Effects of organic fertilizer combined with Pseudomonas fluorescein on maize yield and phosphorus activity in reclaimed soil
-
摘要:
复垦土壤贫瘠,磷素含量极低,严重影响作物的生长发育。研究化肥、有机肥配施荧光假单胞菌对玉米产量和复垦土壤磷素形态以及酶活性的影响,为加速培肥矿区复垦土壤提供技术支持和理论依据。该研究在山西省晋中市采煤塌陷区进行了2 a的定位培肥试验,共设置7个处理:不施肥(CK)、单施化肥(CF)、化肥配施荧光假单胞菌(CFB)、单施有机肥(M)、有机肥配施荧光假单胞菌(MB)、化肥配施有机肥(MCF)、化肥有机肥配施荧光假单胞菌(MCFB)。采集各处理土壤样品测定相关指标,并通过相关性分析和结构方程模型来探究各形态磷与有效磷以及土壤磷酸酶之间的关系。结果表明:1)在整个试验周期(2021—2022年),与CK相比,不同施肥处理均能显著提高玉米产量以及各形态磷素。其中,以MB处理下的玉米产量、有效磷、磷活化系数、不稳定态磷以及部分不稳定态磷含量最高,与CK处理相比,玉米产量显著提高2.40倍,有效磷含量、磷活化系数值、不稳定态磷含量、部分不稳定态磷含量分别显著提高4.50倍、4.67倍、0.98倍、1.16倍。2)与CK处理相比,化肥、有机肥配施荧光假单胞菌能够显著提高土壤微生物量磷以及酸性和碱性磷酸酶活性,配施荧光假单胞菌后,微生物量磷水平和碱性磷酸酶活性均以MB较M处理提升效果最佳,分别显著提高27.08%和9.56%。3)结合相关性分析以及结构方程模型,随着荧光假单胞菌和化肥有机肥的施入,在提高不稳定态磷素含量的同时也提高有效磷的供应能力,促进磷素在农田生态系统中的循环转化,产生积极的正向影响。化肥、有机肥配施荧光假单胞菌能够一定程度上影响复垦土壤玉米产量及产量性状、各形态磷素及有效性和微生物活性,对复垦土壤脆弱的农田生态系统产生积极影响。
Abstract:Reclaimed soil is characterized by the infertility and extremely low phosphorus content, thus severely impeding the growth and development of crops. This study aims to investigate the effects of chemical fertilizer and organic fertilizer combined with Pseudomonas fluorescein on phosphorus fractions and enzyme activity in reclaimed soil, in order to accelerate the soil reclamation in mining areas. A two-year targeted fertilization experiment was conducted in a coal mining subsidence area in Jinzhong City, Shanxi Province, China. Seven treatments were established: no fertilization control (CK), single application of chemical fertilizer (CF), chemical fertilizer combined with P. fluorescein (CFB), single application of organic fertilizer (M), organic fertilizer combined with P. fluorescein (MB), chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer (MCF), and chemical fertilizer and organic fertilizer combined with P. fluorescein (MCFB). The soil samples were collected from the treatment plots. The phosphorus fractions, microbial biomass phosphorus, and soil phosphatase activity were measured after that. In addition, the correlation between soil phosphorus fractions and Olsen P was explored to construct the structural equation model between soil phosphorus fractions and microbial biomass phosphorus, acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase, and Olsen P. Results showed that: 1) Different fertilization treatments significantly increased the maize yield and various phosphorus fractions during the entire experimental period (2021-2022), compared with CK. Among them, the MB treatment was achieved in the highest maize yield, Olsen-P content, phosphorus activation coefficient (PAC) value, labile phosphorus (L-P), and moderately labile phosphorus (M-P) content. The maize yield, Olsen-P content, PAC value, L-P content, and M-P content increased significantly by 2.40, 4.50, 4.67, 0.98, and 1.16 times, respectively, compared with the CK treatment. 2) The application of chemical and organic fertilizer combined with P. fluorescein also increased the soil microbial biomass phosphorus and the activities of acid and alkaline phosphatase enzymes, in terms of microbial activity. After combined application with P. fluorescein, the levels of microbial biomass phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase enzyme activity were most effectively enhanced under the MB treatment, compared with the M treatment, indicating the significant increase of 27.08% and 9.56%, respectively. 3) The correlation analysis showed that there was the closest relationship between labile phosphorus forms (Resin-P, NaHCO3-Pi, and NaHCO3-Po) and Olsen P. Furthermore, there was the much larger direct and positive effects of labile phosphorus on microbial biomass phosphorus, acid phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase activities, and Olsen P, according to the structural equation model. The large standardized path coefficient was found that the application of chemical fertilizer, organic fertilizer, and P. fluorescein on L-P was promoted the circulation and transformation of phosphorus in the farmland ecosystem, indicating a positive impact. In summary, the combined application of different fertilizers with P. fluorescein were promoted the yield and yield traits of maize in the reclaimed soil, together with the forms and availability of phosphorus, and microbial activity, indicating a positive impact on the fragile agroecosystem of reclaimed soil. Among them, the combined organic fertilizer with P. fluorescein significantly increased the Olsen-P content, L-P content, and M-P content, SMBP content, and ALP activity in the reclaimed soil, compared with the sole application of organic fertilizer. The finding can provide the more effective fertilization.
-
Keywords:
- reclaimation /
- soils /
- phosphorus /
- maize yield /
- organic fertilizer /
- soil phosphatase activity
-
0. 引 言
煤炭作为中国主要的能源,被广泛地应用于社会生产的方方面面,并对中国经济的发展起到至关重要的作用。然而,煤炭资源的开采利用对中国经济和社会的发展提供充足动力的同时,也导致了当地生态环境的破坏[1]。据不完全统计,中国已有6.67×106 hm2的土地因以往长期粗放式的开采而损毁,其中大部分是农耕地或是其他农业用地[2]。被破坏的农用地导致了煤矿区的人地矛盾日益严重,并严重威胁中国的粮食安全和绿色农业的可持续发展[3]。因此,对采煤塌陷区的土壤进行生物、化学复垦,使其土壤肥力提高,对于中国保持土壤耕地面积与质量、坚守耕地红线意义非凡。
山西作为中国重要的产煤供煤大省,已探知的煤炭储存面积为6.2万 km2,在2023年的煤炭产量已超13.0亿t,并较2022年同比增加1.13亿t,占全国产量近1/3。但随着煤炭开采,已有4166.02 km2的土地变为采空区。因此,在山西开展矿区土壤复垦研究使其恢复土壤肥力,对实现区域耕地质量提升以及绿色农业的可持续发展具有重要意义。施肥作为提升土壤地力以及提高作物产量最直接有效的措施,已有研究证实不同的施肥措施能有效改善土壤理化性质[4]、增加土壤养分含量[5]、调节微生物种群群落[6]以及提高农作物生物性状及产量[7]。此外,就不同施肥措施对复垦土壤作物产量、土壤养分、微生物活性的影响,近年来已有不少报道[2,8-9]。然而,上述的研究发现均基于5a以上的长期定位培肥试验所得,且复垦初期,土壤多为附近土壤与煤矿废弃物混合而成,导致平整后的耕层土壤理化结构差、肥力极低[10]。鉴于此,如何在传统施肥模式下找到更加高效的施肥方式应用于较一般耕地肥力更加贫瘠的复垦土壤,探明短期复垦对有效养分以及微生物活性影响与机理还需进一步研究。功能微生物菌剂作为一种新兴的绿色肥料,与化学肥料相比,对生态系统影响较小,近年来已广泛利用在可持续农业、环境保护以及生态修复等方面。在众多功能微生物菌中,荧光假单胞菌(Pseudomonas fluorescens)因具有抑制病原菌生长、降解污染物、吸附重金属离子以及高效的解磷能力而具有良好的应用市场[11]。相关研究发现,荧光假单胞菌可以防治农作物病害、提高肥料利用率从而促进作物生长以及明显改善土壤养分水平[12]。综上所述,由于前人针对复垦土壤养分含量及生物活性的研究主要基于传统施肥模式(化肥、有机肥的配合施用)下的长期培肥试验,但在短期复垦条件下,通过配施功能菌剂来影响土壤有效磷含量变化的关键因素及主要措施尚不明确。
因此,本研究选取了山西省晋中市榆次区后沟村经过2a复垦的土壤作为研究对象,通过分析在不同施肥措施下,复垦初期土壤中各形态磷素、酸性和碱性磷酸酶以及玉米产量的变化特征,并探究各形态磷素、微生物量磷以及磷酸酶与有效磷之间的转化关系,以期筛选出一种更适宜荧光假单胞菌发挥效果的施肥模式,为复垦土壤培肥提供可靠的方法和理论依据,保障作物稳产高产。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验地概况与材料
1.1.1 试验地概况
试验地位于山西省晋中市榆次区乌金山镇后沟村(112°48′13.64″E,37°50′11.38″N),属乌金山矿区井田范围。煤矿开采导致地面沉陷使地形呈漏斗形,最大落差3~4 m。2019年9月混堆平整后,从附近山体取土覆盖其上部。试验地于2021年开始复垦种植玉米,2022年为土壤复垦第2年。该区气候属于暖温带季风气候,年均降雨量489 mm,无霜期160 d左右,年均气温9~10 ℃,并在7月份温度最高(平均达22 ℃)。土壤类型为石灰性褐土,质地为中壤土。0~20 cm表土初始理化性质为:有机质(soil organic matter, SOM)3.28 g/kg,全氮(total nitrogen, TN)0.23 g/kg,全磷(total phosphorus, TP)0.23 g/kg,全钾(total potassium, TK)1.98 g/kg,碱解氮(available nitrogen,AN)9.32 mg/kg,有效磷(available phosphorus,AP)2.48 mg/kg,速效钾(available potassium,AK)67.08 mg/kg,pH值为 8.43。
1.1.2 供试菌株
供试菌株为山西农业大学资源环境学院矿区土壤复垦与微生物多样性研究室在山西省石灰性土壤中筛选出具有高效解磷能力的两株荧光假单胞菌W134-1、W137-1,存于中国普通微生物菌种保藏管理中心,两株菌并无拮抗作用。复合菌的解磷量为632.45 mg/L,碱性磷酸酶活性(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)为231.08 μg/(mL·h),酸性磷酸酶活性(acid phosphatase,ACP)为125.54 μg/(mL·h)。采用LB培养基(蛋白胨10 g/L,酵母提取物5 g/L,NaCl 10 g/L)培养至对数生长期(OD600=1)制成菌肥,有效活菌数≥2×108 CFU/g。
1.1.3 供试肥料与作物
供试化肥为尿素(N 46%)、过磷酸钙(P2O5 16%)、硫酸钾(K2O 52%),有机肥为腐熟鸡粪(有机质 30.12%、N 1.67%、P2O5 1.23%、K2O 1.08%),由太谷区鸿昊养殖专业合作社提供。供试玉米品种为五谷 568,全生育期 130 d,由甘肃五谷种业有限公司提供,其种植密度为 58000 株/hm2。
1.2 试验设计
试验采用随机区组共设7个处理,每个处理重复3次,每个小区30 m2(5 m×6 m),各小区间隔60 cm。其中,不加荧光假单胞菌的处理用等量经灭活的LB液体培养基代替,各处理的施肥用量参考当地农户的习惯施肥量并结合前期课题组对该类型菌在盆栽试验中具体情况,按照等量施肥原则,于玉米播种一周前一次性撒施,随即翻耕入土,各处理具体施肥用量见表1。玉米于2022年4月下旬播种,9月20日收获,在玉米生育期内不进行灌溉。
表 1 试验处理及肥料用量Table 1. Experimental treatment and fertilizer dosagekg·hm−2 处理
Treatment尿素
Urea过磷酸钙
Calcium
superphosphate硫酸钾
Potassium
sulfate有机肥
Organic
fertilizer菌肥
Microbial
fertilizer不施肥(CK) 0 0 0 0 0 单施化肥(CF) 653 1384 374 0 0 化肥+菌(CFB) 604 1280 346 0 1500 单施有机肥(M) 0 0 0 18000 0 有机肥+菌(MB) 0 0 0 16500 1500 化肥+有机肥(MCF) 327 692 187 9000 0 化肥有机肥+菌(MCFB) 272 577 156 7500 1500 1.3 样品采集与测定
玉米收获后,采用五点采样法采集各处理0~20 cm土壤样品,共计21份土样,土样去除植物残根和其他杂质后分为两份,一份过筛(2.00 mm)后于4 ℃冰箱保存用于测定土壤磷以及磷酸酶活性,另一部分制成风干土用于测定土壤各磷素形态以及有效磷。
在每个小区随机采取20株植株用于测定玉米穗粒数、百粒质量并计算产量。采用钼锑抗比色法[13]测定土壤全磷(TP),采用Olsen法[14]测定土壤中有效磷(Olsen-P)。采用WANG等[15]改进的Hedley法依次提取出土壤中的树脂态无机磷(Resin-P)、碳酸氢钠态磷(NaHCO3-Pi和NaHCO3-Po)、氢氧化钠态磷(NaOH-Pi和NaOH-Po)、盐酸态磷(HCl-P)以及残余态磷(Residual-P),后均用钼锑抗比色法测定各形态提取液中的磷含量。除此之外,将Resin-P、NaHCO3- Pi和NaHCO3-Po合称为不稳定态磷(L-P),将NaOH- Pi和NaOH- Po合称为中等不稳定态磷(M-P),将HCl-P和Residual-P合称为稳定态磷(S-P)[16]。微生物量磷(SMBP)用氯仿熏蒸浸提法测定[17];酸性、碱性磷酸酶活性(ACP、ALP)采用磷酸苯二钠比色法测定[18]。
1.4 相关参数计算
磷活化系数(phosphorus activation coefficient,PAC)用于表征土壤磷的有效性,并使用全磷(TP)和有效磷含量计算[19]:
磷活化系数(%)=有效磷含量(mg/kg)/全磷含量(mg/kg)×100
1.5 数据处理
采用Microsoft Excel 2016对数据进行初步的整理与计算,采用SPSS 26.0进行单因素方差分析和多重比较以及用最小显著极差法(Duncan)在5%水平上对不同处理的结果进行差异显著性检验,采用IBM SPSS AMOS 24.0软件建立结构方程模型(structural equation modeling,SEM)。通过低χ2/df(χ2/df<3,χ2/df越接近1模型效果越好,P>0.05)、高拟合度指数(GFI>0.9)、低均方根误差(RMSEA<0.05,RMSEA=0表示完全拟合)来评价模型拟合性。
2. 结果与分析
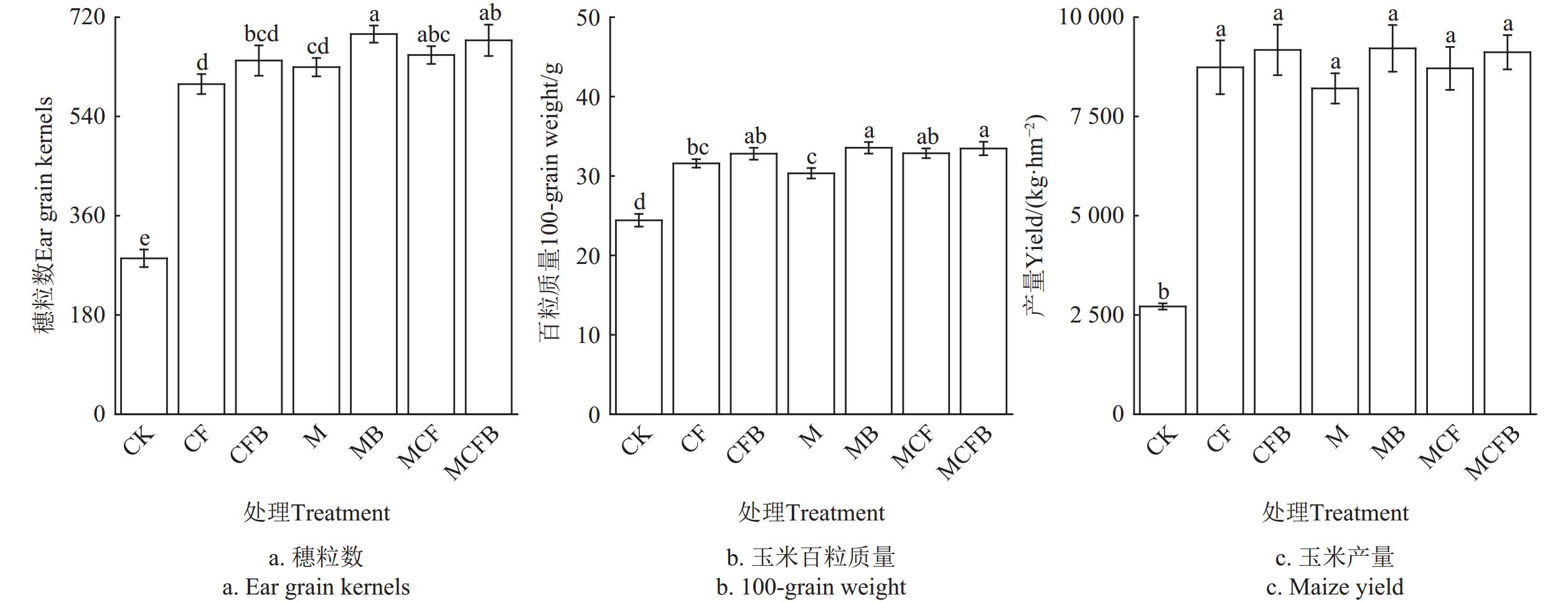
2.1 不同施肥处理对玉米产量的影响
在整个试验周期内,不同施肥处理对玉米的穗粒数、百粒质量以及产量产生显著影响(图1)。与CK相比,各处理下玉米穗粒数、百粒质量以及产量分别显著增加1.12~1.43倍、0.24~0.37倍以及2.02~2.40倍(P<0.05)。较不施荧光假单胞菌处理相比,相应配施处理均以MB处理对穗粒数和百粒质量的增幅最大,较M处理分别显著增加9.53%和10.58%(P<0.05)。在产量方面,未配施荧光假单胞菌的施肥处理以CF处理较CK处理增幅最大,产量显著提高2.22倍;配施荧光假单胞菌后以MB处理较CK处理增幅最大,产量显著提高2.40倍。
2.2 不同处理对复垦土壤全磷、有效磷含量和磷活化系数的影响
不同施肥措施对复垦土壤TP、Olsen-P、PAC值产生显著影响(图2)。与CK相比,Olsen-P含量与PAC值均以MB处理增幅最大,Olsen-P含量显著提高4.50倍、PAC值显著提高4.67倍(P<0.05)。
与相应未配施荧光假单胞菌处理相比,配施处理对土壤TP含量以及PAC值均无显著影响,但MB较M处理相比,在Olsen-P含量上能够显著提高,增幅为11.02%。此外,在均配施荧光假单胞菌条件下,MB处理分别较CFB处理以及MCFB处理相比,Olsen-P含量和PAC值均能显著提高,Olsen-P含量分别显著提高43.95%和22.83%,PAC值分别显著提高49.77%和19.71%( P <0.05)。
2.3 不同处理对复垦土壤各磷组分含量的影响
与CK处理相比,不同施肥措施显著提高复垦土壤L-P、M-P以及S-P含量(图3),其中L-P、M-P分别是其1.98、2.16倍。与相应未配施处理相比,配施荧光假单胞菌后显著提高L-P含量,CFB较CF处理、MB较M处理、MCFB较MCF处理增幅分别为8.58%、13.56%、12.73%(P<0.05)。在配施荧光假单胞菌后,与相应未配施处理相比,M-P含量以CFB较CF处理和MB较M处理提升效果显著,CFB较CF处理显著提高9.61%、MB较M处理显著提高9.76%(P<0.05)。随着荧光假单胞菌的施入,与相应未配施处理相比,S-P含量一定程度减小。其中,以CFB较CF处理、MCFB较MCF处理降幅显著,S-P含量分别显著降低2.65%和3.51%(P<0.05)。此外,L-P和M-P含量均在MB处理下最高,MB较CFB处理,L-P含量显著提高25.36%、M-P显著提高20.46%;MB较MCFB处理,L-P显著提高8.79%;MB较CK处理,L-P显著提高98.46%、M-P显著提高115.63%( P <0.05)。
不同施肥处理能够显著影响复垦土壤Resin-P、NaHCO3-Pi、NaHCO3-Po、NaOH-Pi、NaOH-Po以及HCl-P含量,而对Residual-P则是有一定程度的影响(图4)。
具体而言,各处理与CK处理相比Resin-P含量显著提高40.56%~104.06%、NaHCO3-Pi含量显著提高49.48%~95.95%、NaHCO3-Po含量显著提高31.25%~71.87%、NaOH-Pi含量显著提高53.63%~88.33%、NaOH-Po含量显著提高104.55%~190.91%、HCl-P含量显著提高18.61%~31.75%(P<0.05)。此外,配施荧光假单胞菌各处理较相应未配施处理能够一定程度影响作为活性磷的Resin-P以及NaHCO3-Pi含量。具体而言,Resin-P和NaHCO3-Pi含量均以MB较M处理和MCFB较MCF处理提升效果较佳,MB较M处理Resin-P和NaHCO3-Pi含量分别显著提高16.02%和12.00%;MCFB较MCF处理Resin-P和NaHCO3-Pi含量分别显著提高12.96%和12.65%(P<0.05)。
2.4 不同处理对土壤微生物量磷与磷酸酶活性的影响
不同施肥措施对复垦土壤SMBP水平以及ALP、ACP活性产生显著影响(图5)。与CK相比,不同施肥处理下的SMBP水平以及ALP、ACP活性分别显著提高1.71~3.04倍、 0.78~1.57倍、0.64~1.34倍(P<0.05)。此外,配施荧光假单胞菌各处理较相应未配施处理能够一定程度影响SMBP水平以及ALP活性,但对ACP活性无显著影响。具体而言,配施荧光假单胞菌后,与相应未配施处理相比,SMBP水平均能显著提高,CFB较CF处理、MB较M处理、MCFB较MCF处理增幅分别为14.89%、27.08%、22.71%(P<0.05)。ALP活性以MB较M处理提升效果最佳,显著提高9.56%(P<0.05)。所有处理均以MB处理的SMBP水平以及ALP、ACP活性最高。
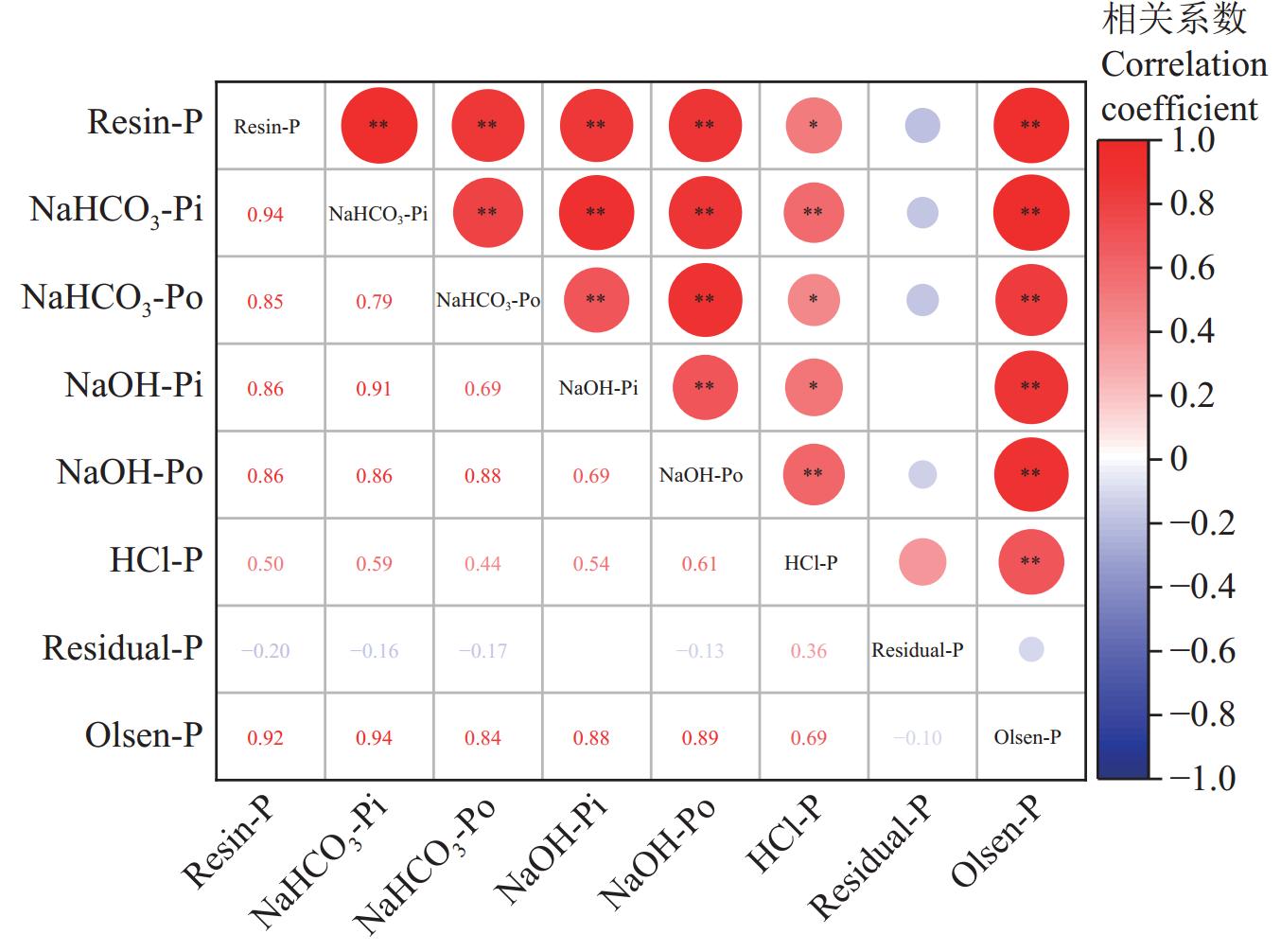
2.5 土壤各形态磷素与有效磷的相关性分析
为了明确各形态磷素与土壤肥力的关系,将复垦土壤各形态磷素与Olsen-P进行相关性分析(图6)。
结果表明Olsen-P含量值与Resin-P、NaHCO3-Pi、NaHCO3-Po、NaOH-Pi、NaOH-Po、HCl-P含量呈显著正相关关系 (P<0.01),与Residual-P含量呈负相关关系。其中,Olsen-P与Resin-P以及NaHCO3-Pi正相关系数较大,分别为0.92和0.94,这说明不同肥料与荧光假单胞菌配施对Resin-P以及NaHCO3-Pi的影响最为密切,这与本文之前的结果分析保持一致。显然,各形态磷素与Olsen-P密切相关。
2.6 土壤各形态磷素与土壤微生物量磷、磷酸酶以及有效磷之间的结构方程模型
通过利用结构方程模型(SEM),在相关性分析的基础上进一步揭示了各形态磷(L-P、M-P、S-P)、微生物量磷(SMBP)、酸碱磷酸酶活性(ALP、ACP)以及有效磷(Olsen-P)之间的因果关系(图7),用于进一步解释和量化各形态磷素对SMBP、ALP、ACP、Olsen-P的影响、评价土壤肥力。模型与数据拟合度较高,可以解释SMBP、ALP、ACP、Olsen-P的方差比例分别是95%、90%、85%、95%。SMBP、ALP受L-P、M-P、S-P的直接影响,ACP受L-P、M-P的直接影响,Olsen-P受L-P、M-P、S-P、SMBP、ALP、ACP的直接影响。其中,以L-P至Olsen-P和SMBP的标准化路径系数较高,分别为0.63和0.61,且均呈显著正相关关系。
![]() 图 7 土壤各形态磷素与土壤微生物量磷、酶活性以及有效磷的结构方程模型注:实线和虚线分别表示正负关系;箭头上面的数字表示标准化后的路径系数;指标附近的R2值表示变量的方差解释比例;*表示P < 0.05。Figure 7. Structural equation model analysis of each P fraction, soil microbial biomass phosphorus, enzyme activity and Olsen PNote: Positive and negative effects are respectively showed in solid line and dotted line. The standardized coefficients are marked above each path. R2 values represent the proportion of the variance explained for each endogenous variable; *means
图 7 土壤各形态磷素与土壤微生物量磷、酶活性以及有效磷的结构方程模型注:实线和虚线分别表示正负关系;箭头上面的数字表示标准化后的路径系数;指标附近的R2值表示变量的方差解释比例;*表示P < 0.05。Figure 7. Structural equation model analysis of each P fraction, soil microbial biomass phosphorus, enzyme activity and Olsen PNote: Positive and negative effects are respectively showed in solid line and dotted line. The standardized coefficients are marked above each path. R2 values represent the proportion of the variance explained for each endogenous variable; *meansP < 0.05. 3. 讨 论
3.1 玉米产量以及各形态磷对化肥、有机肥配施荧光假单胞菌的响应
本研究结果表明,单施化肥、有机肥以及化肥有机肥配施与CK相比均能够显著提高复垦土壤玉米产量,配施荧光假单胞菌后效果更好这与梁利宝等[20]研究结果一致。但较自然耕地以及长期连续培肥的复垦土壤相比,产量较低[21-22]。这是因为初期复垦的土壤作物所必需的N、P、K营养元素均较低、土壤结构差、微生物极少。随着化肥、有机肥以及荧光假单胞菌的施入虽然能够一定程度上改善土壤情况,但和自然耕地以及长期培肥的复垦土壤相比还远远不够。
有机肥、化肥配施荧光假单胞菌可以提高复垦土壤各形态磷素,这与吴文丽等[23]研究在复垦土壤上连续施用菌肥对Hedley磷形态的影响的结果一致。本研究发现,配施荧光假单胞菌后,在相对应未配施处理的基础上,土壤各形态磷素(HCl-P、Residual-P除外)以及PAC值均有所提高,这与CHEN等[16]研究发现,化肥配施粪肥后较单施化肥相比,对HCl-P以及Residual-P含量有所提高的结论不一致,其原因可能是土壤类型和施肥类型共同决定的。CHEN研究的供试土壤是用于水稻种植的自然耕地,其本身基础的理化性质就比较优越。杨振兴等[24]研究发现,磷肥的施入会导致土壤中磷素的积累,而有机肥的施入更会加剧这种累积。因此HCl-P和Residual-P作为难以被植物吸收利用的稳定态磷,成为土壤磷素累积的主要成分。而用于此次试验的复垦土壤处于复垦初期,土壤磷素十分匮乏,为了最大程度地促使种植作物吸收土壤中的磷素,有益微生物会加速对稳定态磷的分解矿化。除此之外,解磷菌的施入可以通过酶解等途径使土壤中的稳定态磷转化,补给作物对磷的需求[25],因此具有解磷效果的荧光假单胞菌施入更能够加速稳定态磷的矿化,本文研究结果:不稳定态磷、中等不稳定态磷含量以及PAC值在配施荧光假单胞菌后有所提高也从侧面进行了佐证(图3)。
3.2 微生物量磷以及酸、碱磷酸酶对化肥、有机肥配施荧光假单胞菌的响应
研究发现,施用有机肥、化肥以及有机肥化肥配施可以显著提高土壤中SMBP水平以及ALP、ACP活性[26]。在本研究中,单施化肥、有机肥能够显著提高SMBP水平,配施荧光假单胞菌后,较相应未配施的处理相比SMBP水平显著提高,并以MB处理的效果最好(图5)。这可能是因为化肥的施入可以为微生物提供磷源,而有机肥的施入在此基础上可以进一步改善土壤的理化性状,为微生物生长提供良好的生活环境[27]。除此之外,菌的施入能够提高复垦土壤有机质、有机磷含量,进而增加了土壤微生物量。另外,单施化肥、有机肥能够显著提高复垦土壤ALP、ACP活性,添加荧光假单胞菌的处理的ALP、ACP活性较相应未添加的各处理相比均有不同程度的提升。其原因可能一方面是因为较自然耕地相比复垦土壤本身就缺磷,而在长期缺磷的环境可以提高土壤磷酸酶的活性[28];另一方面,较自然耕地相比复垦土壤本身微生物数量就稀少,减少了土壤原有微生物对添加的外源微生物的拮抗作用,而土壤中活体微生物数量的增加能够增强了土壤生物活性和生化活性,促进土壤酶活性。
3.3 复垦土壤微生物量磷、磷酸酶活性、有效磷对土壤各形态磷素的响应
Olsen-P作为一种土壤磷指标,可以直接反映土壤有效磷含量的水平,评估土壤磷供应能力,指导磷肥管理和施肥决策,并在土壤肥力评估中发挥重要作用。本研究中Olsen-P水平与Resin-P、NaHCO3-Pi、NaHCO3-Po的相关性较好(分别为0.92、0.94、0.84),并与NaHCO3-Pi的相关性最高(图6),这说明L-P(Resin-P、NaHCO3- Pi、NaHCO3- Po)水平可以反映在荧光假单胞菌配合化肥有机肥施入复垦土壤后,能够提高复垦土壤对作物供磷的潜力,而通过结构方程模型也可以得出L-P的水平可以显著直接正向影响着Olsen-P的含量(图7),这与吴文丽等[23]的研究结果一致。
土壤微生物在碳氮磷循环中发挥着分解、固定和转化的重要作用,促进着碳氮和磷在生态系统中的循环和平衡,被认同是表现土壤质量变化过程中最敏感和最有潜力的指标[29],而土壤磷酸酶可以使有机磷降解、参与磷循环以及影响土壤肥力和磷肥利用效率,对植物生长和土壤环境的健康具有重要影响。在本研究中SMBP、ALP受L-P、M-P、S-P的直接正向影响,而ACP只受L-P、M-P的直接正向影响,这可能是因为土壤磷酸酶活性受土壤pH显著影响[30],所以ACP在本试验地的碱性环境中(土壤pH值8.43)有益作用受到抑制,况且S-P作为稳定态磷本身就很难参与微生物中磷的矿化反应,因此,即使S-P含量变化也无法影响ACP的活性变化。除此之外,L-P与SMBP有显著的直接正向影响且标准化路径系数较大,这说明,除了微生物量的增多可以通过微生物对磷矿化或固定化直接或间接影响各形态磷的转化外[31],随着不稳定态的磷含量增多,也可以促使与磷素相关的微生物增多,本试验配施的荧光假单胞菌数量可能会增多。而这再结合结构方程模型中L-P对ALP、ACP以及Olsen-P的直接正向影响,也从侧面说明了在土壤贫瘠、微生物数量少的复垦土壤中有机肥、化肥配施荧光假单胞菌,可以促使磷素在农田生态系统中的循环转化,并产生积极的正向影响。
综上,由于土壤微生物量磷、土壤磷酸酶活性、有效磷以及磷活化系数可以一定程度上综合反映土壤肥力,因此,探究不同施肥方案对土壤各磷素形态的影响,并在有机肥、化肥配施荧光假单胞菌的施肥措施下建立土壤各形态磷素与土壤微生物量磷、土壤磷酸酶活性、有效磷以及磷活化系数值之间的联系,可以更好地解释有机肥、化肥配施荧光假单胞菌的不同施肥方案是如何影响各形态磷素水平,从而影响土壤肥力,便于更好地评估施肥方案对复垦土壤肥力的影响。
4. 结 论
1)在整个试验周期,与不施肥(CK)相比,不同施肥处理均能显著提高玉米产量以及各形态磷素。其中,以有机肥配施荧光假单胞菌(MB)处理下的玉米产量、有效磷、磷活化系数、不稳定态磷和部分不稳定态磷含量最高,玉米产量显著提高2.40倍,有效磷含量、磷活化系数值、不稳定态磷含量、部分不稳定态磷含量分别显著提高4.50倍、4.67倍、0.98倍、1.16倍。此外,与未配施荧光假单胞菌处理相比,相应配施处理玉米穗粒数、百粒质量、土壤有效磷、不稳定态磷以及部分不稳定态磷含量均以MB较M处理提升效果最佳,分别显著提高9.53%、10.58%、11.02%、13.56%、9.76%。
2)在微生物活性方面,与CK处理相比,化肥、有机肥配施荧光假单胞菌能够显著提高土壤微生物量磷以及酸性和碱性磷酸酶活性,配施荧光假单胞菌后,微生物量磷水平和碱性磷酸酶活性均以MB较M处理提升幅度最大,分别显著提高27.08%和9.56%,而酸性磷酸酶活性受供试土壤pH影响,配施荧光假单胞菌处理较相应未配施处理并没有显著影响其活性。
3)结合相关性分析以及结构方程模型,随着荧光假单胞菌和化肥有机肥的施入,提高了不稳定态磷素含量的同时也提高有效磷的供应能力(显著正相关,标准化路径系数为0.63),促进磷素在复垦土壤农田生态系统中的循环转化,并产生积极的正向影响。
-
图 7 土壤各形态磷素与土壤微生物量磷、酶活性以及有效磷的结构方程模型
注:实线和虚线分别表示正负关系;箭头上面的数字表示标准化后的路径系数;指标附近的R2值表示变量的方差解释比例;*表示P < 0.05。
Figure 7. Structural equation model analysis of each P fraction, soil microbial biomass phosphorus, enzyme activity and Olsen P
Note: Positive and negative effects are respectively showed in solid line and dotted line. The standardized coefficients are marked above each path. R2 values represent the proportion of the variance explained for each endogenous variable; *means
P < 0.05. 表 1 试验处理及肥料用量
Table 1 Experimental treatment and fertilizer dosage
kg·hm−2 处理
Treatment尿素
Urea过磷酸钙
Calcium
superphosphate硫酸钾
Potassium
sulfate有机肥
Organic
fertilizer菌肥
Microbial
fertilizer不施肥(CK) 0 0 0 0 0 单施化肥(CF) 653 1384 374 0 0 化肥+菌(CFB) 604 1280 346 0 1500 单施有机肥(M) 0 0 0 18000 0 有机肥+菌(MB) 0 0 0 16500 1500 化肥+有机肥(MCF) 327 692 187 9000 0 化肥有机肥+菌(MCFB) 272 577 156 7500 1500 -
[1] 郭斌,白昊睿,张波,等. 基于RF和连续小波变换的露天煤矿土壤锌含量高光谱遥感反演[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(10):138-147. GUO Bin, BAI Haorui, ZHANG Bo, et al. Inversion of soil zinc contents using hyperspectral remote sensing based on random forest and continuous wavelet transform in an opencast coal mine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(10): 138-147. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 谢钧宇,张慧芳,罗云琪,等. 连续7年施肥提升复垦土壤肥力提高玉米产量的驱动因子[J]. 农业工程学报,2024,40(1):142-152. XIE Junyu, ZHANG Huifang, LUO Yunqi, et al. Driving factors of improving maize yields in the reclaimed soils by seven years of applied organic manure and chemical fertilizer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2024, 40(1): 142-152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 陈玮,徐占军,郭琦. 煤炭矿区耕地土壤有机质无人机高光谱遥感估测[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(8):98-106. CHEN Wei, XU Zhanjun, GUO Qi. Estimation of soil organic matter by UAV hyperspectral remote sensing in coal mining areas[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(8): 98-106. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 李娇,信秀丽,朱安宁,等. 长期施用化肥和有机肥下潮土干团聚体有机氮组分特征[J]. 土壤学报,2018,55(6):1494-1501. LI Jiao, XIN Xiuli, ZHU Anning, et al. Characteristics of the fraction of organic nitrogen in fluvo-aquic soil aggregates under long-term application of chemical fertilizer and organic manure[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2018, 55(6): 1494-1501. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张文学,王少先,刘增兵,等. 基于土壤肥力质量综合指数评价化肥与有机肥配施对红壤稻田肥力的提升作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2021,27(5):777-790. ZHANG Wenxue, WANG Shaoxian, LIU Zengbing, et al. Evaluating soil fertility improvement effects of chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizers in a red paddy soil using the soil fertility index[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(5): 777-790. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] CHEN X L, HENRIKSEN T M, SVENSSON K, et al. Long-term effects of agricultural production systems on structure and function of the soil microbial community[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2020, 147: 103387. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.103387
[7] HU C, XIA X G, CHEN Y F, et al. Yield, nitrogen use efficiency and balance response to thirty-five years of fertilization in paddy riceupland wheat cropping system[J]. Plant, Soil and Environment, 2019, 65(2): 55-62. doi: 10.17221/576/2018-PSE
[8] 孙晓东,栗海鹏,高文俊,等. 有机肥对煤矿复垦土壤团聚体碳氮磷含量及细菌群落的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2023,29(12):2193-2207. SUN Xiaodong, LI Haipeng, GAO Wenjun, et al. Effects of manures on carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus content and bacterial community in reclaimed soil aggregates[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(12): 2193-2207. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 徐明岗,李然,孙楠,等. 施用有机肥煤矿复垦耕地有机碳的固持效率及组分变化[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2022,28(12):2143-2151. XU Minggang, LI Ran, SUN Nan, et al. Soil organic carbon sequestration efficiency and fractions as affected by organic fertilization rate in reclaimed cultivated land[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(12): 2143-2151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 曹寒冰,谢钧宇,强久次仁,等. 施肥措施对复垦土壤团聚体碳氮含量和作物产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(18):135-143. CAO Hanbing, XIE Junyu, QIANGJIU Ciren, et al. Effects of fertilization regimes on carbon and nitrogen contents of aggregates and maize yield in reclaimed soils[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(18): 135-143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] WANG Y Y, LI P S, ZHANG B X, et al. Identification of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms and determination of their phosphate-solubilizing activity and growth-promoting capability[J]. Bioresources, 2020, 15(2): 2 560-2578.
[12] JIMTHA J C, JISHMA P, KARTHIKA N R, et al. Pseudomonas fluorescens R68 assisted enhancement in growth and fertilizer utilization of Amaranthus tricolor[J]. Biotech, 2017, 7(4): 256.
[13] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京:中国农业科技出版社,1999. [14] OLSEN S R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate[M].Washington:US Deparptment of Agricultural, 1954.
[15] WANG Y, ZHAO X, WANG L, et al. A five-year P fertilization pot trial for wheat only in a rice-wheat rotation of Chinese paddy soil: Interaction of P availability and microorganism[J]. Plant and Soil, 2016, 399(1/2): 305-318. doi: 10.1007/s11104-015-2681-4
[16] CHEN G, YUAN J, CHEN H, et al. Animal manures promoted soil phosphorus transformation via affecting soil microbial community in paddy soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 831: 154917. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154917
[17] 吴金水. 土壤微生物生物量测定方法及其应用[M]. 北京:气象出版社,2006. [18] 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法[M].北京: 农业出版社,1986. [19] WANG Q Q, ZHANG Z H, CHEN W W, et al. Effect of long-term fertilization on phosphorus fractions in different soil layers and their quantitative relationships with soil properties[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2022, 21(9): 2720-2733. doi: 10.1016/j.jia.2022.07.018
[20] 梁利宝,洪坚平,谢英荷,等. 不同培肥处理对采煤塌陷地复垦土壤生化作用强度及玉米产量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报,2011,25(1):192-196,213. LIANG Libao, HONG Jianping, XIE Yinghe, et al. Effect of biochemical action and corn yield of the reclaimed soil on subsided land resulting from coal-mine by different treatments of application fertilizers[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 25(1): 192-196, 213. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 樊晓东. 有机无机与生物炭菌肥配施对采煤复垦土壤氮素累积和玉米产量的影响[D]. 太谷:山西农业大学,2022. FAN Xiaodong. Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizer Combined with Biochar Fertilizer on Nitrogen Accumulation and Maize Yield in Reclaimed Soil[D]. Taigu: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 刘志平,马晓楠,解文艳,等. 山西典型旱地玉米产量及水分利用效率对长期不同施肥模式的响应[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2023,41(4):61-70. LIU Zhiping, MA Xiaonan, JIE Wenyan, et al. Responses of maize yield and water use efficiency to long-term fertilization patterns in dryland of Shanxi Province[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2023, 41(4): 61-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 吴文丽,洪坚平,孟会生,等. 连续施用解磷菌肥对复垦土壤磷酸酶和Hedley磷形态的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料,2016(4):59-64. WU Wenli, HONG Jianping, MENG Huisheng, et al. Effect of continuous application of phosphorus bacterial fertilizer on soil alkaline phosphatase activity and Hedley phosphorus forms in the reclaimed soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2016(4): 59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 杨振兴,周怀平,解文艳,等. 长期施肥褐土不同磷组分对磷素盈余的响应[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2020,26(5):924-933. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.19291 YANG Zhenxing, ZHOU Huaiping, XIE Wenyan, et al. Response of phosphorus components to phosphate surplus in cinnamon soil under long-term fertilization[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(5): 924-933. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11674/zwyf.19291
[25] 郑淇元,谢意太,卞海洋,等. 溶磷菌肥对红壤磷组分及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报,2022,44(1):233-244. ZHENG Qiyuan, XIE Yitai, BIAN Haiyang, et al. Effects of phosphate solubilizing bio-fertilizer on phosphorus fractions and fertility of red soil[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2022, 44(1): 233-244. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 刘彦伶,李渝,张雅蓉,等. 长期施肥对黄壤稻田和旱地土壤磷酸酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤通报,2022,53(4):948-955. LIU Yanling, LI Yu, ZHANG Yarong, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on phosphatase activities in paddy and dryland of yellow soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2022, 53(4): 948-955. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 孙凤霞,张伟华,徐明岗,等. 长期施肥对红壤微生物生物量碳氮和微生物碳源利用的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2010,21(11):2792-2798. SUN Fengxia, ZHANG Weihua, XU Minggang, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and on carbon source utilization of microbes in a red soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(11): 2792-2798. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 范淼珍,尹昌,范分良,等. 长期不同施肥对红壤碳、氮、磷循环相关酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2015,26(3):833-838. FAN Miaozhen, YIN Chang, FAN Fenliang, et al. Effects of different long-term fertilization on the activities of enzymes related to carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles in a red soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(3): 833-838. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 刘晓星,吕光辉,杨晓东,等. 艾比湖流域5种土壤类型的酶活性和理化性质[J]. 干旱区研究,2012,29(4):579-585. LIU Xiaoxing, LYU Guanghui, YANG Xiaodong, et al. Enzyme activities and physical and chemical properties of five different soils in the ebinur lake basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2012, 29(4): 579-585. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 田沐雨,于春甲,汪景宽,等. 氮添加对草地生态系统土壤pH、磷含量和磷酸酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2020,31(9):2985-2992. TIAN Muyu, YU Chunjia, WANG Jingkuan, et al. Effect of nitrogen additions on soil pH, phosphorus contents and phosphatase activities in grassland[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(9): 2985-2992. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] LUO G, LING N, NANNIPIERI P, et al. Long-term fertilisation regimes affect the composition of the alkaline phosphomonoesterase encoding microbial community of a vertisol and its derivative soil fractions[J]. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 2017, 53(4): 375-388.




 下载:
下载: