于库区风险综合评估的影响较小。
基于风险评估结果制定防控策略及管控清单,对于三峡库区的面源污染防控具有重要意义。构建完整的评价指标体系、合理的指标计算方法均为风险评估的基础,在充分考虑数据获取程度和操作人员能力的情况下,应进一步将简化的和精细化的指标计算方法进行结合,不断提升计算方法的高效性。
4. 结 论
本文构建了考虑农业面源污染产生、形成及调控全过程的三峡库区面源污染风险评价体系,提出了基于易获取数据的风险指标计算方法,评价了三峡库区农业面源污染风险,提出了三峡库区横向和纵向污染治理清单,可为面源污染防控政策制定提供有力参考,得到以下结论:
1)三峡库区各县区农业面源污染总体风险处于中风险,库区内湖北省夷陵区、南岸区综合风险值更高,其次是重庆市大渡口区、沙坪坝区等市辖区、巫溪县以及湖北省兴山县和秭归区,之后是开州区、万州区、丰都县、云阳县等区域。
2)化肥强度指数、畜禽养殖强度指数、降雨侵蚀指数、环保投资指数评分值在三峡库区风险综合评分值的占比较高,化肥施用以及畜禽养殖是主要的农业面源污染压力来源,三峡库区各县区现有环保投入相对较少。
3)从纵向管控来说,三峡库区农业面源污染综合治理应以南岸区和夷陵区为优先管控区域,从横向管控来说,大多数县区的污染防控因素为化肥减量和畜禽养殖治理,库区上游和下游地区应当更多关注化肥减量,中游则应更多关注畜禽养殖的污染防控。
-
表 1 三峡库区农业面源污染风险评估指标体系
Table 1 Risk assessment index system of agricultural non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area
一级指标
The first level index二级指标
The second level index三级指标
The third level index三峡库区农业面源污染风险评估综合指数Comprehensive index of agricultural non-point source pollution risk assessment in Three Gorges Reservoir Area 压力指数 化肥强度指数I11 农药强度指数I12 地膜强度指数I13 畜禽养殖强度指数I14 转化指数 降雨侵蚀指数I21 坡长坡度指数I22 土壤可蚀性指数I23 坡耕地指数I24 状态指数 水环境质量指数I31 水环境容量指数I32 水网密度指数I33 水田滞留指数I34 治理指数 环保投资指数I41 表 2 三峡库区农业面源污染风险评估指标权重
Table 2 Weight of agricultural non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area
一级指标
The first level index二级指标
The second level index三级指标
The third level index指标名称
Index name权重
Weight指标名称
Index name权重
Weight三峡库区农业
面源污染风险
评估综合指数
Comprehensive
index of
agricultural
non-point source
pollution risk
assessment in
Three Gorges
Reservoir Area压力指数 0.378 化肥强度指数I11 0.370 农药强度指数I12 0.229 地膜强度指数I13 0.077 畜禽养殖强度指数I14 0.324 转化指数 0.203 降雨侵蚀指数I21 0.396 坡长坡度指数I22 0.134 土壤可蚀性指数I23 0.248 坡耕地指数I24 0.222 状态指数 0.297 水环境质量指数I31 0.347 水环境容量指数I32 0.293 水网密度指数I33 0.153 水田滞留指数I34 0.207 治理指数 0.122 环保投资指数I41 1 表 3 风险分级
Table 3 Grading of the risk
级别Level 风险类别Risk description 评分值Score Ⅰ 无风险或者可接受风险 (0,0.7] Ⅱ 低风险 (0.7,1.0] Ⅲ 中风险 (1.0,3.0] Ⅳ 高风险 (3.0,5.0] Ⅴ 极高风险 (5.0,∞) 表 4 主要数据来源
Table 4 Source of main data
序号No. 数据名称Data name 数据来源Data source 1 农作物播种面积 统计年鉴或经济统计
年鉴或政府工作报告2 化肥施用量 3 农药施用量 4 地膜使用量、地膜覆盖面积 5 畜禽养殖量和种类 6 县域面积 7 GDP及人口 8 节能环保投资 9 多年平均降雨量 水资源公报 10 地表径流量 11 坡耕地面积 第三次国土调查数据 12 水田面积 13 湖库沟渠面积 14 河流水质 生态环境厅环境公开数据 表 5 河流水质数据分布
Table 5 Distribution of water quality data
序号
No.县域名称
County name断面数量
Number
of sections河流名称
Rivers name序号
No.县域名称
County name断面数量
Number of
sections河流名称
Rivers name1 江津区 8 长江、临江河、塘河、璧南河、綦江河、笋溪河 15 忠县 7 长江、渠溪河、黄金河、汝溪河、玉溪河、 东溪河 2 巴南区 7 蒲河、一品河、花溪河、五步河、长江 16 石柱 5 普子河、龙河、磨刀溪、龙河、官渡河 3 大渡口区 1 长江 17 万州区 8 长江、新田河、浦里河、磨刀溪、石桥河、瀼渡河、五桥河、苎溪河 4 九龙坡区 1 长江 18 开州区 5 澎溪河(小江)、江里河、浦里河 5 沙坪坝区 2 嘉陵江、梁滩河 19 云阳县 6 长江、澎溪河(小江)、汤溪河、长滩河 6 渝中区 1 嘉陵江 20 巫溪县 7 汤溪河、梅溪河、大宁河、长溪河、巴岩子河、柏杨河 7 南岸区 2 长江 21 奉节县 6 长江、长滩河 、朱衣河、梅溪河、大溪河、草堂河 8 江北区 4 长江、栋梁河 22 巫山县 6 长江、大宁河、神女溪、抱龙河、三溪河、冷水溪 9 北碚区 5 嘉陵江、璧北河、梁滩河、黑水 23 巴东县 2 神农溪 10 渝北区 7 长江、后河、栋梁河、桥溪河、御临河、 大洪河 24 兴山县 2 香溪河 11 长寿区 8 御临河、大洪河、桃花溪、龙溪河、长江 25 秭归县 9 长江、青干河、叱溪河、童庄河、九畹溪 12 涪陵区 8 长江、乌江、麻溪河、碧溪河、黎香溪、清溪河 26 夷陵区 4 太平溪、黄柏河 13 武隆区 6 乌江、木棕河、芙蓉江、大溪河、石梁河 27 宜昌市区 1 黄柏河 14 丰都县 7 长江、渠溪河、碧溪河、龙河、赤溪河 表 6 三级指标风险评估分值表
Table 6 Risk assessment scores for the third level indicators
县域名称
County name化肥强
度指数
Fertilizer
intensity
index农药强
度指数
Pesticide
intensity
index地膜强
度指数
Mulch
intensity
index畜禽养殖
强度指数
Livestock
breeding
intensity
index降雨侵
蚀指数
Rainfall
erosion
index坡长坡
度指数
Slope gradient
index土壤可蚀
性指数
Soil
erodibility
index坡耕地
指数
Terraced
farmland
index水环境质
量指数
Water
environmental
quality index水环境
容量指数
Water
environmental
capacity index水网密
度指数
Density
index of
water
network水田滞
留指数
Retention
index of
paddy field环保投
资指数
Environment-al
protection
investment
index江津区Jiangjin 0.18 0.08 0.04 0.15 0.27 0.02 0.08 0.03 0.08 0.07 0.03 0.05 0.71 巴南区Banan 0.12 0.03 0.03 0.06 0.27 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.06 0.07 0.04 0.05 0.54 大渡口区Dadukou 0.55 0.10 0.03 0.01 0.21 0.02 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.11 0.02 0.12 0.32 九龙坡区Jiulongpo 0.14 0.16 0.03 0.04 0.20 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.11 0.03 0.04 0.57 沙坪坝区Shapingba 0.26 0.06 0.03 0.02 0.21 0.02 0.08 0.01 0.09 0.11 0.05 0.09 0.71 渝中区Yuzhong 南岸区Nan'an 0.74 0.10 0.03 0.02 0.21 0.05 0.07 0.01 0.08 0.10 0.02 0.09 0.51 江北区Jiangbei 0.22 0.08 0.03 0.02 0.21 0.07 0.07 0.01 0.06 0.10 0.02 0.07 0.76 北碚区Beibei 0.24 0.11 0.04 0.03 0.23 0.06 0.08 0.02 0.10 0.09 0.05 0.10 0.34 渝北区Yubei 0.17 0.02 0.02 0.05 0.22 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07 0.09 0.06 0.08 0.72 长寿区Changshou 0.26 0.04 0.02 0.19 0.20 0.02 0.08 0.03 0.08 0.11 0.02 0.08 0.23 涪陵区Fuling 0.12 0.08 0.03 0.16 0.24 0.04 0.08 0.03 0.07 0.08 0.04 0.06 0.12 武隆区Wulong 0.10 0.03 0.03 0.21 0.30 0.01 0.07 0.02 0.08 0.06 0.12 0.15 0.10 丰都县Fengdu 0.14 0.03 0.03 0.19 0.24 0.04 0.08 0.03 0.09 0.07 0.06 0.10 0.15 忠县Zhongxian 0.16 0.06 0.03 0.16 0.24 0.03 0.08 0.04 0.08 0.08 0.04 0.08 0.16 石柱Shizhu 0.17 0.08 0.02 0.13 0.28 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.11 0.06 0.09 0.07 0.06 万州区Wanzhou 0.13 0.07 0.03 0.15 0.24 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.09 0.07 0.04 0.08 0.24 开州区Kaizhou 0.17 0.05 0.03 0.26 0.27 0.02 0.08 0.03 0.07 0.06 0.08 0.10 0.20 云阳县Yunyang 0.11 0.05 0.03 0.32 0.23 0.03 0.08 0.02 0.08 0.08 0.04 0.09 0.15 巫溪县Wuxi 0.17 0.01 0.03 0.31 0.37 0.02 0.08 0.02 0.09 0.03 0.22 0.27 0.13 奉节县Fengjie 0.12 0.05 0.03 0.21 0.23 0.02 0.07 0.02 0.09 0.06 0.08 0.15 0.08 巫山县Wushan 0.12 0.02 0.02 0.24 0.27 0.03 0.07 0.02 0.08 0.05 0.07 0.26 0.05 巴东县Badong 0.20 0.02 0.02 0.15 0.32 0.02 0.07 0.02 0.10 0.05 0.05 0.31 0.16 兴山县Xingshan 0.15 0.06 0.02 0.30 0.24 0.01 0.07 0.01 0.10 0.08 0.19 0.23 0.22 秭归县Zigui 0.36 0.14 0.02 0.33 0.26 0.02 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.07 0.04 0.28 0.18 夷陵区Yiling 0.34 0.13 0.01 0.29 0.26 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.10 0.07 0.06 0.09 0.61 宜昌市区Yichang 0.34 0.15 0.02 0.27 0.25 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.05 0.06 0.13 0.11 0.11 表 7 污染纵向管控优先级
Table 7 Vertical priorities of pollution control
县域名称
County name总体治理
Overall
governmentality化肥减量
Fertilizer
reduction农药减量
Pesticide
reduction地膜减量
Mulch
reduction畜禽养殖治理
Management of livestock
and poultry breeding河流水质提升
Water quality
improvement增加环保投资
Increase investment in
environmental protection江津区Jiangjin * * ** * 巴南区Banan * * 大渡口区Dadukou * ** * * ** * 九龙坡区Jiulongpo * ** * ** * 沙坪坝区Shapingba * * * * * 渝中区Yuzhong 南岸区Nan'an ** ** * * * 江北区Jiangbei * * * * ** 北碚区Beibei * * * ** * * 渝北区Yubei * ** 长寿区Changshou * * * 涪陵区Fuling * * * 武隆区Wulong * * 丰都县Fengdu * * * 忠县Zhongxian * * 石柱Shizhu * ** 万州区Wanzhou * * * 开州区Kaizhou * * 云阳县Yunyang * ** 巫溪县Wuxi * * * * 奉节县Fengjie * * * 巫山县Wushan * 巴东县Badong * * ** 兴山县Xingshan * * ** 秭归县Zigui * * * ** ** 夷陵区Yiling ** * * * ** * 宜昌市区Yichang * * ** * 注: **代表优先管控、*代表次优先管控,空白为一般管控
Note: ** stands for priority control, * stands for secondarypriority control and the blank is for conventional control表 8 污染横向管控优先级
Table 8 Horizontal priorities of pollution control
区县名称
County name化肥减量
Fertilizer
reduction农药减量
Pesticide
reduction地膜减量
Mulch
reduction畜禽养殖治理
Management of
livestock and
poultry breeding河流水
质提升
Water
quality
improvement江津区Jiangjin 
巴南区Banan 
大渡口区Dadukou 
九龙坡区Jiulongpo 
沙坪坝区Shapingba 
渝中区Yuzhong 南岸区Nan'an 
江北区Jiangbei 
北碚区Beibei 
渝北区Yubei 
长寿区Changshou 
涪陵区Fuling 
武隆区Wulong 
丰都县Fengdu 
忠县Zhongxian 
石柱Shizhu 
万州区Wanzhou 
开州区Kaizhou 
云阳县Yunyang 
巫溪县Wuxi 
奉节县Fengjie 
巫山县Wushan 
巴东县Badong 
兴山县Xingshan 
秭归县Zigui 
夷陵区Yiling 
宜昌市区Yichang 
注:圆圈中黑色面积越大,管控优先级别越高。
Note: The larger the black area of circles, the higher the control priority. -
[1] 王春,青静娴,文传浩,等. 三峡库区农业生态化发展障碍,原因及对策分析[J]. 长江技术经济,2022,6(3):32-36. WANG Chun, QING Jingxian, WEN Chuanhao, et al. Obstacles, causes and countermeasures of agricultural ecologicalization development in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Technology and Economy of Changjiang, 2022, 6(3): 32-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 重庆市生态环境局. 2021重庆市生态环境状况公报[EB/OL]. 重庆:重庆市生态环境局,2022-05-30[2023-03-13].https://sthjj.cq.gov.cn/hjzl_249/hjzkgb/202205/t20220530_10763282_wap.html. [3] 刘建昌,严岩,刘峰,等. 基于多因子指数集成的流域面源污染风险研究[J]. 环境科学,2008,29(3):599-606. LIU Jianchang, YAN Yan, LIU Feng, et al. Risk assessment and safety evaluation using system normative indexes integration method for non-point source pollution on watershed scale[J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(3): 599-606. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 荆延德,张华美. 基于LUCC的南四湖流域面源污染输出风险评估[J]. 自然资源学报,2019,34(1):128-139. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20190111 JING Yande, ZHANG Huamei. Risk assessment of non-point source pollution output in Nansihu Lake basin based on LUCC[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2019, 34(1): 128-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20190111
[5] 任晓强,李娜,管孝艳,等. 白洋淀上游河流水环境风险评价[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2022(2):27-33. REN Xiaoqiang, LI Na, GUAN Xiaoyan, et al. Water environment risk assessment of the upper reaches of baiyangdian lake[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2022(2): 27-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 方广玲,香宝,杜加强,等. 拉萨河流域非点源污染输出风险评估[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(1):247-254. FANG Guangling, XIANG Bao, DU Jiaqiang, et al. Risk assessment of non-point source pollution export in Lasahe basin[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(1): 247-254. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 陈祥义,肖文发,黄志霖,等. 空间数据对分布式水文模型SWAT流域水文模拟精度的影响[J]. 中国水土保持科学,2016,14(1):138-143. CHEN Xiangyi, XIAO Wenfa, HUANG Zhilin, et al. Impact of spatial data on the accuracy of watershed hydrological simulation of SWAT model[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 14(1): 138-143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] DING X, SHEN Z, QIAN H, et al. Development and test of the export coefficient model in the upper reach of the Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2010, 383(3-4): 233-244. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.12.039
[9] 李艳苓,朱昌雄,李红娜,等. 基于层次分析法的农业面源污染防治技术评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报,2019,9(4):355-361. LI Yanling, ZHU Changxiong, LI Hongna, et al. Evaluation of agricultural non-point source pollution control technologies based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2019, 9(4): 355-361. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] GUAN X, REN X, TAO Y, et al. Study of the water environment risk assessment of the upper reaches of the Baiyangdian Lake, China[J]. Water, 2022(14): 2557.
[11] 刘方谊,范先鹏,夏颖,等. 三峡库区典型流域农业面源氮素输出特征[J]. 湖北农业科学,2018,57(10):31-35. LIU Fangyi, FAN Xianpeng, XIA Ying, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen output from agricultural non-point source in typical watershed of Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 57(10): 31-35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 杨志敏,陈玉成,魏世强,等. 重庆市农业面源污染影响因子的系统分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2009,28(5):999-1004. YANG Zhimin, CHEN Yucheng, WEI Shiqiang, et al. Systems analysis of factors affecting agricultural non-point source pollution in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(5): 999-1004. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王家,夏颖,陈琼星,等. 兴山县香溪河流域农业面源污染现状分析[J]. 湖北农业科学,2014,53(23):5724-5730. WANG Jia, XIA Ying, CHEN Qiongxing, et al. Situation of agricultural non-point source pollution of the Xiangxi Brook Watershed in Xingshan County[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(23): 5724-5730. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 刘志欣,邵景安,李阳兵. 重庆市农业面源污染源的EKC实证分析[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2015,40(11):94-101. LIU Zhixin, SHAO Jing'an, LI Yangbing. The empirical analysis of EKC on agricultural non-point source pollution in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Southwest Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 40(11): 94-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 李乐,刘常富. 三峡库区面源污染研究进展[J]. 生态科学,2020,39(2):215-226. LI Le, LIU Changfu. A review of non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Ecological Science, 2020, 39(2): 215-226. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 重庆市市场监督管理局:DB50/T 931-2019. 重庆市农业面源污染风险评估技术规范[S]. 重庆,2019. [17] 汪嘉杨,翟庆伟,郭倩,等. 太湖流域水环境承载力评价研究[J]. 中国环境科学,2017,37(5):1979-1987 WANG Jiayang, ZHAI Qingwei, GUO Qian, et al. Study on water environmental carrying capacity evaluation in Taihu lake Basin[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(5): 1979-1987. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 农业部办公厅关于印发《畜禽粪污土地承载力测算技术指南》的通知[EB/OL]. 2018-1-22[2023-3-23]. http://www.moa.gov.cn/gk/tzgg_1/tfw/201801/t20180122_6135486.htm. [19] 耿维,胡林,崔建宇,等. 中国区域畜禽粪便能源潜力及总量控制研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(1):171-179. GENG Wei, HU Lin, CUI Jianyu, et al. Biogas energy potential for livestock manure and gross control of animal feeding in region level f China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(1): 171-179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 朱建春,张增强,樊志民,等. 中国畜禽粪便的能源潜力与氮磷耕地负荷及总量控制[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2014,33(3):435-445. ZHU Jianchun, ZHANG Zengqiang, FAN Zhimin, et al. Biogas potential, cropland load and total amount control of animal manure in China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(3): 435-445. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 李祚泳,彭荔红. 基于韦伯—费希纳拓广定律的环境空气质量标准[J]. 中国环境监测,2003(4):17-19. LI Zuoyong, PENG Lihong. Environmental air quality standard based on weber-fischna's law[J]. Environmental Monitoring In China, 2003(4): 17-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 信桂新,杨朝现,杨庆媛,等. 用熵权法和改进TOPSIS模型评价高标准基本农田建设后效应[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(1):238-249. XIN Guixin, YANG Chaoxian, YANG Qingyuan, et al. Post-evaluation of well-facilitied capital farmland construction based on entropy weight method and improved TOPSIS model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(1): 238-249. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 董爱红,张文倩,张二信,等. 滴头堵塞程度分级和评价及堵塞风险预测方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(5):56-64. DONG Aihong, ZHANG Wenqian, ZHANG Erxin, et al. Classification and evaluation of emitter clogging degree and prediction method of emitter clogging risk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(5): 56-64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 杨柳,王晨颖,冯畅,等. 考虑水系演变的湘江流域洪水风险四维评价体系构建[J]. 农业工程学报,2023,39(3):92-101. YANG Liu, WANG Chenying, FENG Chang, et al. Four-dimensional assessment system for flood risks with the river network system evolution in Xiangjiang River Basin in Hunan of China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2023, 39(3): 92-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 冯琳,张婉婷,张钧珂,等. 三峡库区面源污染的时空特征及EKC分析[J]. 中国环境科学,2022(7):3325-3333 FENG Lin, ZHANG Wanting, ZHANG Junke, et al. Analysis on spatial-temporal characteristics and Environmental Kuznets Curve of non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022(7): 3325-3333. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 赵尧尧,夏颖,范先鹏,等. 湖北三峡库区农业面源污染负荷、评价及预警系统[J]. 湖北农业科学,2016,55(23):6244-6249. ZHAO Yaoyao, XIA Ying, FAN Xianpeng, et al. Agricultural non-point source pollution load, evaluation and early warning system in Hubei Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(23): 6244-6249. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 宜昌市统计局. 宜昌统计年鉴2021[M]. 北京:中国统计出版社,2021. [28] 宜昌市统计局. 宜昌统计年鉴2017[M]. 北京:中国统计出版社,2017. [29] 胡文杰,王晓荣,付甜,等. 三峡库区兰陵溪小流域农业面源污染排放特征解析[J]. 环境污染与防治,2021(5):568-573. HU Wenjie, WANG Xiaorong, FU Tian, et al. Analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution emission characteristics of Lanlingxi small watershed in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2021(5): 568-573. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 陈成龙,高明,倪九派,等. 三峡库区小流域稻田空间格局对氮磷流失影响[J]. 环境科学,2017,38(5):1889-1897. CHEN Chenglong, GAO Ming, NI Jiupai, et al. Influence of spatial pattern of paddy field on the losses of nitrogen and phosphorus in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(5): 1889-1897. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 冉娇娇,黄平,陈成龙,等. “稻转旱”对低山丘陵区氮素流失通量的影响——以三峡库区渠溪小流域为例[J]. 水土保持研究,2022,29(2):70-75. RAN Jiaojiao, HUANG Ping, CHEN Chenglong, et al. Conversion of rice paddy into dry land and its influence on nitrogen fluxes in the low hilly area-a case study of the Quxi Basin in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 29(2): 70-75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 李露,马啸. 香溪河流域农业面源污染现状及其控制管理[J]. 湖北理工学院学报,2017,33(4):12-18. LI Lu, MA Xiao. Current situation and control management of agriculture non-point source pollution of Xiangxi River Watershed[J]. Journal of Hubei Polytechnic University, 2017, 33(4): 12-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 杨彦兰,申丽娟,谢德体,等. 基于输出系数模型的三峡库区(重庆段)农业面源污染负荷估算[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版),2015,37(3):112-119. YANG Yanlan, SHEN Lijuan, XIE Deti, et al. Estimation of pollution loads from agricultural nonpoint sources in Three Gorges Reservoir Area(Chongqing) based on the export coefficient modeling approach[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 37(3): 112-119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 张广纳,邵景安,王金亮,等. 三峡库区重庆段农村面源污染时空格局演变特征[J]. 自然资源学报,2015(7):1197-1209. ZHANG Guangna, SHAO Jing'an, WANG Jinliang, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of agricultural non-point source pollution in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Chongqing[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2015(7): 1197-1209. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 丁恩俊,谢德体,魏朝富,等. 基于MUSLE模型的三峡库区重庆段农业非点源污染危险性评价[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版),2010(5):96-101. DING Enjun, XIE Deti, WEI Chaofu, et al. MUSLE-Based agricultural nonpoint source pollution risk assessment in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Chongqing[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2010(5): 96-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 吴昌广,曾毅,周志翔,等. 三峡库区土壤可蚀性K值研究[J]. 中国水土保持科学,2010,8(3):8-12. WU Changguang, ZENG Yi, ZHOU Zhixiang, et al. Soil erodibility K value in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 8(3): 8-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王慧琳,邹民忠,方伟文,刘灵敏,郝新梅,康绍忠,毛晓敏. 基于SWAT模型的武强溪流域非点源污染关键源区界定与控制策略. 农业工程学报. 2024(02): 228-238 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 罗凡,罗育池,陈宇华,李燕. 广东沿海城市农业面源氮磷污染排放特征及控制对策研究. 环境污染与防治. 2024(11): 1688-1694 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陆新路,庞树江,王小胜,王帅,李慧芩,王丽君,王明哲. 基于水环境容量的流域非点源污染风险评价. 农业工程学报. 2024(22): 89-97 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: