Predicting shallow landslides in highly vegetation-covered areas using machine learning models
-
摘要:
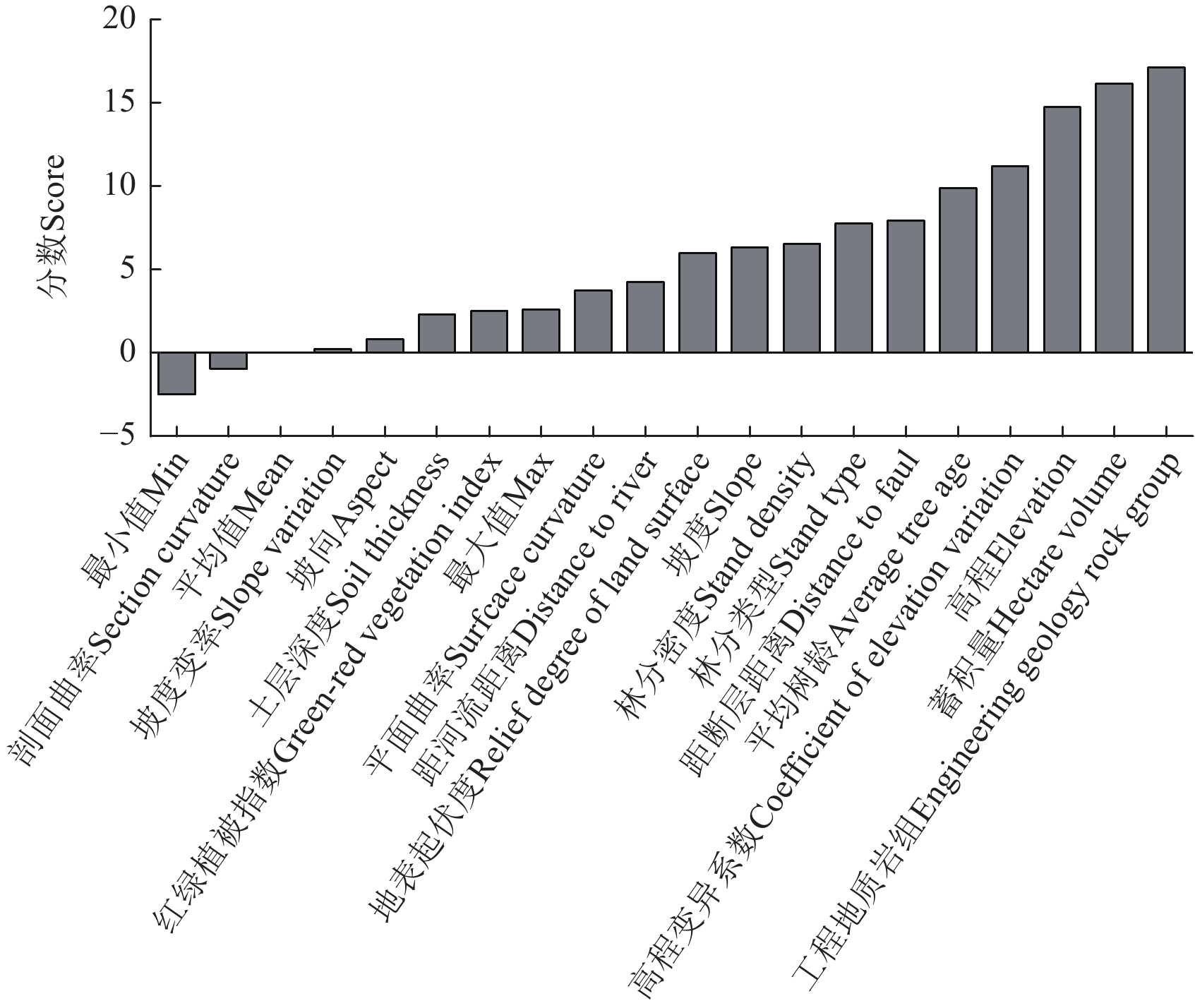
为探究高植被覆盖区浅层滑坡的影响因素并构建最优的滑坡预测模型,该研究以华蓥市山区林地为研究对象,考虑了蓄积量、林分密度、平均树龄、林分类型和红绿植被指数(green-red vegetation index,GRVI)等植被因子,并结合地形地质因素,经过Boruta重要性分析以及共线性诊断,利用Logistic回归模型、广义相加模型、随机森林模型、支持向量机模型和人工神经网络模型等5种机器学习模型构建华蓥市山区林地浅层滑坡预测模型,并结合历史滑坡点检验,提出华蓥市山区林地浅层滑坡的最佳预测模型及高易发性区域的植被特征。结果表明:1)工程地质岩组、距河流距离、距断层距离、林分类型、平均树龄和蓄积量是影响浅层滑坡的主要因子;2)不同因子组合对模型精度有极大的影响,考虑蓄积量、林分密度、平均树龄等植被因子有利于提高模型的预测精度;3)在5种模型中,预测精度最高的模型为随机森林模型,精度可达到95.05%;4)研究区高易发性及以上区域的面积为25.31 km2,占研究区总面积的14.79%,低密度(
1000 ~1500 株/hm2)、高蓄积量(>80 m3/hm2)和高树龄(>30 a)是浅层滑坡发生的主要植被特征。该研究结果可为中国高植被覆盖区极端暴雨型滑坡的预警与防控提供科学决策和技术支撑。Abstract:Extreme rainstorm-triggered shallow landslides can often occur in highly vegetation-covered areas, due mainly to the synergistic interactions among geological, vegetation, and meteorological factors. In this study, a landslide prediction model was constructed with high accuracy, in order to reveal the influence of vegetation factors on shallow landslides. Taking the mountain forest in Huaying city as study site, various vegetation factors were selected, including stock volume, stand density, average tree age, stand types, and green-red vegetation index (GRVI), and combined with topographic and geological factors (engineering geology rock group, distance to faults, distance to river, elevation, coefficient of elevation variation, slope, slope variation, relief degree of land surface, surface curvature, section curvature, aspect, and soil thickness). According to Boruta's importance and multicollinearity analysis, five kinds of shallow landslide prediction models were built using machine learning techniques, including the Logistic regression, Generalized additive model, random forest (RF), Support vector machine, and artificial neural network model. The prediction accuracy of the five models was evaluated by sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC values. Coupling with the previous records of landslide points, the prediction models were validated to determine the vegetation characteristics of high-risk areas in Huaying mountain forests. The research demonstrated that: 1) The susceptibility of shallow landslides was primarily influenced by the engineering geological rock groups, distance from rivers, distance from faults, stand types, average age, and stock volume. There was relatively little influence of environmental and vegetation factors on the susceptibility of shallow landslides. 2) The combination of different factors shared a great impact on the accuracy of the model, in terms of the vegetation factors (stand density, average age, and stock volume). The prediction accuracies of the five models were improved significantly; All factors were only used in the specific models, indicating no factors commonly suitable for all five models. 3) The RF62 model was achieved with the highest prediction accuracy. The AUC value, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the RF62 model were 0.96, 0.83, 0.93, and 0.86, respectively. The second precision model was ANN53, where the AUC value, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 0.926, 0.80, 0.79, and 0.79, respectively. The third prediction accuracy was the support vector machine model, where the AUC value, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 0.90, 0.82, 0.73, and 0.77, respectively. The fourth prediction accuracy was LOGIT325, where the AUC value, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 0.876, 0.83, 0.72, and 0.77, respectively. The worst accuracy was obtained from the GAM597 model, where the AUC value, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 0.87, 0.82, 0.73, and 0.77, respectively. 4) The RF model performed the most accurate to predict the landslides, with 95.05% accuracy and coverage of 25.31 km2 within the highly susceptible areas; artificial neural network model, the support vector machine model, generalized additive model, and logistic regression were followed with 78.57%, 69.78%, 68.13%, and 67.58% accuracy and coverage of 35.43, 22.02, 26.26 and 26.27 km2 within the highly susceptible areas, respectively; 5) The primary vegetation with shallow landslides was characterized by the low density (1000-1500 plants/hm2), high storage volume (>80m3/hm2), and advanced age (>30 a). The findings can provide scientific decision-making and technical assistance for early warning, prevention, and control of rainstorm-induced landslides in high vegetation cover areas of China.
-
Keywords:
- vegetation /
- landslide /
- slope failure /
- forestland /
- machine learning models
-
0. 引 言
受全球气候变化影响,暴雨、干旱、高温、低温、洪水等气象水文灾害发生的强度、频次及灾害损失程度日趋严重,气象水文灾害已经成为国内外关注的热点问题之一[1-3]。实际上,自20世纪50年代开始,气象水文灾害已经严重影响人类社会发展[4-6]。根据世界气象组织(World Meteorological Organization,WMO)发布报告显示,1970—2021年间,极端天气、气候和水事件引起的灾害事件超过11778起,造成超过两百万人死亡,经济损失达4.3万亿美元[7]。
自然灾害风险评估作为灾害风险管理的核心内容,是防灾减灾的重要基础性研究。然而,一个区域往往受到多个致灾因子共同影响,单灾种风险评估并不足以反映该地区的综合风险。鉴于此,当前自然灾害风险评估已表现出从单灾种向多灾种、灾害链、复合灾害综合风险评估转变[8]。如FLEISCHHAUER等[9]基于多灾种危险性和承灾体脆弱性评估框架对欧洲地区进行了多灾种综合风险评估;盖程程等[10]提出一种多灾种耦合风险评估的方法,并从致灾因子和易损性进行风险度量;王望珍等[11]构建多灾种耦合模型并通过风险矩阵法以及Borda序值法对神农架地区进行多灾种风险区划;KC 等[12]通过构建灾害危险性、暴露度以及脆弱性综合评估框架并结合未来气候数据预估了美国县域尺度的气象灾害风险;CHANG等[13]基于灾害危险性、承灾体暴露度、脆弱性以及城市韧性评估了济南市的综合风险等级。总体来看,有关综合风险评估并没有统一的指标体系和评估方法。
中巴经济走廊是“一带一路”倡议的六大经济走廊之一,对于推进中巴两国在能源、安全、经济等领域的合作具有至关重要的作用。大量研究表明,该地区对气候变化极其敏感并且容易发生极端天气事件[14-15],因此,开展气象水文综合风险评估具有一定的现实意义。目前,中巴经济走廊的气象水文灾害风险评估主要集中在单灾种风险评估,如陈金雨等[16-17]采用危险性、暴露度及脆弱性风险评估框架分别评估了中巴经济走廊极端高温、低温风险。吴瑞英等[18-19]运用COMORPH降水数据驱动FloodArea水动力模型,通过博弈论组合赋权方法对中巴经济走廊洪灾风险进行了评估。杜世雄等[20]通过强度-面积-持续时间(intensity-area-duration,IAD)分析中巴经济走廊多年来极端降水变化趋势。但该地区往往受到多种致灾因子的影响,单灾种风险评估并不足以反映其综合风险。联合国开发计划署(United Nations Development Programme,UNDP)最新发布的研究报告表明:在气候变化影响下,该地区面临热浪、干旱、洪水等一系列气象水文灾害的风险越来越大。鉴于此,开展中巴经济走廊气象水文综合风险评估迫在眉睫。
据EM-DAT灾害数据库记载,1961—2015年间巴基斯坦气象水文灾害主要有暴雨、洪水、高温、干旱以及低温等,其中发生于2010年的巴基斯坦特大洪水受灾人数达1200万人,近2 000人罹难。故本文选择暴雨、高温、低温、干旱、洪水5个灾种,通过层次分析法和熵权法确定各指标综合权重,构建“综合风险 = 综合危险性+综合脆弱性”风险评估框架并结合风险矩阵法对中巴经济走廊气象水文灾害综合风险区划进行研究,分别计算0.25°×0.25°格点、县级行政区尺度的综合风险结果,并通过Borda序值法细化区县尺度综合风险等级。研究结果不仅可以为各级政府有效地指导防灾工作提供依据,减少灾害损失,还可以帮助各级政府编制、完善和实施灾害应急预案,增强对灾害的应急管理能力,提高灾害应急救助工作的科学性。
1. 数据与方法
1.1 研究区概况
中巴经济走廊(China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, CPEC)北起中国喀什地区,南至巴基斯坦的瓜达尔港,全长超过3000 km(图1)。
巴基斯坦主要由俾路支省、信德省、旁遮普省、开伯尔-普赫图赫瓦省(开普省)、联邦直辖部落区、伊斯兰堡首都区、阿扎德克什米尔地区和吉尔吉特-巴尔蒂斯坦(北部地区)组成。该区域地貌类型复杂,气候类型多样。北部为山地地区,以高寒山地气候为主,主要受到暴雨、洪水以及低温灾害影响;中、南部地形平坦开阔,以热带草原和热带沙漠气候为主,主要受到干旱、高温以及洪水灾害影响。
1.2 数 据
逐日降水、最高气温、最低气温来源于中国科学数据发布的1961—2015年中巴经济走廊逐日气象数据集[21];标准化降水蒸散指数(Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index,SPEI)来源于中国科学数据发布的1961—2015 年中巴经济走廊 SPEI数据集[22];DEM来源于地理空间数据云;地表覆盖数据来源于国家基础地理信息中心。
选取人口密度、人口结构(年龄和性别比例)、道路密度、建筑密度、农作物种植面积、耕地面积占比作为暴露度评价指标,其中人口密度和人口结构数据来源于哥伦比亚大学国际地球科学信息网络中心所提供的修订后的第四版2015年世界网格人口数据集(GPWv4)、路网数据来源于NASA社会经济数据和应用中心制作发布的全球性公路数据集gROADS,从Quickbird正射影像提取建筑物基底图,结合中巴经济走廊标准格网制作了道路密度数据以及建筑密度数据。哈佛大学MapSPAM团队基于多种数据源生产的全球作物生产分配模型,其包括全球2010年41种作物的种植面积、收获面积、产量、作物加工产品产量、作物收获面积与产量总产值等数据[23],其中小麦与水稻为研究区的主要农作物。耕地面积占比数据主要来自于哥白尼全球土地服务中心提供的2015年耕地数据。选择脆弱人口比例(年龄大于65岁的老人和5岁以下的儿童)以及性别比例作为敏感性评价指标,处理人口结构数据得到脆弱人口比例和性别比例。恢复能力指标选择灌溉能力和GDP,其中GDP数据采用KUMMU等发表在Scientific data上的全球2015年GDP栅格数据。灌溉数据选择张琨等[24-25]发表在时空三极环境大数据平台2015年全球灌溉农田灌溉用水量遥感估算数据集。
本文风险评估最小评估单元为空间分辨率为0.25°的格网,共1419个评估单元。将人口密度、GDP、人口结构、耕地、DEM等数据采用ArcMap分区统计功能与气象数据统一空间分辨率。限于数据获取难度,在时间尺度上,选取2010年地表覆盖数据、路网、农作物种植面积和建筑密度数据及2015年GDP和人口数据。
1.3 研究方法
1.3.1 风险评估框架
基于中巴经济走廊气象、社会经济等数据建立综合风险评估体系(表1)。具体评估步骤如下:
表 1 中巴经济走廊气象水文综合风险评价指标体系Table 1. Integrated risk assessment indicator system for hydrometeorological disaster in China-Pakistan Economic Corridor因子层
Factor level指标层(权重)
Indicator level (weight)AHP EW 组合权重
Combined weight危险性
Hazard暴雨 强度(0.554) 0.211 0.143 0.193 频次(0.258) 暴雨雨量(0.189) 高温 强度(0.526) 0.273 0.177 0.247 频次(0.288) 持续时间(0.187) 低温 强度(0.537) 0.026 0.604 0.179 频次(0.286) 持续时间(0.177) 干旱 强度(0.548) 0.182 0.029 0.141 烈度(0.323) 持续时间(0.129) 洪水 总降水量(0.371) 0.308 0.046 0.238 高程(0.219) 坡度(0.238) 水系距离(0.172) 脆弱性
Vulnerability暴露度 人口密度(0.286) 0.333 0.429 0.368 道路密度(0.141) 建筑密度(0.21) 农作物面积(0.177) 耕地面积占比(0.186) 敏感性 脆弱人口比例(0.5) 0.333 0.015 0.219 性别比例(0.5) 恢复能力
“−”灌溉能力(0.5) 0.333 0.556 0.413 GDP(0.5) 注:“−”为负向指标,其余为正向指标。AHP为层次分析法;EW为熵权法。 Note: "−" represents negative indicator, the rest are positive indicators. AHP is analytic hierarchy process; EW is entropy weight method. 1)构建致灾因子危险性和承灾体脆弱性的“H-V”风险评估框架[10-11, 26],对于每一评价单元,综合风险计算式如下:
R=H+V (1) 式中R代表综合风险,H代表综合危险性指数,V代表承灾体综合脆弱性指数。H计算如下:
H=n∑i=1WiHi (2) 式中n代表灾种数;Wi代表灾种i所对应的权重,Hi为灾种i所对应的危险性指数,Hi可由式(3)计算得出:
Hi=m∑j=1WijHij(i=1,2,3,4,5,j=1,2,...,m) (3) 式中 m代表灾种i的指标个数;Hij代表灾种i第j个指标的归一化指数,Wij代表灾种i第j个指标所对应的权重。
对于每一评估单元,其综合脆弱性计算式为
V=weE+wsS−wrR (4) 式中E、S、R分别代表每一评估单元暴露度、敏感性以及恢复能力;而we、ws、wr分别为评估单元暴露度、敏感性以及恢复能力所对应的权重;而暴露度、敏感性以及恢复能力计算原理与危险性指数计算原理相同。
2)对所有评价指标进行归一化处理。不同类型数据的量纲不同,为消除各指标原始数据尺度的差异性,需要对各指标数据进行归一化处理[27]。
3)采用层次分析法和熵权法确定致灾因子危险性和承灾体脆弱性综合权重,计算综合危险性指数与承灾体综合脆弱性指数并绘制多灾种危险性等级图、承灾体综合脆弱性等级图以及综合风险等级图。
4) 运用风险矩阵法以及Borda序值法绘制区县尺度综合风险等级图。
1.3.2 指标体系构建
1)致灾因子危险性
危险性是指自然灾害过程中灾害量化结果超过特定的临界值时,给社会经济系统造成危害的可能性和危险程度。中巴经济走廊气象水文灾害主要有暴雨、高温、低温、干旱以及洪水,各灾种危险性定义如下:
暴雨危险性:参考新疆维吾尔自治区地方标准,将24 h降水量超过24 mm的强降雨定义为暴雨,即每个格点大于24 mm作为暴雨事件的阈值。定义暴雨事件强度为每次暴雨事件过程中平均每天每个格点的降水量(mm/d);频次为平均每年暴雨事件的发生次数;而暴雨雨量为每个格点超过暴雨事件阈值的降水量之和(mm)。将暴雨的强度、频次和雨量作为暴雨灾害的危险性指标。
高温危险性:采用逐日最高气温的第95个百分位来定义极端高温的阈值,故首先将1961—2015年逐日最高气温按升序排列,选择每年第95个百分位值的平均值定义为极端高温的阈值,将年平均最高气温小于研究区平均最高气温的栅格剔除,强度为极端高温事件的最高气温,频次为年均极端高温事件的发生次数,持续时间为事件的年平均历时[16]。将高温的强度、频次、持续时间作为高温危险性指标。
低温危险性:将1961—2015年最低气温按升序排列,采用逐日最低气温的第5个百分位来定义极端低温的阈值,剔除年平均最低气温大于研究区平均最低气温的栅格。其中强度为极端低温事件最低气温,频次为年均极端低温事件发生次数,持续时间为事件的年平均历时,低温危险性指标为极端低温事件的强度、频次以及持续时间[17]。
干旱危险性:选取干旱的强度、烈度,持续时间作为干旱的危险性评价指标,其中干旱强度为干旱事件所有栅格的SPEI均值;烈度为干旱事件中所有栅格对应的干旱指标与干旱阈值之差的累计平均值,持续时间为干旱事件历时。
洪水危险性:暴雨是导致洪水的重要因素,选取总降水量、高程、坡度以及水系距离作为洪灾危险性指标。其中通过EM-DAT数据库记载的1961—2015年期间洪灾开始与结束时间范围内降水的总和作为总降水量;此外,从地表覆盖数据中提取水系,并通过计算欧式距离来确定水系距离。
2)承灾体脆弱性
脆弱性是指受到不利影响的趋向或者趋势的物理、社会、经济、环境以及文化制度等因子。而脆弱性可以通过其组成部分暴露度、敏感性以及恢复能力的交互作用呈现式(4)。其中暴露度指实体(人口、建筑以及基础设施等)暴露于多种自然灾害的影响[28]。故本文选择人口密度、道路密度、建筑密度、农作物种植面积以及耕地面积占比。其中,农作物种植面积为小麦、水稻种植面积的总和。而敏感性一般是指自然灾害引发的极端灾害事件发生危害,损失和破坏的可能性。本文选择性别比例以及脆弱人口比例作为敏感性指标。恢复能力是对自然灾害影响进行调整和应对的能力,由于指标获取的难度,本文选择GDP及灌溉能力作为恢复能力指标,其中,灌溉可以有效降低干旱对农作物的影响,故将其作为一种恢复能力指标。
1.3.3 指标权重计算
1)层次分析法
层次分析法是一种定性和定量分析的决策方法,可以用来确定各评价指标的主观权重[29-30]。
2)熵权法
熵权法可以客观反映各评价指标的权重[31],通过各指标间的信息熵大小确定权重。
3)组合权重
为充分考虑AHP和熵权法的特性,本文引入距离函数并采用线性组合法得出组合权重[32-33],确定组合权重的表达式为
wl=aw′l+bwl″ (5) 式中 {w}_{l} 为组合权重, {w}_{l}'为AHP法得到的第 l 个指标的主观权重, {w}_{l}'' 为熵权法得到的第 l 个指标的客观权重, a 、 b 是权重的分配系数, a+b=1 。
主观权重与客观权重的距离函数表达式为
d\left({w}_{l}',{w}_{l}''\right)=\left[\frac{1}{2}\sum _{i=1}^{n}({w}_{l}'-{w}_{l}''{)}^{2}\right]^{\tfrac{1}{2}} (6) a 与 b 的差值是分配系数间的差异:
D=\left|a-b\right| (7) 构造方程组如下:
\left\{\begin{aligned}&d{\left({w}_{l}',{w}_{l}''\right)}^{2}=(a-b{)}^{2}\\ &a+b=1\end{aligned}\right. (8) 求解方程组得到系数a和b,将分配系数代入式(5)得出组合权重。计算结果见表1。
1.3.4 综合风险等级划分
风险矩阵法将自然灾害风险的两大基本要素—致灾因子综合危险性和承灾体综合脆弱性,根据自然断点法进行等级划分,形成风险评价矩阵[34]。通过构建风险矩阵进行综合风险等级划分,参考文献 [11]将综合风险分为低、中低、中、高4个等级,分别表示为I、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ。
1.3.5 基于Borda序值法优化综合风险区划
风险矩阵法等级划分比较直观简洁,但容易出现风险结。风险结是指在同一风险等级中,属性基本相同,但还能进行细分的风险模块[35-36]。本文通过Borda序值法消除风险结,优化综合风险等级。
1)危险度序值 {E}_{i} :危险度序值是对所有评价单元的多灾种综合危险性等级进行排序的结果。以 {P}_{1}\mathrm{、} {P}_{2}\mathrm{、}{P}_{3}\mathrm{、}{P}_{4}\mathrm{、}{P}_{5} 分别代表低、中低、中、中高以及高的风险等级,在每一风险等级的评价单元的个数分别为 {M}_{1}\mathrm{、}{M}_{2}\mathrm{、}{M}_{3}\mathrm{、}{M}_{4}\mathrm{、}{M}_{5} ;每一评价单元的危险性等级 {P}_{i}\left(i=1,2,\cdots,5\right) ,其中危险度序值 {E}_{i} 计算如下:
{E}_{i}={D}_{i}+\frac{\left(1+{M}_{i}\right)}{2} (9) 其中 {D}_{i} 计算原理如下:
D_i=\left\{\begin{aligned}&\displaystyle\sum\nolimits _{r=1}^{i-1}{M}_{r},&i > 1\\ &0,&i=1\end{aligned}\right. (10) 2)脆弱度序值:脆弱度序值是对研究区内所有评价单元的承灾体脆弱性进行排序的结果。以Q1、Q2、Q3、Q4、Q5分别代表低、中低、中、中高以及高的脆弱性等级,在每一风险等级的评价单元的个数分别为N1、N2、N3、N4、N5;每一评价单元的脆弱性等级为 {Q}_{j}(j= 1,2,\cdots,5) ,其中脆弱度序值计算如下:
{F}_{j}={C}_{j}+\frac{\left(1+{N}_{j}\right)}{2} (11) 其中, {C}_{j} 计算原理如下:
{C}_{j}=\left\{\begin{aligned}&\displaystyle\sum\nolimits _{t=1}^{j-1}{N}_{t},&j > 1\\ &0,&j=1\end{aligned}\right. (12) 3)Borda数:Borda数是对每一评价单元综合风险程度的量化,计算原理如下:
{B}_{k}=\left(S-{E}_{k}\right)+\left(S-{F}_{k}\right)\left(k=1,2,\cdots,1419\right) (13) 式中 S 为评价单元的个数,本研究中是利用中巴经济走廊1419个格点进行计算,故在本文中 S 取1419。
4)Borda序值:其赋值方法是将所有评价单元的Borda数由大到小排列,相同Borda数对应的Borda序值分别为0,1,…, n 。若评价单元的Borda数排在第一位,其对应的Borda序值为0,表明该评价单元综合风险最小。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 致灾因子危险性
中巴经济走廊致灾因子危险性空间分布特征如图2所示。总体而言,中巴经济走廊东部、南部暴雨危险性等级高,其中高危险性地区主要分布于旁遮普省东北部以及信德省东南部地区,低危险性等级地区主要分布于俾路支省、中国喀什等地区(图2a)。俾路支省西部、信德省东南部地区高温危险性等级高,中国喀什、吉尔吉特-巴尔蒂斯坦(北部地区)高温危险性等级低(图2b)。低温高危险性地区主要集中在中国喀什、吉尔吉特-巴尔蒂斯坦(北部地区)(图2c)。对比暴雨、高温、低温危险性等级空间分布,干旱灾害分布范围较广,在开普省、旁遮普省以及俾路支省等地区干旱危险性等级最高,中国喀什地区干旱危险性等级低(图2d)。旁遮普省北部以及信德省洪水危险性等级高,而中国喀什地区洪水危险性较低(图2e)。中巴经济走廊综合危险性评估结果如图2f所示,高危地区主要位于信德省、旁遮普省,约占中巴经济走廊总面积的9%。
2.2 脆弱性评估
中巴经济走廊人口、建筑、道路、农作物以及耕地等承灾体集中分布于旁遮普省、信德省以及开普省,进而导致以上地区暴露度水平高(图3a)。总体来看,中巴经济走廊大部分地区处于低暴露度水平。结合危险性评估结果,中巴经济走廊的22.50%的人口、30.60%的建筑、13.30%的道路、20.70%的耕地以及26.40%农作物等承灾体暴露于高危险性地区,以上地区发生气象水文灾害的概率较大,且暴露度水平高,一旦发生灾害,容易导致造成巨大的人员伤亡和经济损失,因此,在进行政策制定时,以上地区要重点防范气象水文灾害。在面对灾害时,不同性别、年龄结构对气象水文灾害的承受能力是不同的。通过计算得出俾路支省、信德省以及开普省相对而言敏感性等级高,而中国喀什敏感性等级低(图3b)。恢复能力空间分布特征与暴露度空间分布高度相关,旁遮普省以及开普省部分地区由于经济水平高以及灌溉水平高,使得以上地区恢复能力高,而其他地区相对来说恢复能力较低(图3c)。其中,俾路支省、信德省旁遮普省以及开普省脆弱性等级相对较高,而中国喀什脆弱性等级相对较低(图3d)。
2.3 综合风险评估
中巴经济走廊气象水文灾害综合风险评估结果表明,综合风险呈现明显的空间异质性(图4)。高风险地区主要分布于信德省的中、东部地区,旁遮普省的北部、南部地区,开伯尔-普什图省(开普省)的部分地区以及俾路支省的西部地区。除中国喀什外,其他省份都有中风险区的分布。中低风险区主要分布于吉尔吉特-巴尔蒂斯坦,以及俾路支省的大部分地区。低风险区主要分布于中国喀什地区、俾路支省、吉尔吉特-巴尔蒂斯坦等。
从中巴经济走廊及各行政单元不同等级综合风险面积占比来看,中风险区>高风险区>中低风险区>低风险区,所占比例分别为37.70%、30.94%、17.27%、14.09%(表2)。其中信德省、自由克什米尔、旁遮普省高风险地区面积占比相对较高,占比分别为66.50%、60.00%、47.57%;中国喀什地区、北部地区低风险区占比高,分别为95.92%、34.19%。
表 2 中巴经济走廊及各行政单元不同等级风险区所占面积比例Table 2. Percentage of area with different risk classification over the major administrative unit of China-Pakistan Economic Corridor% 省份
Province低风险Low 中低风险
Mid-low中风险Middle 高风险High 自由克什米尔Azad Kashmir 0 20.00 20.00 60.00 信德省Sindh 0 0.97 32.52 66.50 旁遮普省Punjab 0.32 3.88 48.22 47.57 俾路支省Balochistan 8.35 24.27 47.77 19.61 开普省Khyber Pakhtunkhwa 14.29 24.68 35.71 25.32 吉尔吉特-巴尔蒂斯坦
Gilgit–Baltistan34.19 52.14 11.11 2.56 喀什Kashgar 95.92 3.06 1.02 0 中巴经济走廊CPEC 14.09 17.27 37.70 30.94 中巴经济走廊综合风险评估结果与中巴经济走廊多灾种危险性等级空间分布特征有明显差别,与承灾体脆弱性等级空间分布特征也有一定的差异,这也充分说明,气象水文灾害综合风险是由多灾种综合危险性和承灾体综合脆弱性二者叠加的结果。
为进一步细化评估结果,本文将综合危险性等级、综合脆弱性等级以县级行政区划进行分区统计,进而确定县级行政区划的综合风险等级。其中高风险等级的区县有51个(图5a)。但风险矩阵法的局限在于在进行等级相加时会出现风险结,本文使用Borda序值法消除部分风险结,使得风险区划结果更加具体。其中伊斯兰堡、拉合尔综合风险等级最高(24级),而中国乌恰县,巴基斯坦的加拉特县综合风险最低(1级)(图5b)。
3. 讨 论
本文基于暴雨、高温、低温、干旱以及洪水灾害的危险性、承灾体暴露度、脆弱性以及恢复能力,对中巴经济走廊气象水文灾害综合风险进行了等级划分,为各级政府部门防灾减灾政策的制定提供了参考。
通过统计1961—2015年中巴经济走廊发生的气象水文灾害事件可知洪水灾害是该区域的发生次数最多的灾害,占总灾害事件的67%。本文的计算结果表明洪水中高风险区主要分布于旁遮普省、信德省以及开普省部分地区。政府部门应该加强以上区域的水资源管理,包括修复和维护水坝、堤防以及排水系统,以减少洪水造成的破坏。加强对河流、水库和湖泊的监测,以便能够及时预警并采取相对应的减灾措施来应对未来的洪水风险。洪灾是一种突发性自然灾害,无法避免,政府应在高风险地区修建大量临时避难所,保证食物、饮用水以及药品的供应,进而减轻洪水对于人们日常生活的影响。近年来,全球气温上升,极端高温事件频发,相关机构应加强对于高温灾害的宣传和教育,避免在高温时段户外活动。另外,应该改善城市规划和绿化,增加地表植被覆盖率并建造人工湖泊等,以降低城市的热岛效应,以适应更频繁和严重的高温灾害。干旱以及低温事件相比其他灾种影响占比较小,对于干旱灾害,应该进一步优化灌溉技术,进而有效应对干旱条件下的农业挑战,实现农业生产的可持续发展。本文通过计算,极端低温高风险区主要位于喀什地区以及吉尔吉特-巴尔蒂斯坦(北部地区),气象部门应提前进行天气预报以及预警,相关机构应完善暖气设备,有效防止水管结冰和破裂,个人应遵循当地政府和应急管理机构的指南和建议准备紧急用品等,进而有效降低低温灾害的影响。伊斯兰堡、拉合尔综合风险等级最高,政府应该在以上地区防灾减灾投入更多的人力物力,以便能够更好地应对气象水文灾害风险。
构建中巴经济气象水文灾害综合风险评估框架时,尽管评估指标具有科学性和合理性,但由于数据获取困难,导致研究使采用的数据时空分辨率较低,部分脆弱性指标数据的限制和资料欠缺,使得评估指标不够全面,可能会在一定的程度上影响风险评估结果的准确性。未来可以构建空间分辨率更高的气象数据以及承灾体脆弱性数据,选取更多的评价指标,优化风险评估框架。在今后的研究中,可以构建高时空分辨率的气象数据,细化最小评估单元,进而提高风险评估的准确性,为政府应急政策的制定提供更加科学的指导。
4. 结 论
1) 本文通过组合权重法计算了暴雨、高温、低温、干旱、洪水的权重,并绘制多灾种综合危险性等级图,其中高危险性等级区域分布于旁遮普省东北部、信德省东南部,研究区高危险性等级区域面积占比为9%。
2) 以承灾体暴露度、敏感性以及恢复能力来综合表征承灾体综合脆弱性,旁遮普省、俾路支省、信德省、开普省部分地区脆弱性等级高。其中旁遮普省暴露度水平高,但由于社会经济发达以及灌溉系统完善,应对气象水文灾害的适应能力强,因而该省脆弱性等级较低。
3) 通过风险矩阵法绘制中巴经济走廊综合风险等级区划图,高风险地区主要分布于信德省的中、东部地区,旁遮普省的北部、南部地区,开伯尔-普什图省(开普省)的部分地区以及俾路支省的西部地区。信德省高风险面积占比最高,占比高达66.50%。将最小评估单元进行空间升尺度后并消除部分风险结,伊斯兰堡、拉合尔综合风险等级达到24级,而中国乌恰县,巴基斯坦的加拉特县综合风险等级为1级。
中巴经济走廊综合风险评估框架及其结果提供了决策支持,对当地的防灾减灾工作具有重要意义。然而,本文的研究方法存在一定的局限性。未来的研究可以进一步优化综合风险评估框架,考虑滑坡、融雪性洪水等灾害,使评估结果更加科学合理。
-
表 1 影响因子数据来源
Table 1 Data sources of the impact factor
影响因子
Impact factor原始数据
Raw data分辨率
Resolution数据来源
Data sources高程、高程变异系数、坡度、坡度变率、
地形起伏度、平面曲率、剖面曲率、坡向华蓥市地形图 5 m 四川省地质环境监测总站 距断层距离、工程
地质岩组华蓥市地质略图 1: 400000 距河流距离 华蓥市水系图 1: 20000 土层厚度、乔木密度、蓄积量、林分类型、
平均树龄2019年华蓥市森林资源二类调查图 1: 10000 华蓥市自然资源和林业局 红绿植被指数 2014、2021年华蓥市遥感影像图 4 m Bigmap地图下载器Google地图源 表 2 因子共线性诊断
Table 2 collinearity diagnostics of factors
影响因子
Impact factors诊断1Diagnosis 1 诊断2 Diagnosis 2 容忍度Tolerance 方差膨胀系数VIF 容忍度Tolerance 方差膨胀系数VIF 平面曲率
Plane curvature0.911 1.097 0.923 1.083 距河流距离 Distance from river 0.703 1.422 0.752 1.329 地形起伏度 Terrain relief 0.080 12.531 - - 坡度 Slope 0.063 15.748 0.914 1.094 林分密度 Stand density 0.566 1.767 0.617 1.622 林分类型 Stand types 0.263 3.806 0.281 3.559 距断层距离 Distance from fault 0.749 1.335 0.828 1.208 平均树龄 Average tree age 0.166 6.031 0.177 5.663 高程变异系数 Elevation variation coefficient 0.095 10.487 - - 高程 Elevation 0.143 6.977 0.619 1.616 蓄积量 Stock volume 0.240 4.174 0.245 4.077 工程地质岩组
Engineering geological rock group0.593 1.686 0.622 1.607 表 3 Logistic模型筛选
Table 3 Logistic regression model screening
模型编号 Model number 模型因子 Model factor AUC值 AUC value LOGIT325 工程地质岩组、坡度、 0.876 距河流距离、距断层距离、 蓄积量、 林分密度 LOGIT114 工程地质岩组、坡度、 0.875 距河流距离、距断层距离、 高程、平均树龄、林分密度 LOGIT309 工程地质岩组、坡度、 0.875 距河流距离、距断层距离、 高程、 平均树龄 LOGIT364 工程地质岩组、坡度、
距河流距离、距断层距离、0.875 高程、蓄积量 LOGIT595 工程地质岩组、坡度、 0.875 距河流距离、距断层距离、 蓄积量 表 4 广义相加模型筛选
Table 4 Generalized additive model screening
模型编号 Model number 模型因子 Model factor AUC值 AUC value GAM597 工程地质岩组、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
蓄积量、 林分密度0.872 GAM655 工程地质岩组、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
蓄积量0.868 GAM346 工程地质岩组、蓄积量、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
林分密度、平均树龄0.863 GAM325 工程地质岩组、坡度、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
林分密度、蓄积量0.862 GAM330 工程地质岩组、林分密度、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
蓄积量、林分类型0.861 表 5 随机森林模型筛选
Table 5 Random Forest model screening
模型编号
Model number模型因子
Model factorAUC值
AUC valueRF62 高程、平面曲率、林分类型、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
平均树龄、 林分密度0.960 RF310 高程、工程地质岩组、
平面曲率、距断层距离、
平均树龄、林分密度0.954 RF202 高程、平面曲率、
林分类型、距断层距离、
林分密度、平均树龄0.953 RF112 工程地质岩组、高程、距河流距离、距断层距离、
林分密度、平均树龄、平面曲率0.952 RF196 林分密度、平均树龄、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
高程、平面曲率0.952 表 6 支持向量机模型筛选
Table 6 supports vector machine models screening
模型编号
Model number模型因子 Model factor AUC值
AUC valueSVM169 高程、工程地质岩组、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
蓄积量、坡度、平均树龄0.900 SVM53 高程、工程地质岩组、坡度、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
蓄积量、平均树龄、林分类型0.897 SVM11 高程、工程地质岩组、
林分类型、距断层距离、蓄积量、
林分密度、平均树龄、距河流距离0.896 SVM50 工程地质岩组、高程、坡度、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
林分密度、平均树龄、蓄积量0.896 SVM41 林分密度、高程、工程地质岩组、
距河流距离、距断层距离、
坡度、蓄积量、林分类型0.892 表 7 人工神经网络模型筛选
Table 7 Artificial Neural Network Models screening
模型编号 Model number 模型因子 Model factor AUC值 AUC value ANN533 平面曲率、林分类型、
工程地质岩组、
平均树龄、坡度0.926 ANN733 高程、
平面曲率、距断层距离、
蓄积量0.892 ANN441 高程、平面曲率、
林分类型、距断层距离、
坡度、平均树龄0.890 ANN30 工程地质岩组、蓄积量、坡度、
距河流距离、林分类型、
林分密度、平均树龄、平面曲率0.889 ANN175 林分类型、工程地质岩组、
坡度、距断层距离、
高程、蓄积量、平均树龄0.888 表 8 研究区浅层滑坡易发性分区与灾害点分布
Table 8 Shallow landslide susceptibility zones and distribution of disaster points in the study area
模型
Models易发性分区
Susceptibiliity zone面积
Area/hm2面积占比
Area ratio/%滑坡栅格
Landslide
raster滑坡占比
Proportion of landslides/%LOGIT325 非易发区 98.13 57.37 8 4.40 低易发区 36.33 21.24 21 11.54 中易发区 10.31 6.03 30 16.48 高易发区 17.03 9.96 39 21.43 极高易发区 9.24 5.40 84 46.15 GAM597 非易发区 98.12 57.37 8 4.40 低易发区 34.86 20.38 19 10.44 中易发区 11.79 6.89 31 17.03 高易发区 17.43 10.19 41 22.53 极高易发区 8.83 5.17 83 45.60 RF62 非易发区 86.47 50.52 2 1.10 低易发区 44.74 26.14 1 0.55 中易发区 14.64 8.56 6 3.30 高易发区 17.85 10.43 63 34.62 极高易发区 7.46 4.36 110 60.44 SVM169 非易发区 115.56 67.51 11 6.04 低易发区 26.72 15.62 16 8.79 中易发区 6.86 4.01 28 15.38 高易发区 11.89 6.95 31 17.03 极高易发区 10.13 5.92 96 52.75 ANN533 非易发区 110.62 64.63 7 3.85 低易发区 19.92 11.64 9 4.95 中易发区 5.17 3.02 23 12.64 高易发区 9.18 5.37 19 10.44 极高易发区 26.25 15.34 124 68.13 -
[1] YAN C L, REN X, CHEN F, et al. Geomechanically issues in the exploitation of natural gas hydrate [J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 81(5): 403-422.
[2] SEGONI S, PAPPAFICO G, LUTI T. Landslide susceptibility assessment in complex geological settings: Sensitivity to geological information and insights on its parameterization[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(10): 2443-2453. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01340-2
[3] KIRSCHBAUM D, KAPNICK S B, STANLEY T, et al. Changes in extreme precipitation and landslides over High Mountain Asia [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(4).DOI: 10.1029/2019GL085347.
[4] JAIN N, ROY P, MARTHA T R, et al. Causal analysis of unprecedented landslides during July 2021 in the Western Ghats of Maharashtra, India [J]. Landslides, 2023, 21(10): 99-109.
[5] LI M Y, MA C, DU. C, et al. Landslide response to vegetation by example of July 25–26, 2013, extreme rainstorm, Tianshui, Gansu Province, China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 80: 751-764.
[6] DENG J Y, MA C, ZHANG Y, et al. Shallow landslide characteristics and its response to vegetation by example of July 2013, extreme rainstorm, Central Loess Plateau, China [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2022, 81(3):100.1-100.18.
[7] SAITO H, NAKAYAMA D, MATSUYAMA H. Relationship between the initiation of a shallow landslide and rainfall intensity-duration thresholds in Japan-ScienceDirect[J]. Geomorphology, 2010, 118(1/2): 167-175. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.12.016
[8] MURIELLE G, ROY C, ALEXIA S. The influence of plant root systems on subsurface flow: Implications for slope stability[J]. Bioscience, 2011, 61(11): 869-879. doi: 10.1525/bio.2011.61.11.6
[9] HONG H Y. Assessing landslide susceptibility based on hybrid multilayer perceptron with ensemble learning[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2023, 2: 832.
[10] XU L, YAN D D, ZHAO T Y. Probabilistic evaluation of loess landslide impact using multivariate model [J]. Landslides, 2021, 18: 1011-1023.
[11] WU S W, CHAN W Y, LIN C Y. A predictive model incorporating geomorphic factors for assessing the longevity of landslide-dammed lakes [J]. Landslides, 2023, 21(10): 53-70.
[12] LARSEN I J, MONTGOMERY D R, KORUP O. Landslide erosion controlled by hillslope material[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3(4): 247-251. doi: 10.1038/ngeo776
[13] BA Q, CHEN Y, DENG S, et al. A comparison of slope units and grid cells as mapping units for landslide susceptibility assessment [J]. Earth Science Informatics, 2018, 11 (3): 373-388.
[14] ZHANG J Y, MA X L, ZHANG J L. Insights into geospatial heterogeneity of landslide susceptibility based on the SHAP-XGBoost model[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 332: 117357. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117357
[15] YANG C, LIU L L, HUANG F, et al. Machine learning-based landslide susceptibility assessment with optimized ratio of landslide to non-landslide samples[J]. Gondwana Research, 2023, 123: 198-216. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2022.05.012
[16] 贺鹏,童立强,郭兆成,等. GIS 支持下基于层次分析法的西藏札达地区滑坡灾害易发性评价研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2016, 16(25):193-200. HE Peng, TONG Liqiang, GUO Zhaocheng, et al. Evaluation research on the landslide disaster liability in Zhada region of Tibet [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(25): 193-200.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 毛华锐,孙小飞,周颖智. 基于频率比-投影寻踪模型的渝东北三峡库区滑坡敏感性制图 [J]. 科学技术与工程,2022, 22(5):1803-1813. MAO Huarui, SUN Xiaofei, ZHOU Yingzhi. Mapping landslide susceptibility of the Three Gorges Reservoir area in northeast Chongqing using the frequency ratio and projection pursuit model[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(5): 1803-1813. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] HUANG P C. Establishing a shallow landslide prediction method by using machine learning techniques based on the physics based calculation of soil slope stability[J]. Landslides, 2023, 20 (8): 2741-2756.
[19] QI T J, ZHAO Y, MENG X M, et al. AI-based susceptibility analysis of shallow landslides induced by heavy rainfall in Tianshui, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(9): 1819.
[20] 郭郑曦,康必均,齐实,等. 考虑植被因素的林地浅表层滑坡易发性评价——以川东华蓥市山地为例[J]. 灾害学,2022,37(2):182-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2022.02.029 GUO Zhengxi, KANG Bijun, QI Shi, et al. Susceptibility evaluation of shallow landslide in forestland considering vegetation factors: A case study of the mountainous area of huaying city in eastern Sichun[J]. Journal of Catastrophe, 2022, 37(2): 182-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2022.02.029
[21] CHEN W, ZHANG S, LI R. Performance evaluation of the GIS-based data mining techniques of best-first decision tree, random forest, and naïve Bayes tree for landslide susceptibility modeling [J]. Science of Total Environment, 2018, 644 (10): 1006-1018.
[22] 邵霄怡. 地震区域滑坡发生概率评价技术研究[D]. 北京:中国地震局地质研究所,2021. SHAO Xiaoyi. Study on the Technology on the Occurrence Probability of Coseismal Landslides[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 司康平,田原,汪大明,等. 滑坡灾害危险性评价的3种统计方法比较——以深圳市为例[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),2009,45(4):639-646. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2009.04.014 SI Kangping, TIAN Yuan, WANG Daming, et al. Comparison of three statistical methods on landslide susceptibility analysis: A case study of Shenzhen City[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2009, 45(4): 639-646. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2009.04.014
[24] 杨强,王高峰,丁伟翠,等. 多种组合模型的区域滑坡易发性及精度评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(2):36-51. YANG Qiang, WANG Gaofeng, DING Weicui, et al. Susceptibility and accuracy evaluation of regional landsldie based on multiple hybrid models[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(2): 36-51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] SUN D L, GU Q Y, WEN H J, et al. Assessment of landslide susceptibility along mountain highways based on different machine learning algorithms and mapping units by hybrid factors screening and sample optimization[J]. Gondwana Research, 2023, 123: 89-106. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2022.07.013
[26] CHEN W, ZHANG S, LI R, et al. Performance evaluation of the GIS-based data mining techniques of best-first decision tree, random forest, and naïve Bayes tree for landslide susceptibility modeling[J]. Science of Total Environment, 2018, 644: 1006-1018.
[27] 吴孝情,赖成光,陈晓宏,等. 基于随机森林权重的滑坡危险性评价:以东江流域为例[J]. 自然灾害学报,2017,26(5):119-129. WU Xiaoqing, LAI Chengguang, CHEN Xiaohong, et al. A landslide hazard assessment based on random forest weight: A case study in the Dongjiang River Basin[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2017, 26(5): 119-129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 吴雨辰,周晗旭,车爱兰. 基于粗糙集–神经网络的IBURI 地震滑坡易发性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(6):1226-1235. WU Yuchen, ZHOU Hanxu, CHE Aailan. Susceptibility of landslides caused by IBURI earthquake based on rough set-neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(6): 1226-1235. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] LI R W, ZHANG M Y, PEI W S, et al. Risk evaluation of thaw settlement using machine learning models for the Wudaoliang-Tuotuohe region, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Catena, 2023, 220: 106700.
[30] CHANG Z L, HUANG J S, HUANG F M, et al. Uncertainty analysis of non-landslide sample selection in landslide susceptibility prediction using slope unit-based machine learning models [J]. Gondwana Research, 2023, 117 (5): 307-320.
[31] 艾骁. 基于机器学习的地震滑坡易发性评估模型构建[D]. 哈尔滨:中国地震局工程力学研究所,2021. AI Xiao. Construction of Earthquake Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Model Based on Machine Learning: A Case Study of Beijing Mountainous Area[D]. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 杨正荣,喜文飞,史正涛,等. 复杂植被山区滑坡蠕变与植被覆盖度关系研究[J]. 测绘科学,2023,48(1):157-165. YANG Zhengrong, XI Wenfei, SHI Zhengtao, et al. Study on the relationship between landslide creep and vegetation cover in mountainous areas with complex vegetation[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2023, 48(1): 157-165. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 李凯,孙悦迪,江宝骅,等. 基于像元二分法的白龙江流域植被覆盖度与滑坡时空格局分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2014,50(3):376-382. LI Kai, SUN Yuedi, JIANG Baohua, et al. Analysis on spatial-temporal patterns of the vegetation coverage and landslides in Bailongjiang River Basin based on the dimidiate pixel model [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2014, 50(3): 376-382. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] XU Y, ZHANG D, LIN J Q, et al. Prediction of phytoplankton biomass and identification of key influencing factors using interpretable machine learning models[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2024, 158 (1):111320.
[35] SHI H Y, LUO G P, HELLWICH O, et al. Comparing the use of all data or specific subsets for training machine learning models in hydrology: A case study of evapotranspiration prediction [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2023, 627: 130399.
[36] 李通,王云琦,何相昌,等. 风荷载作用下三种乔木对边坡变形和稳定的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2023,39(5):110-119. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202301034 LI Tong, WANG Yunqi, HE Xiangchang, et al. Influences of three typical trees on slope deformation and stability under wind load[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2023, 39(5): 110-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202301034
[37] 毛正君,张瑾鸽,毕银丽,等. 紫花苜蓿对黄土边坡浅层破坏防护时间效应的数值分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(15):72-83. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.15.008 MAO Zhengjun, ZHANG Jinge, BI Yinli, et al. Numerical analysis of protection time effect on planting alfalfa in loess slope with shallow failure[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(15): 72-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.15.008
[38] TAO W H, SHAO F F, SU L J, et al. An analytical model for simulating the rainfall-interception-infiltration-runoff process with non-uniform rainfall[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 344 (10): 118490.
[39] CUI Y S, PAN C. Hydrological responses to litter density on runoff-infiltration patterns and water conservation in Pinus tabuliformis plantation [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2023, 619:129293.
[40] BENEDETTA E M, VERONICA T, GUGLIELMO R. Effects of roots cohesion on regional distributed slope stability modelling[J]. Catena, 2023, 222:106853.
[41] POLLEN N. Temporal and spatial variability in root reinforcement of streambanks: Accounting for soil shear strength and moisture[J]. Catena, 2007, 69(3): 197-205. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2006.05.004
[42] 李云鹏. 北京典型植物根系固土机理及含植被坡体稳定分析研究[D]. 北京:北京林业大学,2017. LI Yunpeng. Research on Root Reinforcement Mechanisms and Evaluation of Vegetation Slope Stability in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[43] SIMON A, COLLISON A J C. Quantifying the mechanical and hydrologic effects of riparian vegetation on streambank stability[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2002, 27(5): 527-546.
[44] ŠILHAN K, DE P G, ZHANG Y. Tree-ring eccentricity-based dating of landslide movements:Defining a new effective approach[J]. Catena, 2024, 234 (1):107576.
[45] 鱼舜尧,向琳,喻静,等. 林分密度对四川云顶山柏木人工林林下物种多样性和土壤抗冲性的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报,2022,28(6):1594-1600. YU Shunyao, XIANG Lin, YU Jing, et al. Effects of stand density on understory species diversity and soil anti scour ability of Cupressus funebris plantation in Yunding Mountain, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(6): 1594-1600. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 郭其乐,郭鹏,师丽魁,邹春辉,郭康军,檀艳静. 连阴雨胁迫下成熟期麦穗发芽霉变估测. 农业工程学报. 2024(22): 124-135 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载: